Back

Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Esophagus
A0231 - Pancreatic Heterotopia at Gastroesophageal Junction
Sunday, October 23, 2022
5:00 PM – 7:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Vikash Kumar, MD
The Brooklyn Hospital Center
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Vikash Kumar, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD1, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP2, Heidi Budke, MD2, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG2
1The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Blanchard Valley Health System, Findlay, OH
Introduction: Pancreatic heterotopia is defined as pancreatic tissue found outside the normal anatomical location. It is often an incidental finding but becomes clinically evident when complicated by pathologic changes such as inflammation, bleeding, obstruction, and malignant transformation. We present a case of a 57 years old female who presented with dyspepsia and was found to have ectopic pancreatic tissue at the gastroesophageal junction on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
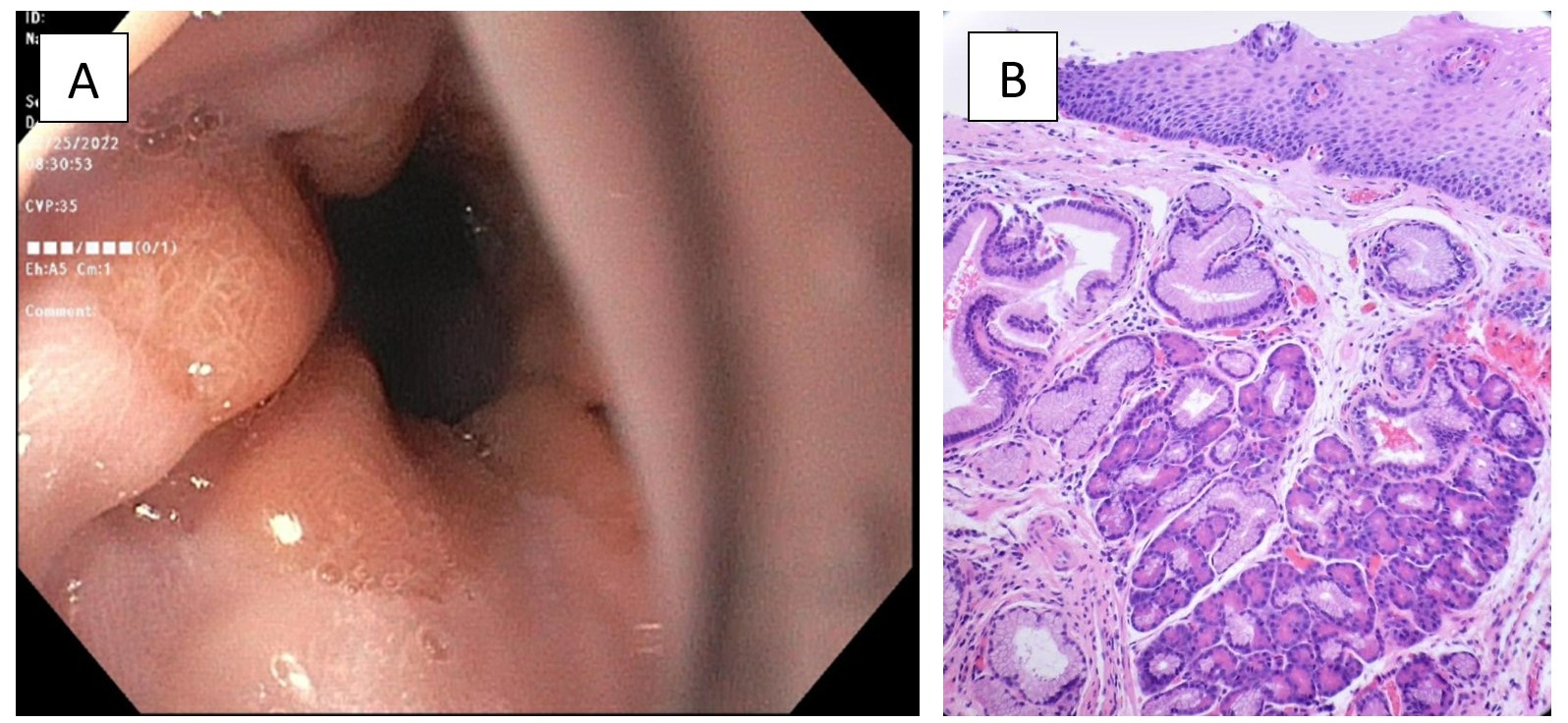
Case Description/Methods: A 57-year-old female with a past medical history of Cecal polyp presents to the gastroenterology clinic for epigastric pain under the rib cage ongoing for several months; pain worsens if she bends over. She denies nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, dysphagia, or weight loss. She used to take pantoprazole but stopped taking it two months ago. CT chest was significant for small hiatal hernia. EGD significant normal esophagus but irregular Z-line (Figure 1A), small hiatal hernia, and gastric erythema. Z-line was mildly irregular and was biopsied, which shows junctional mucosa showing focal pancreatic metaplasia/heterotopia with no malignant changes. Negative for intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia (Figure 1B)
Discussion: Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach is usually located within 5 cm of the pylorus and is more common along the greater curve, but the involvement of the GE junction is very rare [1]. Symptoms vary depending on the affected location and size of the mass. Patients with ectopic pancreatic tissue at the GE junction can be asymptomatic or present with epigastric pain, reflux or heartburn. These patients can be managed conservatively with medical treatment [2]. The risk of malignancy arising in the heterotopic pancreas is exceedingly rare, but several documented cases have appeared in the literature. Pancreatic heterotopia should be considered as a source of a potentially malignant lesion, and early treatment or close monitoring for aberrant pancreas is recommended.
1. Xiong Y, Xie Y, Jin DD, Wang XY. Heterotopic pancreas adenocarcinoma in the stomach: A case report
and literature review. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(10):1979-1987. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1979
2. Jenkins JK, Smith F, Mularz S, Chaudhary S. Heterotopic Pancreas Located at the Gastroesophageal
Junction in a Hiatal Hernia: A Case Report. Cureus. 2021;13(12):e20630. Published 2021 Dec 23.
doi:10.7759/cureus.20630
Disclosures:
Vikash Kumar, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD1, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP2, Heidi Budke, MD2, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG2. A0231 - Pancreatic Heterotopia at Gastroesophageal Junction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Blanchard Valley Health System, Findlay, OH
Introduction: Pancreatic heterotopia is defined as pancreatic tissue found outside the normal anatomical location. It is often an incidental finding but becomes clinically evident when complicated by pathologic changes such as inflammation, bleeding, obstruction, and malignant transformation. We present a case of a 57 years old female who presented with dyspepsia and was found to have ectopic pancreatic tissue at the gastroesophageal junction on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
Case Description/Methods: A 57-year-old female with a past medical history of Cecal polyp presents to the gastroenterology clinic for epigastric pain under the rib cage ongoing for several months; pain worsens if she bends over. She denies nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, dysphagia, or weight loss. She used to take pantoprazole but stopped taking it two months ago. CT chest was significant for small hiatal hernia. EGD significant normal esophagus but irregular Z-line (Figure 1A), small hiatal hernia, and gastric erythema. Z-line was mildly irregular and was biopsied, which shows junctional mucosa showing focal pancreatic metaplasia/heterotopia with no malignant changes. Negative for intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia (Figure 1B)
Discussion: Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach is usually located within 5 cm of the pylorus and is more common along the greater curve, but the involvement of the GE junction is very rare [1]. Symptoms vary depending on the affected location and size of the mass. Patients with ectopic pancreatic tissue at the GE junction can be asymptomatic or present with epigastric pain, reflux or heartburn. These patients can be managed conservatively with medical treatment [2]. The risk of malignancy arising in the heterotopic pancreas is exceedingly rare, but several documented cases have appeared in the literature. Pancreatic heterotopia should be considered as a source of a potentially malignant lesion, and early treatment or close monitoring for aberrant pancreas is recommended.
1. Xiong Y, Xie Y, Jin DD, Wang XY. Heterotopic pancreas adenocarcinoma in the stomach: A case report
and literature review. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(10):1979-1987. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1979
2. Jenkins JK, Smith F, Mularz S, Chaudhary S. Heterotopic Pancreas Located at the Gastroesophageal
Junction in a Hiatal Hernia: A Case Report. Cureus. 2021;13(12):e20630. Published 2021 Dec 23.
doi:10.7759/cureus.20630

Figure: Figure 1A: Endoscopy showing irregular Z- line.
Figure 1B: Biopsy showing junctional mucosa with focal pancreatic metaplasia or heterotopia
Figure 1B: Biopsy showing junctional mucosa with focal pancreatic metaplasia or heterotopia
Disclosures:
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijay Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tonya DeVaul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heidi Budke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinaya Gaduputi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD1, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP2, Heidi Budke, MD2, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG2. A0231 - Pancreatic Heterotopia at Gastroesophageal Junction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
