Back


Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Colon
D0123 - Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Pancreatic Metastasis
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Eitan Scheinthal, DO
CMSRU/Cooper University Hospital
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Eitan Scheinthal, DO1, Michael Schwartz, MD1, Adib Chaaya, MD2, Julieta Barroeta, MD1
1CMSRU/Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ
Introduction: The vast majority of pancreatic tumors are of primary origin. Colonic metastasis to the pancreas is rare and portends a poor prognosis. The diagnosis remains challenging, hinging on histopathological examination of the tissue sample. Optimal treatment remains unknown.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old woman with sigmoid colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) stage IV (pT4a pN2b pM1c) with hepatic and ovarian metastases was evaluated for progressive obstructive jaundice with worsening, non-radiating left-sided abdominal pain over one week. Associated symptoms included tea colored urine, acholic stools and generalized pruritus. Abdominal exam was without guarding and confirmed these findings. Admission labs were notable for AST 177, ALT 97, ALP 1095, T Bili 9.7, D Bili 8.6, CEA 103.0, AFP 1.8 and CA 19-9 11. CEA had increased from 67.3 three months prior. CT showed intra and extrahepatic ductal dilatation. RUQUS demonstrated a hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic head and a dilated main pancreatic duct not present on MRI one year prior. EUS confirmed the mass measuring 29 mm x 20 mm. FNA was performed with cytology positive for malignant cells. Immunohistochemical stains were positive for CK20, CK19, CDX2, SATB2, and CA19.9, and negative for CK7 and PAX-8 (Fig 4.). These findings support a diagnosis consistent with metastasis of primary colonic adenocarcinoma origin.
Discussion: Metastatic tumors of the pancreas are rare, comprising only 2% of pancreatic tumors. Of these, renal cell carcinoma, lobular carcinoma, and endometrial carcinoma constitute the majority. CRC is even less common, with preferential metastasis sites including the liver, lung, peritoneum and lymph. Metastasis occurs contiguously, via the lymphatics or by hematogenous spread. Adenocarcinoma predominantly metastasizes to the liver through the lymphatics whereas mucinous or signet ring cell adenocarcinoma commonly metastasize to the peritoneum. Up to 20% of patients are asymptomatic. Survival is often limited, with 90% of lesions unresectable at the time of diagnosis. Those with multiple metastases may be treated with palliative chemotherapy. Here, the histologic pattern confirmed invasive CRC with adjacent pancreatic architecture. Regorafenib was investigated as salvage therapy. While this patient’s advanced disease precluded additional surgical treatment, those with solitary solid tumor metastasis to the pancreatic may benefit from surgical resection, with 5 year survival rates reaching 50% for solitary metastasis.
Disclosures:
Eitan Scheinthal, DO1, Michael Schwartz, MD1, Adib Chaaya, MD2, Julieta Barroeta, MD1. D0123 - Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Pancreatic Metastasis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1CMSRU/Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ
Introduction: The vast majority of pancreatic tumors are of primary origin. Colonic metastasis to the pancreas is rare and portends a poor prognosis. The diagnosis remains challenging, hinging on histopathological examination of the tissue sample. Optimal treatment remains unknown.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old woman with sigmoid colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) stage IV (pT4a pN2b pM1c) with hepatic and ovarian metastases was evaluated for progressive obstructive jaundice with worsening, non-radiating left-sided abdominal pain over one week. Associated symptoms included tea colored urine, acholic stools and generalized pruritus. Abdominal exam was without guarding and confirmed these findings. Admission labs were notable for AST 177, ALT 97, ALP 1095, T Bili 9.7, D Bili 8.6, CEA 103.0, AFP 1.8 and CA 19-9 11. CEA had increased from 67.3 three months prior. CT showed intra and extrahepatic ductal dilatation. RUQUS demonstrated a hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic head and a dilated main pancreatic duct not present on MRI one year prior. EUS confirmed the mass measuring 29 mm x 20 mm. FNA was performed with cytology positive for malignant cells. Immunohistochemical stains were positive for CK20, CK19, CDX2, SATB2, and CA19.9, and negative for CK7 and PAX-8 (Fig 4.). These findings support a diagnosis consistent with metastasis of primary colonic adenocarcinoma origin.
Discussion: Metastatic tumors of the pancreas are rare, comprising only 2% of pancreatic tumors. Of these, renal cell carcinoma, lobular carcinoma, and endometrial carcinoma constitute the majority. CRC is even less common, with preferential metastasis sites including the liver, lung, peritoneum and lymph. Metastasis occurs contiguously, via the lymphatics or by hematogenous spread. Adenocarcinoma predominantly metastasizes to the liver through the lymphatics whereas mucinous or signet ring cell adenocarcinoma commonly metastasize to the peritoneum. Up to 20% of patients are asymptomatic. Survival is often limited, with 90% of lesions unresectable at the time of diagnosis. Those with multiple metastases may be treated with palliative chemotherapy. Here, the histologic pattern confirmed invasive CRC with adjacent pancreatic architecture. Regorafenib was investigated as salvage therapy. While this patient’s advanced disease precluded additional surgical treatment, those with solitary solid tumor metastasis to the pancreatic may benefit from surgical resection, with 5 year survival rates reaching 50% for solitary metastasis.

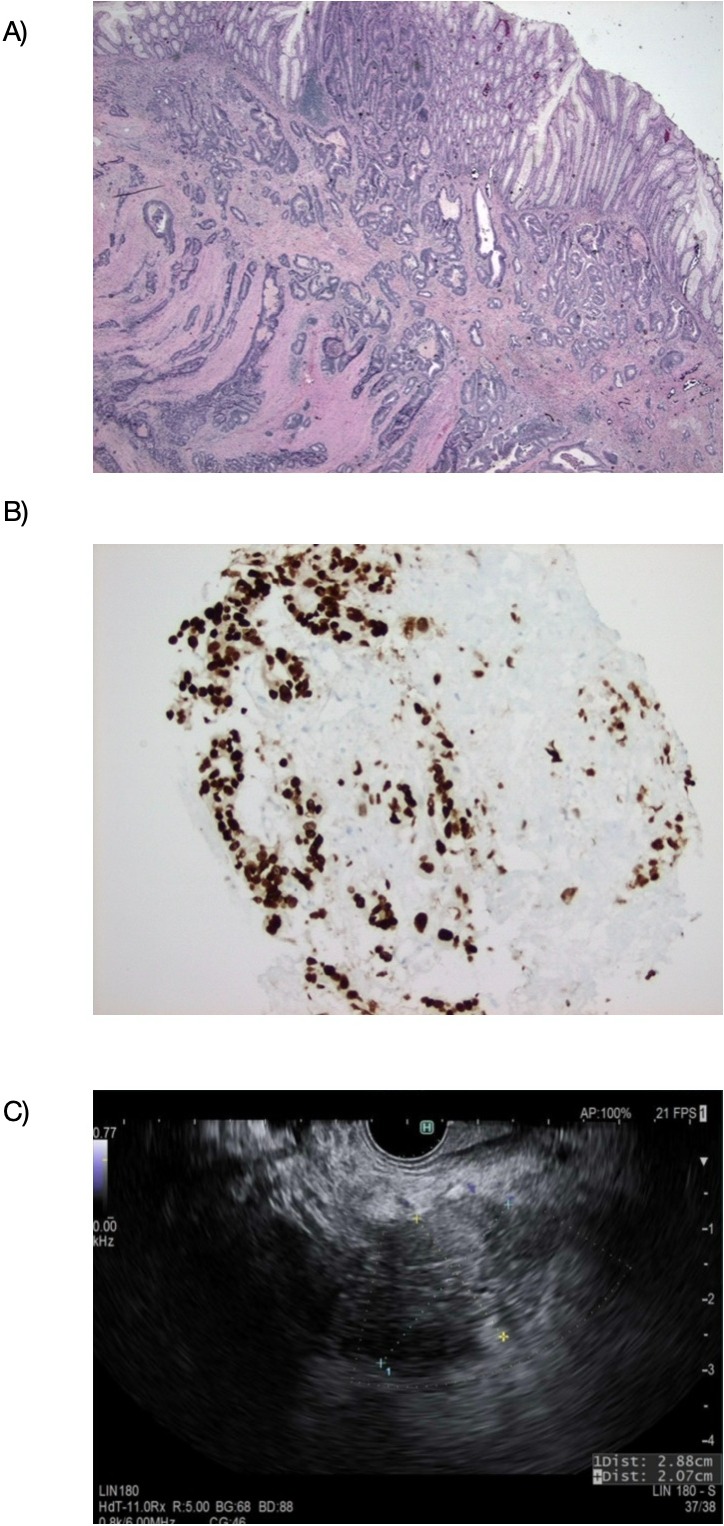
Figure: Figure 1. Colorectal adenocarcinoma metastasis to the pancreas
(A) Invasive colonic adenocarcinoma, low grade (H&E, 200x).
(B) Metastatic adenocarcinoma involving pancreas (H&E, 200x), with confirmatory immunohistochemical stain for CDX2 (200x).
(C) Pancreatic head mass on endoscopic ultrasound.
(A) Invasive colonic adenocarcinoma, low grade (H&E, 200x).
(B) Metastatic adenocarcinoma involving pancreas (H&E, 200x), with confirmatory immunohistochemical stain for CDX2 (200x).
(C) Pancreatic head mass on endoscopic ultrasound.
| Laboratory Test | Value |
AST | 177 |
ALT | 97 |
ALP | 1095 |
Total Bilirubin | 9.7 |
Direct Bilirubin | 8.6 |
CEA | 103.0 |
| AFP | 1.8 |
CA 19-9 | 11 |
Table: Admission Labs
Disclosures:
Eitan Scheinthal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Schwartz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adib Chaaya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julieta Barroeta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eitan Scheinthal, DO1, Michael Schwartz, MD1, Adib Chaaya, MD2, Julieta Barroeta, MD1. D0123 - Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Pancreatic Metastasis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

