Back

Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Esophagus
A0213 - Oral Viscous Budesonide Ameliorates PPI-Refractory Lymphocytic Esophagitis: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report
Sunday, October 23, 2022
5:00 PM – 7:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
.jpg)
David Leung, MD
Scripps Green-Scripps Clinic
La Jolla, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
David Leung, MD1, Amr Moslli Sirjie, MD2, Fei Bao, MD3, Franklin Tsai, MD1, Walter Coyle, MD1, Quan M. Nhu, MD, PhD4
1Scripps Green-Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 2Scripps, San Diego, CA; 3Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 4Scripps Clinic & Scripps Research, San Diego, CA
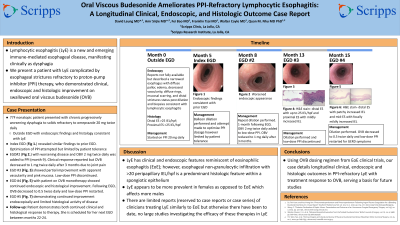
Introduction: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a new and emerging immune-mediated esophageal disease, manifesting clinically as dysphagia. Its natural history and effective treatments remain poorly characterized. We present a patient with LyE complicated by esophageal strictures refractory to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy, who demonstrated clinical, endoscopic and histologic improvement on swallowed oral viscous budesonide (OVB).
Case Description/Methods: A 77-year-old nonsmoker nonatopic female with a history of remote buccal lichen planus, lymphocytic colitis, depression, anxiety, osteoarthritis, presented with chronic progressively worsening dysphagia to solids refractory to omeprazole 20 mg twice daily. Initial EGD elsewhere showed a narrowed esophagus with diffuse pallor, edema, decreased vascularity, diffuse rings, mucosal scarring, and distal strictures status post dilation. Esophageal biopsies showed LyE with >25 intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL)/hpf proximally and distally. Our index EGD, 5 months after the initial outside EGD, revealed similar findings requiring esophageal dilation to 15-mm. Optimization of omeprazole was attempted but was limited to 20 mg daily due to dizziness. Repeat EGD after 3 months (month 8) showed worsening disease. OVB at 2 mg twice daily was added at month 9 to low-dose PPI, with clinical improvement within 2 weeks. OVB was reduced to 1 mg twice daily after 3 months due to joint pain. After 5 months on OVB and low-dose PPI, EGD showed partial improvement, with histologic remission proximally but not distally. EGD after 2 additional months on OVB monotherapy, off PPI, showed continued endoscopic improvement with decreased edema, improved vascularity, and improved esophageal caliber with no mucosal scarring. Mild diffuse esophageal rings were still present but appeared improved. Two distal esophageal strictures were dilated to 15-mm. Pan-esophageal biopsies improved histologically. Patient remains clinically improved on reduced OVB dose at 0.5 mg twice daily.
Discussion: LyE has clinical and endoscopic features reminiscent of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE); however, esophageal non-granulocytic infiltration with >20 peripapillary IEL/hpf is a predominant histologic feature within a spongiotic epithelium. Guidance for LyE therapy has not been established. Using OVB dosing regimen from EoE clinical trials, our case details longitudinal clinical, endoscopic and histologic outcomes in PPI-refractory LyE with treatment response to OVB, serving a basis for future studies.
Disclosures:
David Leung, MD1, Amr Moslli Sirjie, MD2, Fei Bao, MD3, Franklin Tsai, MD1, Walter Coyle, MD1, Quan M. Nhu, MD, PhD4. A0213 - Oral Viscous Budesonide Ameliorates PPI-Refractory Lymphocytic Esophagitis: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
David Leung, MD1, Amr Moslli Sirjie, MD2, Fei Bao, MD3, Franklin Tsai, MD1, Walter Coyle, MD1, Quan M. Nhu, MD, PhD4
1Scripps Green-Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 2Scripps, San Diego, CA; 3Scripps Clinic, La Jolla, CA; 4Scripps Clinic & Scripps Research, San Diego, CA
Introduction: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a new and emerging immune-mediated esophageal disease, manifesting clinically as dysphagia. Its natural history and effective treatments remain poorly characterized. We present a patient with LyE complicated by esophageal strictures refractory to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy, who demonstrated clinical, endoscopic and histologic improvement on swallowed oral viscous budesonide (OVB).
Case Description/Methods: A 77-year-old nonsmoker nonatopic female with a history of remote buccal lichen planus, lymphocytic colitis, depression, anxiety, osteoarthritis, presented with chronic progressively worsening dysphagia to solids refractory to omeprazole 20 mg twice daily. Initial EGD elsewhere showed a narrowed esophagus with diffuse pallor, edema, decreased vascularity, diffuse rings, mucosal scarring, and distal strictures status post dilation. Esophageal biopsies showed LyE with >25 intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL)/hpf proximally and distally. Our index EGD, 5 months after the initial outside EGD, revealed similar findings requiring esophageal dilation to 15-mm. Optimization of omeprazole was attempted but was limited to 20 mg daily due to dizziness. Repeat EGD after 3 months (month 8) showed worsening disease. OVB at 2 mg twice daily was added at month 9 to low-dose PPI, with clinical improvement within 2 weeks. OVB was reduced to 1 mg twice daily after 3 months due to joint pain. After 5 months on OVB and low-dose PPI, EGD showed partial improvement, with histologic remission proximally but not distally. EGD after 2 additional months on OVB monotherapy, off PPI, showed continued endoscopic improvement with decreased edema, improved vascularity, and improved esophageal caliber with no mucosal scarring. Mild diffuse esophageal rings were still present but appeared improved. Two distal esophageal strictures were dilated to 15-mm. Pan-esophageal biopsies improved histologically. Patient remains clinically improved on reduced OVB dose at 0.5 mg twice daily.
Discussion: LyE has clinical and endoscopic features reminiscent of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE); however, esophageal non-granulocytic infiltration with >20 peripapillary IEL/hpf is a predominant histologic feature within a spongiotic epithelium. Guidance for LyE therapy has not been established. Using OVB dosing regimen from EoE clinical trials, our case details longitudinal clinical, endoscopic and histologic outcomes in PPI-refractory LyE with treatment response to OVB, serving a basis for future studies.
Disclosures:
David Leung indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amr Moslli Sirjie indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fei Bao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Franklin Tsai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walter Coyle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Quan Nhu: Cancer Expert Now – Consultant. Regeneron – Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
David Leung, MD1, Amr Moslli Sirjie, MD2, Fei Bao, MD3, Franklin Tsai, MD1, Walter Coyle, MD1, Quan M. Nhu, MD, PhD4. A0213 - Oral Viscous Budesonide Ameliorates PPI-Refractory Lymphocytic Esophagitis: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.


