Back
Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Liver
D0510 - Liver Abnormalities in Celiac Disease and Response to a Gluten-Free Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Daryl Ramai, MD, MSc
University of Utah
Salt Lake City, UT
Presenting Author(s)
Daryl Ramai, MD, MSc1, Anuraag Jena, MBBS2, Praveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antriksh Kumar, MBBS2, Chhagan Birda, MBBS2, Arup Choudhury, MBBS2, Naveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD3, Jayanta Samanta, MBBS, MD, DM2
1University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, Chandigarh, India; 3University of Foggia, Foggia, Puglia, Italy
Introduction: Clinical presentation of Celiac's disease (CeD) may vary from asymptomatic to patients presenting with malabsorption, growth impediment, osteoporosis, and iron deficiency anemia. There is a paucity of data on CeD and liver involvement as well as the effect of a gluten free diet on hepatic function.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Medline & Embase databases from inception for studies reporting on CeD and liver abnormalities. Pooled proportion of patients of CeD with deranged transaminases, etiology of liver diseases with CeD, and the response to a gluten free diet in form of normalization of transaminases were estimated using a random effects model. Subgroup and influence analysis based on age group, geographic distribution, and duration of gluten free diet was also performed.
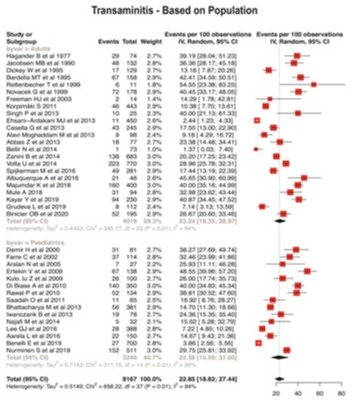
Results: Total 38 studies (8167 patients) were included. The pooled proportion of patients of CeD with elevated transaminases was 22.85% (95% CI: 18.82-27.44, I 2=94%) overall with similar prevalence noted among adults (23.24%) and children (22.38%). The commonest etiology for the liver abnormalities was reported as celiac hepatitis at 49.54% (95% CI: 31.79-67.4, I 2=87%) followed by other liver diseases. Compliance to a gluten free diet was noted in 88.16% of adults and 94.01% of children (overall 90.11%). The proportion of CeD patients with liver abnormalities who showed response to a gluten free diet was 86.83% (95% CI: 82.35-90.31, I2=66%) overall with similar response among adults (86.01%) and pediatric population (89.24%). Western studies reported better response to a gluten free diet at 87.75% compared to the east (78.84%)
Discussion: Hepatic involvement was noted in 23% of CeD patients. Celiac hepatitis was reported in more than half of affected patients. Patients who had good adherence to a gluten free diet showed good recovery and normalization of liver transaminases.
Disclosures:
Daryl Ramai, MD, MSc1, Anuraag Jena, MBBS2, Praveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antriksh Kumar, MBBS2, Chhagan Birda, MBBS2, Arup Choudhury, MBBS2, Naveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD3, Jayanta Samanta, MBBS, MD, DM2. D0510 - Liver Abnormalities in Celiac Disease and Response to a Gluten-Free Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, Chandigarh, India; 3University of Foggia, Foggia, Puglia, Italy
Introduction: Clinical presentation of Celiac's disease (CeD) may vary from asymptomatic to patients presenting with malabsorption, growth impediment, osteoporosis, and iron deficiency anemia. There is a paucity of data on CeD and liver involvement as well as the effect of a gluten free diet on hepatic function.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Medline & Embase databases from inception for studies reporting on CeD and liver abnormalities. Pooled proportion of patients of CeD with deranged transaminases, etiology of liver diseases with CeD, and the response to a gluten free diet in form of normalization of transaminases were estimated using a random effects model. Subgroup and influence analysis based on age group, geographic distribution, and duration of gluten free diet was also performed.
Results: Total 38 studies (8167 patients) were included. The pooled proportion of patients of CeD with elevated transaminases was 22.85% (95% CI: 18.82-27.44, I 2=94%) overall with similar prevalence noted among adults (23.24%) and children (22.38%). The commonest etiology for the liver abnormalities was reported as celiac hepatitis at 49.54% (95% CI: 31.79-67.4, I 2=87%) followed by other liver diseases. Compliance to a gluten free diet was noted in 88.16% of adults and 94.01% of children (overall 90.11%). The proportion of CeD patients with liver abnormalities who showed response to a gluten free diet was 86.83% (95% CI: 82.35-90.31, I2=66%) overall with similar response among adults (86.01%) and pediatric population (89.24%). Western studies reported better response to a gluten free diet at 87.75% compared to the east (78.84%)
Discussion: Hepatic involvement was noted in 23% of CeD patients. Celiac hepatitis was reported in more than half of affected patients. Patients who had good adherence to a gluten free diet showed good recovery and normalization of liver transaminases.

Figure: Forrest plot demonstrating the pooled proportion of celiac disease patients having elevated transaminase levels.
Disclosures:
Daryl Ramai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anuraag Jena indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praveen Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antriksh Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chhagan Birda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arup Choudhury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naveen Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antonio Facciorusso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jayanta Samanta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daryl Ramai, MD, MSc1, Anuraag Jena, MBBS2, Praveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antriksh Kumar, MBBS2, Chhagan Birda, MBBS2, Arup Choudhury, MBBS2, Naveen Kumar, MBBS2, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD3, Jayanta Samanta, MBBS, MD, DM2. D0510 - Liver Abnormalities in Celiac Disease and Response to a Gluten-Free Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
