Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
D0019 - Investigation of Linerixibat 40 Mg BID for Cholestatic Pruritus of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC); Further Data From the Phase 2b GLIMMER Study to Support the Phase 3 GLISTEN Study
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom


Megan M. McLaughlin
GSK
Collegeville, PA
Presenting Author(s)
James Fettiplace, MD1, Brandon Swift, PhD2, Shu Zhang, 3, Robyn Von Maltzahn, 1, Megan M. McLaughlin, 3
1GSK, London, England, United Kingdom; 2GSK, Research Triangle Park, NC; 3GSK, Collegeville, PA
Introduction: Reduction of pruritic bile acids (BA) in circulation is under investigation for the treatment of cholestatic pruritus in PBC. Due to lack of previously approved therapies, what constitutes a meaningful within-patient change in itch has not been determined. GLIMMER was a Phase 2b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose response study of linerixibat, a minimally absorbed ileal BA transporter inhibitor, in PBC patients with moderate to severe pruritus. Data from GLIMMER were reanalyzed to look at multiple itch responder definitions in the linerixibat 40mg twice daily (BID) group, the Phase 3 dose. Changes in total serum BA (TSBA) are also reported.
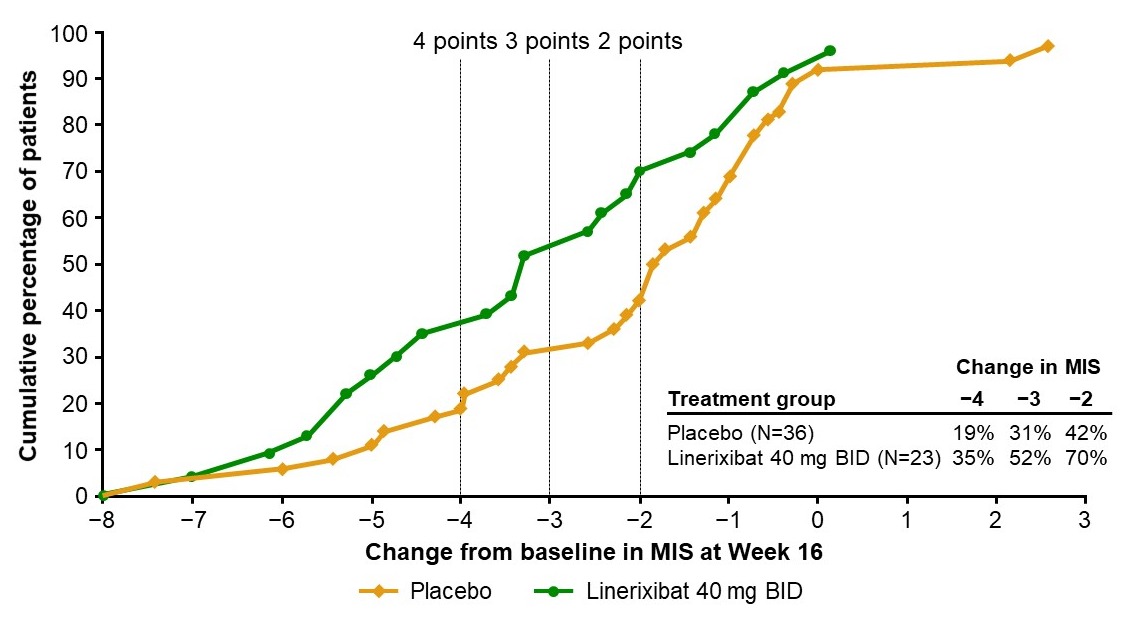
Methods: Patients (N=147) assessed itch daily on a 0–10 numeric rating scale. Proportion of responders was assessed using reductions in monthly itch score (MIS) at Week 16 compared to baseline (BL). An empirical cumulative distribution function (eCDF) graph was generated for the percentage of patients with change from BL in MIS for the linerixibat 40mg BID (N=23) and placebo (N=36) groups. BA samples were reanalyzed using an enzymatic assay that quantifies TSBA consistent with the Phase 2a study method. Changes from BL in TSBA were analyzed using a mixed model repeated measures (MMRM) analysis.
Results: The eCDF curves showed clear separation of linerixibat 40 mg BID and placebo groups. The percentages of patients with an improvement from BL in MIS at Week 16 were greater in the linerixibat group than the placebo group for a wide range of responder threshold values. The largest differences were observed between thresholds of -3 to -2, where the cumulative percentages were >20% greater in the linerixibat group versus placebo. Linerixibat 40mg BID (n=22) reduced mean (SD) TSBA from a BL of 18.6 µM (21.8) by -6.94 µM (17.5) after 12-weeks of treatment. A MMRM analysis showed a significant decrease of 39% (p=0.0001) from BL and 37% (p=0.0030) from placebo (n=36) over the 12-week double-blind treatment period.
Discussion: Consistent with inhibition of reuptake of BA, 40 mg BID linerixibat resulted in significant reductions in TSBA. The proportion of patients with change from BL in MIS at Week 16 was greater in the linerixibat 40mg BID group than placebo over a range of responder threshold values. Linerixibat 40mg BID is being studied in the ongoing Phase 3 GLISTEN study (NCT04950127). Responder thresholds of 2-, 3- and 4-point improvements in MIS compared to BL are key secondary endpoints.
Disclosures:
James Fettiplace, MD1, Brandon Swift, PhD2, Shu Zhang, 3, Robyn Von Maltzahn, 1, Megan M. McLaughlin, 3. D0019 - Investigation of Linerixibat 40 Mg BID for Cholestatic Pruritus of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC); Further Data From the Phase 2b GLIMMER Study to Support the Phase 3 GLISTEN Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1GSK, London, England, United Kingdom; 2GSK, Research Triangle Park, NC; 3GSK, Collegeville, PA
Introduction: Reduction of pruritic bile acids (BA) in circulation is under investigation for the treatment of cholestatic pruritus in PBC. Due to lack of previously approved therapies, what constitutes a meaningful within-patient change in itch has not been determined. GLIMMER was a Phase 2b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose response study of linerixibat, a minimally absorbed ileal BA transporter inhibitor, in PBC patients with moderate to severe pruritus. Data from GLIMMER were reanalyzed to look at multiple itch responder definitions in the linerixibat 40mg twice daily (BID) group, the Phase 3 dose. Changes in total serum BA (TSBA) are also reported.
Methods: Patients (N=147) assessed itch daily on a 0–10 numeric rating scale. Proportion of responders was assessed using reductions in monthly itch score (MIS) at Week 16 compared to baseline (BL). An empirical cumulative distribution function (eCDF) graph was generated for the percentage of patients with change from BL in MIS for the linerixibat 40mg BID (N=23) and placebo (N=36) groups. BA samples were reanalyzed using an enzymatic assay that quantifies TSBA consistent with the Phase 2a study method. Changes from BL in TSBA were analyzed using a mixed model repeated measures (MMRM) analysis.
Results: The eCDF curves showed clear separation of linerixibat 40 mg BID and placebo groups. The percentages of patients with an improvement from BL in MIS at Week 16 were greater in the linerixibat group than the placebo group for a wide range of responder threshold values. The largest differences were observed between thresholds of -3 to -2, where the cumulative percentages were >20% greater in the linerixibat group versus placebo. Linerixibat 40mg BID (n=22) reduced mean (SD) TSBA from a BL of 18.6 µM (21.8) by -6.94 µM (17.5) after 12-weeks of treatment. A MMRM analysis showed a significant decrease of 39% (p=0.0001) from BL and 37% (p=0.0030) from placebo (n=36) over the 12-week double-blind treatment period.
Discussion: Consistent with inhibition of reuptake of BA, 40 mg BID linerixibat resulted in significant reductions in TSBA. The proportion of patients with change from BL in MIS at Week 16 was greater in the linerixibat 40mg BID group than placebo over a range of responder threshold values. Linerixibat 40mg BID is being studied in the ongoing Phase 3 GLISTEN study (NCT04950127). Responder thresholds of 2-, 3- and 4-point improvements in MIS compared to BL are key secondary endpoints.

Figure: Figure: Cumulative percentage of patients with specified change from baseline in monthly itch score (MIS) at Week 16
Disclosures:
James Fettiplace: GlaxoSmithKline – Employee, Stock Options.
Brandon Swift: GlaxoSmithKline – Employee, Stock Options.
Shu Zhang: GlaxoSmithKline – Employee, Stock Options.
Robyn Von Maltzahn: GlaxoSmithKline – Employee, Stock Options.
Megan McLaughlin: GlaxoSmithKline – Employee, Stock Options.
James Fettiplace, MD1, Brandon Swift, PhD2, Shu Zhang, 3, Robyn Von Maltzahn, 1, Megan M. McLaughlin, 3. D0019 - Investigation of Linerixibat 40 Mg BID for Cholestatic Pruritus of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC); Further Data From the Phase 2b GLIMMER Study to Support the Phase 3 GLISTEN Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
