Back
Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 3B - Colon / Small Bowel / Esophagus
52 - Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety up to 52 Weeks in Adult and Adolescent Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results From Parts B and C of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Three-Part, Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study (Late-Breaking Abstract)
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:15 PM – 3:25 PM ET
Location: Hall C1

Evan Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG
Professor of Medicine and Adjunct Professor of Epidemiology, Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing
University of North Carolina School of Medicine
Chapel Hill, NC
Late Breaking Abstract Presenter(s)
Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG1, Marc E. Rothenberg2, Margaret H. Collins2, Ikuo Hirano3, Mirna Chehade4, Albert J. Bredenoord5, Alfredo J. Lucendo6, Jonathan M. Spergel7, Xian Sun8, Jennifer D. Hamilton8, Eric Mortensen8, Elizabeth Laws9, Jennifer Maloney8, Leda P. Mannent10, Jaman Maroni8, Kiran Patel9, Arsalan Shabbir8; 1University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 3Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 4Mount Sinai Center for Eosinophilic Disorders, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 5Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 6Hospital General de Tomelloso, Tomelloso, Spain; 7Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA; 8Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 9Sanofi, Bridgewater, NJ; 10Sanofi, Chilly-Mazarin, France
Introduction: In Parts A and B of the 3-part phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study (NCT03633617), dupilumab 300mg weekly (DPL qw) vs placebo (PBO) demonstrated significant efficacy and acceptable safety up to 24 weeks in adults and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). For patients (pts) who completed Parts A and B, Part C was an extended active treatment period for 28 weeks (wks) with pts receiving treatment up to 52 wks. We previously reported continued improvements in all aspects of disease up to 52 wks in DPL pts who completed Part A/C, and that PBO pts from Part A who received DPL in Part C showed similar efficacy. Here we present results from pts who completed Part B and continued to Part C, which assessed efficacy and safety of DPL up to 52 wks in a larger number of pts.
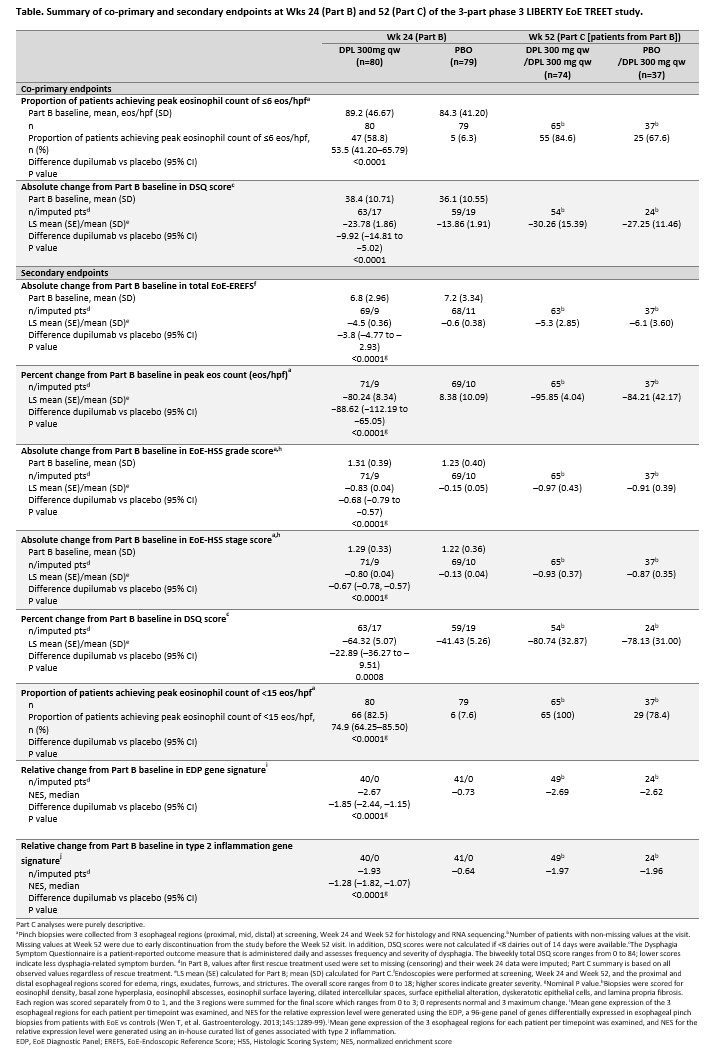
Methods: Of 80 DPL qw pts in Part B, 74 continued DPL qw in Part C (DPL/DPL). Of 79 PBO pts in Part B, 37 pts received DPL qw in Part C (PBO/DPL). Part B co-primary endpoints were proportion of pts achieving peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) count <6 eos/high power field (hpf) and absolute change from Part B baseline (BL) in Dysphagia Symptom Score (DSQ) score at Wk 24. Secondary endpoints are listed in the Table. In Part C, all co-primary and secondary endpoints were assessed at Wk 52 as secondary endpoints. Safety was also assessed.
Results: Part B BL characteristics were similar across groups. At Wk 52 of Part C, 84.6% of DPL/DPL and 67.6% of PBO/DPL groups achieved peak eos count of <6 eos/hpf and mean (SD) absolute change from Part B BL in DSQ score was −30.26 (15.39) for DPL/DPL and −27.25 (11.46) for PBO/DPL pts (Table). At Wk 52, 100% DPL/DPL and 78.4% PBO/DPL groups achieved peak eos count of <15eos/hpf, and compared to Part B BL, peak eos count, EREFS, HSS grade and stage scores were reduced, and EDP and T2 NESs were suppressed in DPL/DPL and PBO/DPL groups at Wk 52. Dupilumab demonstrated an acceptable safety profile in Part C; the most common (occurring >10%) treatment-emergent adverse events in DPL/DPL and PBO/DPL groups were injection-site reactions (13.5% and 10.8%), COVID-19 (9.5% and 10.8%) and nasopharyngitis (4.1% and 10.8%).
Conclusion: As observed in Part A/C, dupilumab qw demonstrated persistent improvements in clinical, symptomatic, histologic, endoscopic and molecular features of EoE up to 52 wks and had an acceptable safety profile. PBO pts from Part B who received dupilumab in Part C showed similar efficacy to dupilumab qw pts of Part B.
Disclosures:
Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG, Marc E. Rothenberg, Margaret H. Collins, Ikuo Hirano, Mirna Chehade, Albert J. Bredenoord, Alfredo J. Lucendo, Jonathan M. Spergel, Xian Sun, Jennifer D. Hamilton, Eric Mortensen, Elizabeth Laws, Jennifer Maloney, Leda P. Mannent, Jaman Maroni, Kiran Patel, Arsalan Shabbir, 52, Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety up to 52 Weeks in Adult and Adolescent Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results From Parts B and C of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Three-Part, Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Introduction: In Parts A and B of the 3-part phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET study (NCT03633617), dupilumab 300mg weekly (DPL qw) vs placebo (PBO) demonstrated significant efficacy and acceptable safety up to 24 weeks in adults and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). For patients (pts) who completed Parts A and B, Part C was an extended active treatment period for 28 weeks (wks) with pts receiving treatment up to 52 wks. We previously reported continued improvements in all aspects of disease up to 52 wks in DPL pts who completed Part A/C, and that PBO pts from Part A who received DPL in Part C showed similar efficacy. Here we present results from pts who completed Part B and continued to Part C, which assessed efficacy and safety of DPL up to 52 wks in a larger number of pts.
Methods: Of 80 DPL qw pts in Part B, 74 continued DPL qw in Part C (DPL/DPL). Of 79 PBO pts in Part B, 37 pts received DPL qw in Part C (PBO/DPL). Part B co-primary endpoints were proportion of pts achieving peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil (eos) count <6 eos/high power field (hpf) and absolute change from Part B baseline (BL) in Dysphagia Symptom Score (DSQ) score at Wk 24. Secondary endpoints are listed in the Table. In Part C, all co-primary and secondary endpoints were assessed at Wk 52 as secondary endpoints. Safety was also assessed.
Results: Part B BL characteristics were similar across groups. At Wk 52 of Part C, 84.6% of DPL/DPL and 67.6% of PBO/DPL groups achieved peak eos count of <6 eos/hpf and mean (SD) absolute change from Part B BL in DSQ score was −30.26 (15.39) for DPL/DPL and −27.25 (11.46) for PBO/DPL pts (Table). At Wk 52, 100% DPL/DPL and 78.4% PBO/DPL groups achieved peak eos count of <15eos/hpf, and compared to Part B BL, peak eos count, EREFS, HSS grade and stage scores were reduced, and EDP and T2 NESs were suppressed in DPL/DPL and PBO/DPL groups at Wk 52. Dupilumab demonstrated an acceptable safety profile in Part C; the most common (occurring >10%) treatment-emergent adverse events in DPL/DPL and PBO/DPL groups were injection-site reactions (13.5% and 10.8%), COVID-19 (9.5% and 10.8%) and nasopharyngitis (4.1% and 10.8%).
Conclusion: As observed in Part A/C, dupilumab qw demonstrated persistent improvements in clinical, symptomatic, histologic, endoscopic and molecular features of EoE up to 52 wks and had an acceptable safety profile. PBO pts from Part B who received dupilumab in Part C showed similar efficacy to dupilumab qw pts of Part B.

Disclosures:
Dellon ES: Abbott, Adare Pharma Solutions, Aimmune Therapeutics, Allakos, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Biorasi, Calypso Biotech, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, GSK, Gossamer Bio, Parexel, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Robarts Clinical Trials, Salix Pharmaceuticals, Shire/Takeda – consultant; Adare Pharma Solutions, Allakos, GSK, Meritage Pharma, Miraca Life Sciences, Nutricia, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire/Takada – research funding; Allakos, Banner Pharmaceuticals, Holoclara – educational grant.
Rothenberg ME: Allakos, AstraZeneca, BMS, ClostraBio, PulmOne, Spoon Guru ‒ consultant; ClostraBio, PulmOne, Spoon Guru ‒ equity interest; Teva Pharmaceuticals ‒ royalties from reslizumab; Mapi Research Trust ‒ royalties from PEESSv2; UpToDate ‒ royalties; inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Collins MH: Allakos, Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, BMS, Calypso Biotech, EsoCap, GSK, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire – consultant; AstraZeneca, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire – research funding.
Hirano I: Ellodi/Adare Pharma, Allakos, Pfizer/Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, GSK, Gossamer Bio, Nexstone, Calyx/Parexel, Phathom, Receptos/BMS, Sanofi/Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire/Takeda – consultant; Ellodi/Adare Pharma Solutions, Allakos, Receptos/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire/Takada – research funding.
Chehade M: Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi Pharmaceuticals, Allakos, AstraZeneca, BMS, Phathom Pharmaceuticals; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sanofi, Shire/Takeda – consultant; Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi Pharmaceuticals, Allakos, AstraZeneca, Danone, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Shire/Takeda – research funding.
Bredenoord AJ: AstraZeneca, Dr Falk, Laborie, Medtronic, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Alimentiv – consultant; Bayer, Nutricia, SST – research funding.
Lucendo AJ: Dr. Falk Pharma, EsoCap – consultant; Dr. Falk Pharma, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – research funding.
Spergel JM: Allakos, DBV Technologies, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Shire, Takeda – consultant; DBV Technologies, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – grant support.
Sun X, Hamilton JD, Mortensen E, Maloney J, Maroni J, Shabbir A: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – employees and shareholders.
Mannent LP, Laws E, Patel K: Sanofi – employees, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Acknowledgments and funding sources: We would like to thank Eilish McCann and Siddhesh Kamat of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for their contribution to this analysis. Research sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03633617. Medical writing/editorial assistance was provided by Jennifer L. F. Port, PhD, of Excerpta Medica, and was funded by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., according to the Good Publication Practice guideline.
Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG, Marc E. Rothenberg, Margaret H. Collins, Ikuo Hirano, Mirna Chehade, Albert J. Bredenoord, Alfredo J. Lucendo, Jonathan M. Spergel, Xian Sun, Jennifer D. Hamilton, Eric Mortensen, Elizabeth Laws, Jennifer Maloney, Leda P. Mannent, Jaman Maroni, Kiran Patel, Arsalan Shabbir, 52, Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety up to 52 Weeks in Adult and Adolescent Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results From Parts B and C of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Three-Part, Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

