Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
D0015 - Racial Disparities and Social Determinants in Pancreatic Transplantation
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Mohammad Darweesh, MD
East Tennessee State University
Johnson City, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammad Darweesh, MD1, Rasheed Musa, MD1, Ratib Mahfouz, MD2, Hisham Laswi, MD3, Mahmoud Mansour, MD4, Adham E. Obeidat, MBBS5, Bhavesh Gajjar, MD1
1East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN; 2Brown University/Kent Hospital, Providence, RI; 3John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 4University of Missouri Columbia, Columbia, MO; 5University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI
Introduction: Pancreatic transplantation is still the only treatment that can restore normoglycemic and complete insulin independence. Potentially life-threatening complications of diabetes, hypoglycemia unawareness, and intolerable problems with insulin therapy can all be indications of pancreatic transplantation. In this study, we aimed to investigate the healthcare determinants and racial disparities in pancreatic transplantation.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted utilizing the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database (NIS) for the years 2016 to 2018. Patients who underwent pancreatic transplantation were identified using ICD-10 diagnosis codes from all listed discharge diagnoses. Patients younger than 18 years of age, and missing information for age, gender, or race were excluded. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to compare different predictors of pancreatic transplantation in the included population.
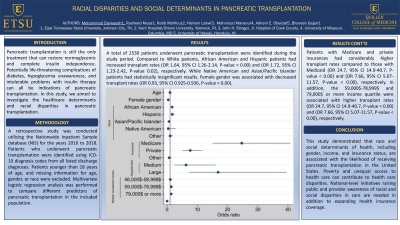
Results: A total of 2530 patients underwent pancreatic transplantation were identified during the study period. Compared to White patients, African American and Hispanic patients had increased transplant rates (OR 1.64, 95% CI 1.26-2.14, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 1.72, 95% CI 1.23-2.42, P-value 0.02), respectively. While Native American and Asian/Pacific Islander patients had statistically insignificant results. Female gender was associated with decreased transplant rates (OR 0.93, 95% CI 0.925-0.936, P-value < 0.00). Patients with Medicare and private insurances had considerably higher transplant rates compared to those with Medicaid (OR 24.7, 95% CI 14.9-40.7, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 7.66, 95% CI 5.07-11.57, P-value < 0.00), respectively. In addition, the 59,000$-78,999$ and 79,000$ or more income quartile were associated with higher transplant rates (OR 24.7, 95% CI 14.9-40.7, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 7.66, 95% CI 5.07-11.57, P-value < 0.00), respectively.
Discussion: This study demonstrated that race and social determinants of health, including gender, income, and insurance status, are associated with the likelihood of receiving pancreatic transplantation in the United States. Poverty and unequal access to health care can contribute to health care disparities. National-level initiatives raising public and provider awareness of racial and social disparities in care are needed in addition to expanding health insurance coverage.

Disclosures:
Mohammad Darweesh, MD1, Rasheed Musa, MD1, Ratib Mahfouz, MD2, Hisham Laswi, MD3, Mahmoud Mansour, MD4, Adham E. Obeidat, MBBS5, Bhavesh Gajjar, MD1. D0015 - Racial Disparities and Social Determinants in Pancreatic Transplantation, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN; 2Brown University/Kent Hospital, Providence, RI; 3John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 4University of Missouri Columbia, Columbia, MO; 5University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI
Introduction: Pancreatic transplantation is still the only treatment that can restore normoglycemic and complete insulin independence. Potentially life-threatening complications of diabetes, hypoglycemia unawareness, and intolerable problems with insulin therapy can all be indications of pancreatic transplantation. In this study, we aimed to investigate the healthcare determinants and racial disparities in pancreatic transplantation.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted utilizing the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database (NIS) for the years 2016 to 2018. Patients who underwent pancreatic transplantation were identified using ICD-10 diagnosis codes from all listed discharge diagnoses. Patients younger than 18 years of age, and missing information for age, gender, or race were excluded. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to compare different predictors of pancreatic transplantation in the included population.
Results: A total of 2530 patients underwent pancreatic transplantation were identified during the study period. Compared to White patients, African American and Hispanic patients had increased transplant rates (OR 1.64, 95% CI 1.26-2.14, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 1.72, 95% CI 1.23-2.42, P-value 0.02), respectively. While Native American and Asian/Pacific Islander patients had statistically insignificant results. Female gender was associated with decreased transplant rates (OR 0.93, 95% CI 0.925-0.936, P-value < 0.00). Patients with Medicare and private insurances had considerably higher transplant rates compared to those with Medicaid (OR 24.7, 95% CI 14.9-40.7, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 7.66, 95% CI 5.07-11.57, P-value < 0.00), respectively. In addition, the 59,000$-78,999$ and 79,000$ or more income quartile were associated with higher transplant rates (OR 24.7, 95% CI 14.9-40.7, P-value < 0.00) and (OR 7.66, 95% CI 5.07-11.57, P-value < 0.00), respectively.
Discussion: This study demonstrated that race and social determinants of health, including gender, income, and insurance status, are associated with the likelihood of receiving pancreatic transplantation in the United States. Poverty and unequal access to health care can contribute to health care disparities. National-level initiatives raising public and provider awareness of racial and social disparities in care are needed in addition to expanding health insurance coverage.

Figure: Multivariate logistic regression analysis investigates different variables in predicting the likelihood of pancreatic transplantation in the United States.
Disclosures:
Mohammad Darweesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rasheed Musa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ratib Mahfouz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hisham Laswi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Mansour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adham Obeidat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavesh Gajjar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Darweesh, MD1, Rasheed Musa, MD1, Ratib Mahfouz, MD2, Hisham Laswi, MD3, Mahmoud Mansour, MD4, Adham E. Obeidat, MBBS5, Bhavesh Gajjar, MD1. D0015 - Racial Disparities and Social Determinants in Pancreatic Transplantation, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
