Back

Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Colon
A0085 - Gastrointestinal Tract Injuries Associated With Sevelamer: A Systematic Review
Sunday, October 23, 2022
5:00 PM – 7:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Abdelkader Chaar, MD
Yale University School of Medicine
New Haven, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Osama Qasim Agha, MD1, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Fares Alahdab, MD, MSc3, Yasmin Alishahi, MD, FACG4
1Creighton University/St. Joseph Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT; 3Houston Methodist Academic Institute, Houston, TX; 4University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Sevelamer is a phosphate binder that is used to treat hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Sevelamer is known to cause multiple gastrointestinal side effects including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. However, sevelamer crystals were observed in rare cases in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with associated serious injuries including inflammation, ulceration, ischemia, and perforation. In this study, we conducted a systematic review to investigate the association of sevelamer with GIT injuries.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search in MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials to identify eligible reports of sevelamer-associated gastrointestinal tract injuries. The bibliographies of identified articles, Goggle scholars, and websites of relevant professional associations were also searched for relevant studies. Two independent reviewers identified eligible studies and data were extracted in Excel. Only studies that had sevelamer crystals seen in the histopathological exams were included.
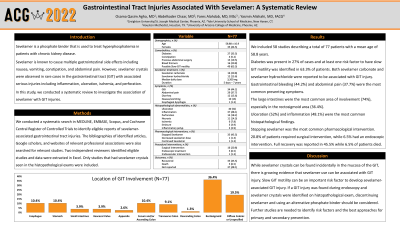
Results: We included 58 studies describing a total of 77 patients with a mean age of 58.8 years. Diabetes was present in 27% of cases and at least one risk factor to have slow GIT motility was identified in 63.3% of patients. Both sevelamer carbonate and sevelamer hydrochloride were reported to be associated with GIT injury. Gastrointestinal bleeding (44.2 %) and abdominal pain (37.7 %) were the most common presenting symptoms. The large intestines were the most common area of involvement (74 %), especially in the rectosigmoid area (36.4 %). Ulceration (52 %) and inflammation (48.1 %) were the most common histopathological findings. Stopping sevelamer was the most common pharmacological intervention. 20.8% of patients required surgical intervention, while 6.5% had an endoscopic intervention. Full recovery was reported in 45.5% while 6.5% of patients died.
Discussion: While sevelamer crystals can be found incidentally in the mucosa of the GIT, there is growing evidence that sevelamer use can be associated with GIT injury. Slow GIT motility can be an important risk factor to develop sevelamer-associated GIT injury. If a GIT injury was found during endoscopy and sevelamer crystals were identified on histopathological exam, discontinuing sevelamer and using an alternative phosphate binder should be considered. Further studies are needed to identify risk factors and the best approaches for primary and secondary prevention.
Disclosures:
Osama Qasim Agha, MD1, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Fares Alahdab, MD, MSc3, Yasmin Alishahi, MD, FACG4. A0085 - Gastrointestinal Tract Injuries Associated With Sevelamer: A Systematic Review, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Creighton University/St. Joseph Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT; 3Houston Methodist Academic Institute, Houston, TX; 4University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Sevelamer is a phosphate binder that is used to treat hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Sevelamer is known to cause multiple gastrointestinal side effects including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. However, sevelamer crystals were observed in rare cases in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with associated serious injuries including inflammation, ulceration, ischemia, and perforation. In this study, we conducted a systematic review to investigate the association of sevelamer with GIT injuries.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search in MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials to identify eligible reports of sevelamer-associated gastrointestinal tract injuries. The bibliographies of identified articles, Goggle scholars, and websites of relevant professional associations were also searched for relevant studies. Two independent reviewers identified eligible studies and data were extracted in Excel. Only studies that had sevelamer crystals seen in the histopathological exams were included.
Results: We included 58 studies describing a total of 77 patients with a mean age of 58.8 years. Diabetes was present in 27% of cases and at least one risk factor to have slow GIT motility was identified in 63.3% of patients. Both sevelamer carbonate and sevelamer hydrochloride were reported to be associated with GIT injury. Gastrointestinal bleeding (44.2 %) and abdominal pain (37.7 %) were the most common presenting symptoms. The large intestines were the most common area of involvement (74 %), especially in the rectosigmoid area (36.4 %). Ulceration (52 %) and inflammation (48.1 %) were the most common histopathological findings. Stopping sevelamer was the most common pharmacological intervention. 20.8% of patients required surgical intervention, while 6.5% had an endoscopic intervention. Full recovery was reported in 45.5% while 6.5% of patients died.
Discussion: While sevelamer crystals can be found incidentally in the mucosa of the GIT, there is growing evidence that sevelamer use can be associated with GIT injury. Slow GIT motility can be an important risk factor to develop sevelamer-associated GIT injury. If a GIT injury was found during endoscopy and sevelamer crystals were identified on histopathological exam, discontinuing sevelamer and using an alternative phosphate binder should be considered. Further studies are needed to identify risk factors and the best approaches for primary and secondary prevention.
| Demographics | Age (years) Males females | 58.88 ± 10.9 34 (44.2 %) 35 (44.5 %) |
| Comorbidities | Diabetes Constipation Previous abdominal surgery Blood thinners Possible Slow GIT motility | 27 (35.5 %) 4 (5.2 %) 15 (19.5 %) 16 (20.8 %) 49 (63.3%) |
| Sevelamer treatment | Sevelamer carbonate Sevelamer hydrochloride Both Average dose Median dose Duration | 16 (20.8 %) 12 (15.6 %) 1 (1.3%) 4,176.29 mg 3,200.00 mg 5 days – 7 years |
| Symptoms | GIB Abdominal pain Diarrhea Nausea/vomiting Esophageal dysphagia | 34 (44.2 %) 29 (37.7 %) 12 (15.6 %) 10 (13%) 1 (1.3%) |
| Location of GIT injury | Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines Ileocecal valve Large intestines Cecum and/or ascending colon Transverse Colon Descending colon Rectosigmoid Diffuse colonic or unspecified Appendix | 8 (10.4 %) 8 (10.4 %) 3 (3.9 %) 3 (3.9 %) 57 (74 %) 8 (10.4 %) 7 (9.1 %) 1 (1.3%) 28 (36.4 %) 15 (19.5 %) 2 (2.6 %) |
| Histopathological abnormalities* | Ulceration Inflammation Perforation Necrosis Ischemia Stricture Inflammatory polyp | 40 (52 %) 37 (48.1 %) 14 (18.2 %) 11 (14.3 %) 6 (7.8 %) 3 (3.9 %) 3 (3.9 %) |
| Pharmacological interventions | Stopped Sevelamer Decreased sevelamer dose Continued Sevelamer | 35 (45.5 %) 1 (1.3 %) 1 (1.3 %) |
| Procedural interventions | Surgical intervention Endoscopic treatment Endovascular intervention | 16 (20.8) 5 (6.5 %) 1 (1.3 %) |
| Outcomes | Recovered Death Not reported | 35 (45.5 %) 5 (6.5 %) 37 (48.1 %) |
Table: Table 1: Characteristics of included studies
GIT: gastrointestinal tract, GIB: Gastrointestinal bleeding, * Includes both microscopic and macroscopic findings
GIT: gastrointestinal tract, GIB: Gastrointestinal bleeding, * Includes both microscopic and macroscopic findings
Disclosures:
Osama Qasim Agha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelkader Chaar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fares Alahdab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasmin Alishahi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Qasim Agha, MD1, Abdelkader Chaar, MD2, Fares Alahdab, MD, MSc3, Yasmin Alishahi, MD, FACG4. A0085 - Gastrointestinal Tract Injuries Associated With Sevelamer: A Systematic Review, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
