Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
A0262 - Using Prokinetic Agents in Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIPO)

Yushan Wang, MD
Tufts Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
1Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Tufts School of Medicine, Boston, MA
Introduction: Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) is a rare disease. Dilatation may involve the colon or small bowel and is usually due to an underlying neuropathic disorder. Clinical manifestations of CIPO include abdominal distention, bloating, and pain, which can be acute, chronic, or recurrent. Diagnosis of CIPO should be suspected in patients with these symptoms for at least 3 months in the absence of a mechanical cause. Diagnosis requires exclusion of mechanical obstruction and other causes of dysmotility.
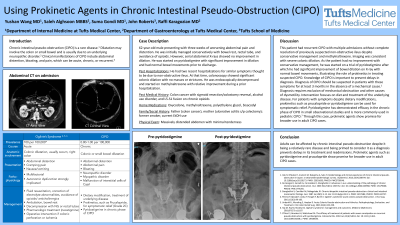
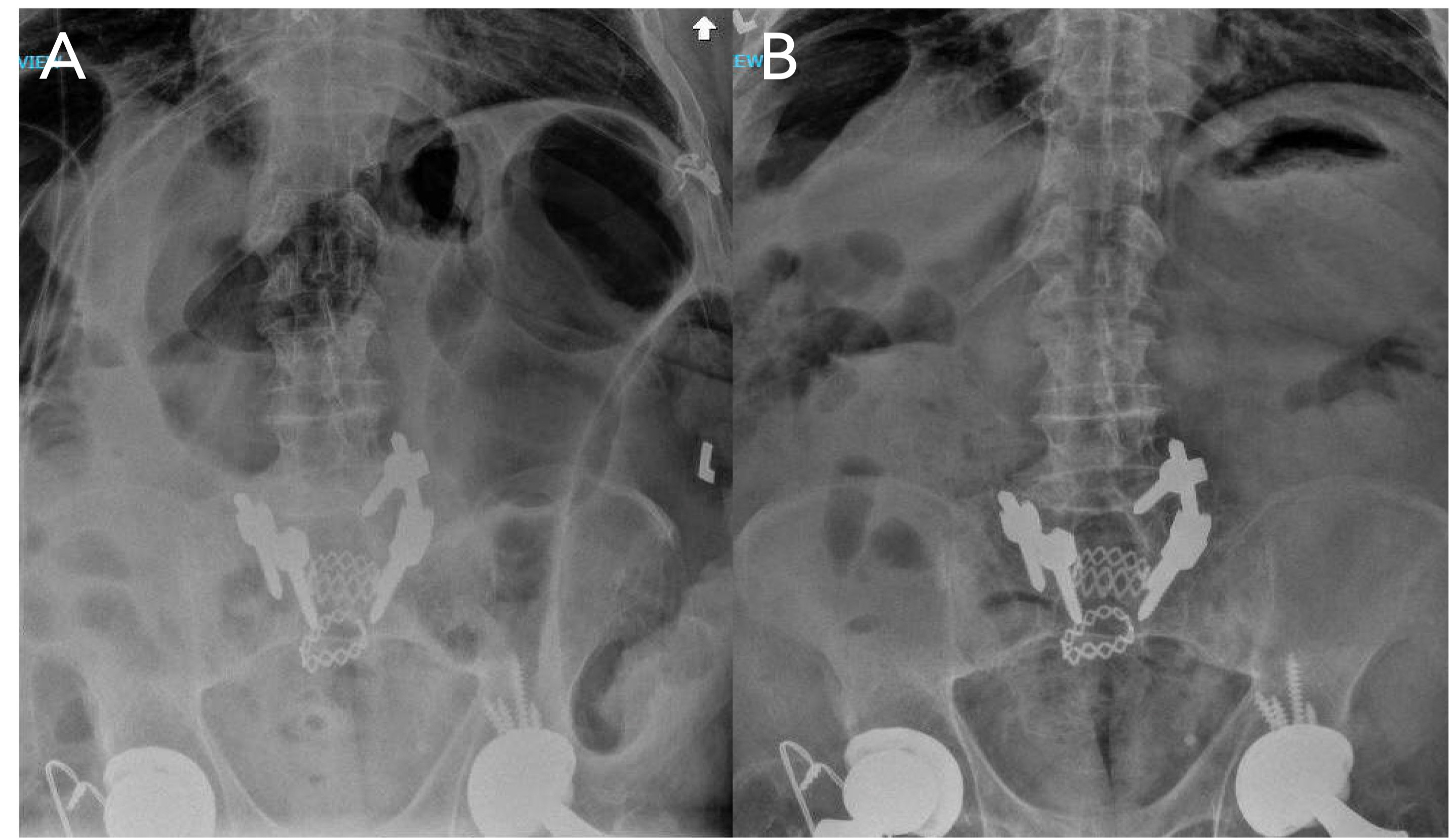
Case Description/Methods: This is a case of a 62-year-old male presenting with three weeks of worsening abdominal pain and distention. History includes colon cancer with sigmoid resection/colostomy reversal, alcohol use disorder, and L5-S1 fusion on chronic opioids. He had two recent hospitalizations for similar symptoms thought to be due to non-obstructive ileus. At that time, colonoscopy showed significant colonic dilation with no masses or strictures. He was endoscopically decompressed and started on methylnaltrexone with relative improvement during a prior hospitalization. On this presentation, he had a massively distended abdomen with minimal tenderness. He was initially managed conservatively with bowel rest, rectal tube, and avoidance of opioids. However, serial abdominal X-rays showed no improvement in dilation. He was started on pyridostigmine with significant improvement in dilation and had normal bowel movements prior to discharge.
Discussion: This patient had recurrent CIPO with multiple admissions without complete resolution of previously suspected non-obstructive ileus despite conservative management and methylnaltrexone. Imaging was consistent with severe colonic dilation. As the patient had no improvement with conservative management, he was started on a trial of pyridostigmine after which he had significant improvement of bowel dilation on X-ray with normal bowel movements, illustrating the role of prokinetics in treating suspected CIPO. Knowledge of CIPO is important to prevent delays in diagnosis. Intervention focuses on diet and treatment of the underlying disease. For patients with symptoms despite dietary modifications, prokinetics such as prucalopride or pyridostigmine can be used for symptomatic relief. Pyridostigmine has demonstrated efficacy in the chronic phase of CIPO in small observational studies and is more commonly used in pediatric CIPO. Through this case, prokinetic agents show promise for broader use in adult CIPO cases.
Acute Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction | Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction | |
Prevalence | 100 per 100,000* | 0.80-1.00 per 100,000 |
Course | Acute | Chronic |
Presentation | Abdominal distention Cramping pain Nausea/vomiting | Abdominal distention Abdominal pain Bloating |
Anatomic involvement | Colonic dilatation, usually cecum, right colon | Colonic or small bowel dilatation |
Pathophysiology | Multifactorial Autonomic dysfunction strongly implicated | Neuropathic disorder of enteric or extrinsic nervous system Myopathic disorder of smooth muscle Malfunction of interstitial cells of Cajal |
Management | Fluid resuscitation, correction of electrolyte abnormalities, avoidance of opioids/ anticholinergics Ambulation, bowel rest Decompression with nasogastric or rectal tubes Pharmacologic treatment with neostigmine Operative intervention in cases of colonic perforation or ischemia | Dietary modification, treatment of underlying disease Prokinetics, such as Prucalopride, for symptomatic relief (Grade 2C) Pyridostigmine in chronic phase of CIPO |
*Inpatient admissions
Disclosures:
Yushan Wang, MD1, Saleh Alghsoon, MBBS1, Suma Gondi, MD1, John Roberts, 2, Raffi Karagozian, MD1. A0262 - Using Prokinetic Agents in Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction (CIPO), ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
