Back
Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Presidential Plenary Session 1
2 - Comparison of Baveno VI Criteria, Expanded Baveno VI Criteria, Chess Alarm Score and Other Noninvasive Scores for Predicting Esophageal Varices and Varices Needing Treatment
Monday, October 24, 2022
8:12 AM – 8:24 AM ET
Location: Hall C2

Nimy John, MD (she/her/hers)
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Auxiliary Award (Trainee)
Nimy John, MD, Yash Shah, MD, Cody J. Timmermann, MD, Fares Mashal, MD, Matthew G. Deneke, MD, Mary Rude, MD, Ragesh B. Thandassery, MD, DM
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction: Many non-invasive scores have been proposed for predicting the presence of esophageal varices (EV) in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease(cACLD),to avoid unnecessary esophagogastroduodenoscopy(EGD). No extensive studies have described real-world experience with non-invasive scores
Methods: In cross-sectional analysis from Jan 2015 and Dec 2021,we studied Baveno VI criteria (liver stiffness >20 kPa & platelet count < 150X109cells/L), exp Baveno VI criteria (liver stiffness >25 kPa & platelet count< 110 X109cells/L), CHESS ALARM score (Model=0.033×Age-0.598×Male-0.018×Platelet+0.032×liver stiffness), APRI score and FIB-4 score in predicting the presence of EV,varices needing treatment (VNT) in cACLD patients, in Mid-West United States
Results: Of 424 patients(42.8%males,mean age59.2±12.5 years,78.3%Caucasian and 14.9%Afro American). Etiology of cACLD was NAFLD (55.3%),chronic hepatitis C (32.7%),alcohol (23.1%). EV present in 126 (29.7%), VNT in 32 (7.5%). 221 patients(52%) met Baveno VI criteria and 173(40.7%) met exp Baveno VI criteria. Among patients with EV on EGD, 87.7% met Baveno VI criteria, and 77.4% met exp Baveno VI criteria. Of all patients who had VNT (n=32), 85.7 % met expanded Baveno criteria. Baveno VI criteria (p< 0.001), expanded Baveno VI criteria (p< 0.001) and CHESS-ALARM score (p< 0.001, at cut off >0.37) independently correlated with presence of EV on logistic regression analysis.
Baveno VI criteria had a predictive accuracy of 93.1% to rule out EV, and exp Baveno VI criteria had a predictive accuracy of 98.3% to rule out VNT.
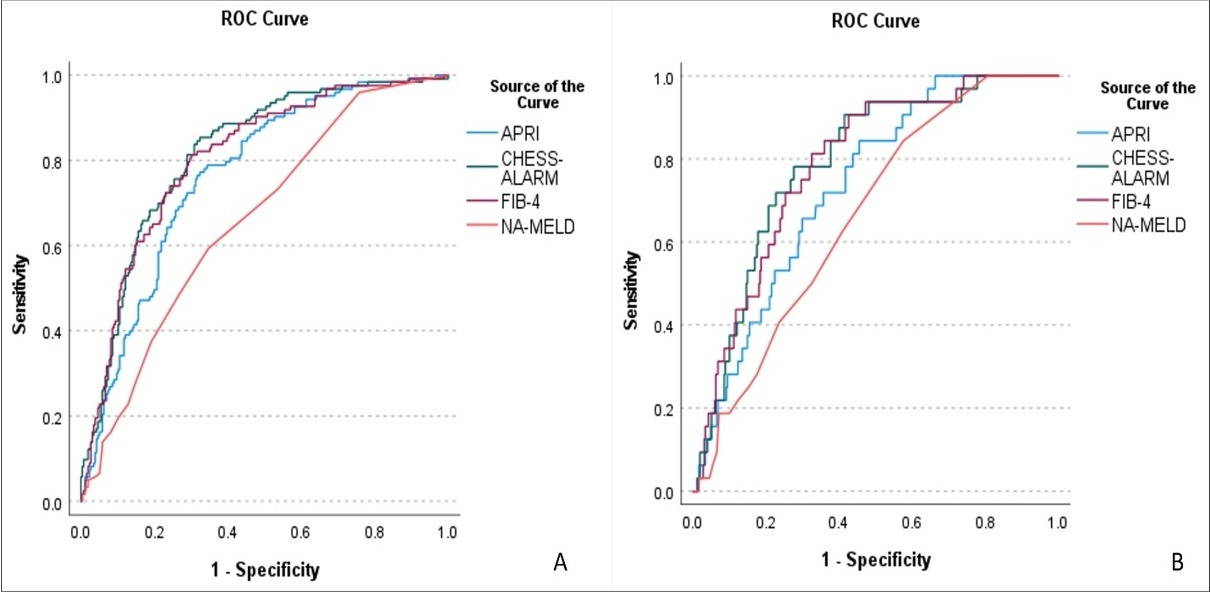
On comparison of non-invasive scores, predictive accuracy (AUROC) for EV on EGD was highest for CHESS-ALARM score (0.82, CI=0.77 to 0.86), then FIB-4 (0.80, CI=0.76 to 0.85), APRI (0.76, CI=0.72 to 0.81) and lowest for MELD-NA (0.66, CI=0.60 to 0.72). CHESS-ALARM score at -0.36 with sensitivity 82.9% and specificity 70% to predict EV.
AUROC for predicting VNT on EGD was highest for CHESS-ALARM score (0.79, CI=0.72 to 0.86), followed by FIB-4 (0.78, CI=0.72 to 0.85), APRI (0.73, CI=0.66 to 0.81), and the lowest for MELD-NA (0.66, CI=0.58 to 0.74). CHESS-ALARM score of -0.36 has sensitivity of 90.2 and specificity of 66.2% to predict VNT
Discussion: Baveno VI criteria has high predictive accuracy in ruling out EV in cACLD. Expanded Baveno VI criteria has high accuracy to rule out VNT. CHESS-ALARM score has high predictive accuracy for identifying EV and VNT. Application of these scores could reduce the burden of EGD in cACLD
Disclosures:
Nimy John, MD, Yash Shah, MD, Cody J. Timmermann, MD, Fares Mashal, MD, Matthew G. Deneke, MD, Mary Rude, MD, Ragesh B. Thandassery, MD, DM, 2, Comparison of Baveno VI Criteria, Expanded Baveno VI Criteria, Chess Alarm Score and Other Noninvasive Scores for Predicting Esophageal Varices and Varices Needing Treatment, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nimy John, MD, Yash Shah, MD, Cody J. Timmermann, MD, Fares Mashal, MD, Matthew G. Deneke, MD, Mary Rude, MD, Ragesh B. Thandassery, MD, DM
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction: Many non-invasive scores have been proposed for predicting the presence of esophageal varices (EV) in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease(cACLD),to avoid unnecessary esophagogastroduodenoscopy(EGD). No extensive studies have described real-world experience with non-invasive scores
Methods: In cross-sectional analysis from Jan 2015 and Dec 2021,we studied Baveno VI criteria (liver stiffness >20 kPa & platelet count < 150X109cells/L), exp Baveno VI criteria (liver stiffness >25 kPa & platelet count< 110 X109cells/L), CHESS ALARM score (Model=0.033×Age-0.598×Male-0.018×Platelet+0.032×liver stiffness), APRI score and FIB-4 score in predicting the presence of EV,varices needing treatment (VNT) in cACLD patients, in Mid-West United States
Results: Of 424 patients(42.8%males,mean age59.2±12.5 years,78.3%Caucasian and 14.9%Afro American). Etiology of cACLD was NAFLD (55.3%),chronic hepatitis C (32.7%),alcohol (23.1%). EV present in 126 (29.7%), VNT in 32 (7.5%). 221 patients(52%) met Baveno VI criteria and 173(40.7%) met exp Baveno VI criteria. Among patients with EV on EGD, 87.7% met Baveno VI criteria, and 77.4% met exp Baveno VI criteria. Of all patients who had VNT (n=32), 85.7 % met expanded Baveno criteria. Baveno VI criteria (p< 0.001), expanded Baveno VI criteria (p< 0.001) and CHESS-ALARM score (p< 0.001, at cut off >0.37) independently correlated with presence of EV on logistic regression analysis.
Baveno VI criteria had a predictive accuracy of 93.1% to rule out EV, and exp Baveno VI criteria had a predictive accuracy of 98.3% to rule out VNT.
On comparison of non-invasive scores, predictive accuracy (AUROC) for EV on EGD was highest for CHESS-ALARM score (0.82, CI=0.77 to 0.86), then FIB-4 (0.80, CI=0.76 to 0.85), APRI (0.76, CI=0.72 to 0.81) and lowest for MELD-NA (0.66, CI=0.60 to 0.72). CHESS-ALARM score at -0.36 with sensitivity 82.9% and specificity 70% to predict EV.
AUROC for predicting VNT on EGD was highest for CHESS-ALARM score (0.79, CI=0.72 to 0.86), followed by FIB-4 (0.78, CI=0.72 to 0.85), APRI (0.73, CI=0.66 to 0.81), and the lowest for MELD-NA (0.66, CI=0.58 to 0.74). CHESS-ALARM score of -0.36 has sensitivity of 90.2 and specificity of 66.2% to predict VNT
Discussion: Baveno VI criteria has high predictive accuracy in ruling out EV in cACLD. Expanded Baveno VI criteria has high accuracy to rule out VNT. CHESS-ALARM score has high predictive accuracy for identifying EV and VNT. Application of these scores could reduce the burden of EGD in cACLD

Figure: Comparison of noninvasive scores for predicting esophageal varices and varices needing treatment. A: ROC for predicting esophageal varices, B: ROC for predicting varices needing treatment
Disclosures:
Nimy John indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yash Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cody Timmermann indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fares Mashal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Deneke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Rude indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ragesh Thandassery indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nimy John, MD, Yash Shah, MD, Cody J. Timmermann, MD, Fares Mashal, MD, Matthew G. Deneke, MD, Mary Rude, MD, Ragesh B. Thandassery, MD, DM, 2, Comparison of Baveno VI Criteria, Expanded Baveno VI Criteria, Chess Alarm Score and Other Noninvasive Scores for Predicting Esophageal Varices and Varices Needing Treatment, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.



