Back

Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
A0041 - IgG4-Related Autoimmune Pancreatitis Following RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination
Sunday, October 23, 2022
5:00 PM – 7:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Ankoor H. Patel, MD
Rutgers - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
New Brunswick, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Ankoor H. Patel, MD1, Rajan N. Amin, MD2, Alexander T. Lalos, MD, FACG3
1Rutgers - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ; 3Rutgers/Robert Wood Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1 is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease and can often mimic tumor-like masses. Currently, there are no cases in which IgG4-RD involving the hepatobiliary system has been reported following the COVID-19 vaccination. We present the first case of AIP type 1 to be associated with the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old African-American male was in his normal state until 2021. He received 2 doses of the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine in March/April 2021. In June, he presented to his PCP with complaints of fatigue and a rapid 20lb weight loss. He was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. He denied any significant alcohol intake or history of illicit drugs, hepatotoxic medications, or liver disease. Physical exam was unremarkable.
He was started on metformin and repaglinide but his blood sugar remained uncontrolled. In September, he was found to have liver enzyme abnormalities so repaglinide was stopped. However, he had worsening jaundice and developed pruritus. He was then referred to gastroenterology.
Routine blood tests revealed mild anemia and elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, total and direct bilirubin. Hepatitis B and C were negative. Ca 19-9 and CEA were normal. IgG and IgG4 levels were elevated to 1703 mg/dL and 679.9 mg/dL, respectively. Contrast enhanced CT abdomen/pelvis revealed a hypervascular arterially enhancing pancreatic head mass measuring up to 5.5cm with moderate intrahepatic biliary dilatation and mild common bile duct dilatation to the pancreatic head. He underwent an ERCP with biliary stent placement and an endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreas biopsy. The biopsy specimen was diffusely positive for IgG4 but was “over-stained” and felt to be non-diagnostic. Liver biopsy was not obtained.
AIP was suspected given the absence of malignancy on the biopsy, normal Ca 19-9 and CEA levels, and the very elevated IgG4 level. He was started on prednisone 40mg daily with a tapering schedule. Within two weeks, his liver enzymes were normal. Imaging obtained at six weeks demonstrated resolution of the pancreatic mass with continued normal liver transaminases.
Discussion: Autoimmune phenomena following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination are being increasingly reported. We report the first case of IgG4-RD and AIP type 1 to be associated with the COVID-19 vaccine. Patients with new onset DM or cholestasis with or without signs of obstructive jaundice in the era of COVID-19 vaccination should be screened for IgG4-RD.
Disclosures:
Ankoor H. Patel, MD1, Rajan N. Amin, MD2, Alexander T. Lalos, MD, FACG3. A0041 - IgG4-Related Autoimmune Pancreatitis Following RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rutgers - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ; 3Rutgers/Robert Wood Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1 is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease and can often mimic tumor-like masses. Currently, there are no cases in which IgG4-RD involving the hepatobiliary system has been reported following the COVID-19 vaccination. We present the first case of AIP type 1 to be associated with the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old African-American male was in his normal state until 2021. He received 2 doses of the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine in March/April 2021. In June, he presented to his PCP with complaints of fatigue and a rapid 20lb weight loss. He was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. He denied any significant alcohol intake or history of illicit drugs, hepatotoxic medications, or liver disease. Physical exam was unremarkable.
He was started on metformin and repaglinide but his blood sugar remained uncontrolled. In September, he was found to have liver enzyme abnormalities so repaglinide was stopped. However, he had worsening jaundice and developed pruritus. He was then referred to gastroenterology.
Routine blood tests revealed mild anemia and elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, total and direct bilirubin. Hepatitis B and C were negative. Ca 19-9 and CEA were normal. IgG and IgG4 levels were elevated to 1703 mg/dL and 679.9 mg/dL, respectively. Contrast enhanced CT abdomen/pelvis revealed a hypervascular arterially enhancing pancreatic head mass measuring up to 5.5cm with moderate intrahepatic biliary dilatation and mild common bile duct dilatation to the pancreatic head. He underwent an ERCP with biliary stent placement and an endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreas biopsy. The biopsy specimen was diffusely positive for IgG4 but was “over-stained” and felt to be non-diagnostic. Liver biopsy was not obtained.
AIP was suspected given the absence of malignancy on the biopsy, normal Ca 19-9 and CEA levels, and the very elevated IgG4 level. He was started on prednisone 40mg daily with a tapering schedule. Within two weeks, his liver enzymes were normal. Imaging obtained at six weeks demonstrated resolution of the pancreatic mass with continued normal liver transaminases.
Discussion: Autoimmune phenomena following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination are being increasingly reported. We report the first case of IgG4-RD and AIP type 1 to be associated with the COVID-19 vaccine. Patients with new onset DM or cholestasis with or without signs of obstructive jaundice in the era of COVID-19 vaccination should be screened for IgG4-RD.

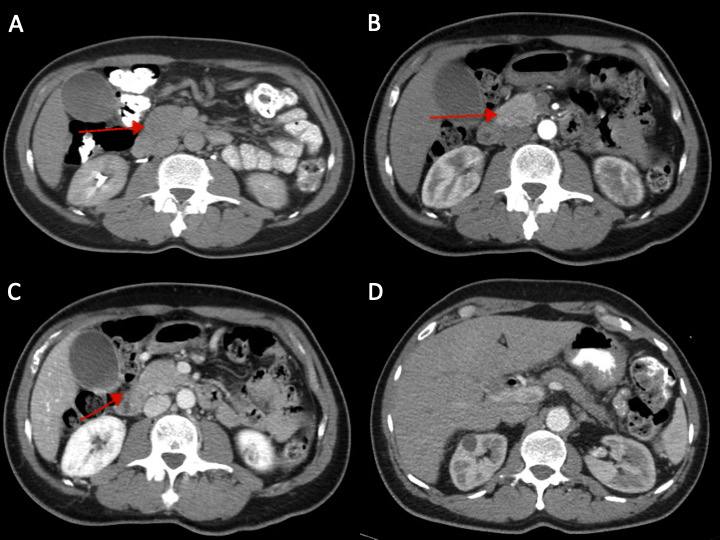
Figure: Figure 1: (A) Increased fullness to the pancreatic head with a hypoenhancing mass-like lesion measuring up to 3 cm. (B, C) Hypervascular arterial enhancing pancreatic head mass measuring up to 3.6 x 2.6 x 5.5 cm in the largest dimensions (D) Compared to prior studies (previous images), the pancreas is no longer swollen and edematous but appears somewhat atrophic. No definite enhancing masses seen in the head of the pancreas.
Disclosures:
Ankoor Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajan Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Lalos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ankoor H. Patel, MD1, Rajan N. Amin, MD2, Alexander T. Lalos, MD, FACG3. A0041 - IgG4-Related Autoimmune Pancreatitis Following RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
