Back

Poster Session A - Sunday Afternoon
Category: Pediatrics
A0607 - Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Sigmoid Duplication Cyst in a 6-Year-Old Child
Sunday, October 23, 2022
5:00 PM – 7:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- JH
John G. Hong, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
John G. Hong, MD, J. Antonio Quiros, MD, Peter Midulla, MD, John Tackett, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Colo-colonic intussusception is rare with a prevalence of 0.2-4.4% and usually associated with colonic polyps and malignancy in adults. Distal colo-colonic intussusception is extremely rare in children and those caused by enteric duplication cysts as lead points are unusual. While enteric duplication is more commonly seen in children, the most common location is in the ileum and only 6.8 to 13% occur in the hindgut. It is usually diagnosed with ultrasound or CT and treated with surgery for removal.
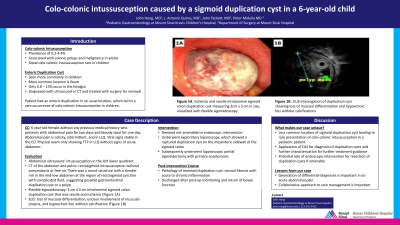
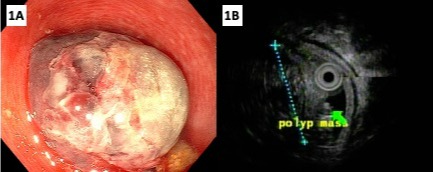
Case Description/Methods: We present a previously healthy 6-year-old female who had abdominal pain for two days and bloody stools for one day. Abdominal pain was colicky and intermittent, and located in left lower quadrant. When examined, she was tender to palpation in the left lower quadrant but otherwise unremarkable. She had an abdominal ultrasound which showed intussusception in the left lower quadrant. CT of the abdomen and pelvis showed rectosigmoid intussusception without pneumatosis or free air. There was a round structure with a slender rim in the mid-low abdomen at the region of rectosigmoid junction with complicated fluid, suggesting possible gastrointestinal duplication cyst or a polyp. She underwent flexible sigmoidoscopy, which showed 2 cm x 3 cm intraluminal sigmoid colon duplication cyst that was sessile and ischemic (Figure 1A). Mucosa around the duplication cyst was friable, erythematous, and had loss of vascularity. Endoscopic ultrasound interrogation of the duplication cyst showed loss of mucosal differentiation, unclear involvement of muscular propria, and hypoechoic foci without calcification (figure 1B). It was not amenable for endoscopic removal. She subsequently underwent exploratory laparoscopy, which showed a ruptured duplication cyst on the mesenteric sidewall of the sigmoid colon. She then had laparoscopic partial sigmoidectomy with anastomosis. Pathology of resected duplication cyst showed serosal fibrosis with acute to chronic inflammation. She was discharged with return of bowel function and tolerating oral diet.
Discussion: The presented case is unique given the less common location of sigmoid duplication cyst and rare presentation of colo-colonic intussusception in a pediatric patient. This case also highlights the application of endoscopy and specifically EUS not only to diagnose and further characterize enteric duplication cysts, but also to potentially intervene therapeutically.
Disclosures:
John G. Hong, MD, J. Antonio Quiros, MD, Peter Midulla, MD, John Tackett, MD. A0607 - Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Sigmoid Duplication Cyst in a 6-Year-Old Child, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Colo-colonic intussusception is rare with a prevalence of 0.2-4.4% and usually associated with colonic polyps and malignancy in adults. Distal colo-colonic intussusception is extremely rare in children and those caused by enteric duplication cysts as lead points are unusual. While enteric duplication is more commonly seen in children, the most common location is in the ileum and only 6.8 to 13% occur in the hindgut. It is usually diagnosed with ultrasound or CT and treated with surgery for removal.
Case Description/Methods: We present a previously healthy 6-year-old female who had abdominal pain for two days and bloody stools for one day. Abdominal pain was colicky and intermittent, and located in left lower quadrant. When examined, she was tender to palpation in the left lower quadrant but otherwise unremarkable. She had an abdominal ultrasound which showed intussusception in the left lower quadrant. CT of the abdomen and pelvis showed rectosigmoid intussusception without pneumatosis or free air. There was a round structure with a slender rim in the mid-low abdomen at the region of rectosigmoid junction with complicated fluid, suggesting possible gastrointestinal duplication cyst or a polyp. She underwent flexible sigmoidoscopy, which showed 2 cm x 3 cm intraluminal sigmoid colon duplication cyst that was sessile and ischemic (Figure 1A). Mucosa around the duplication cyst was friable, erythematous, and had loss of vascularity. Endoscopic ultrasound interrogation of the duplication cyst showed loss of mucosal differentiation, unclear involvement of muscular propria, and hypoechoic foci without calcification (figure 1B). It was not amenable for endoscopic removal. She subsequently underwent exploratory laparoscopy, which showed a ruptured duplication cyst on the mesenteric sidewall of the sigmoid colon. She then had laparoscopic partial sigmoidectomy with anastomosis. Pathology of resected duplication cyst showed serosal fibrosis with acute to chronic inflammation. She was discharged with return of bowel function and tolerating oral diet.
Discussion: The presented case is unique given the less common location of sigmoid duplication cyst and rare presentation of colo-colonic intussusception in a pediatric patient. This case also highlights the application of endoscopy and specifically EUS not only to diagnose and further characterize enteric duplication cysts, but also to potentially intervene therapeutically.

Figure: Figure 1A. Flexible sigmoidoscopy showing duplication cyst.
Figure 1B. Endoscopic ultrasound interrogation of the duplication cyst.
Figure 1B. Endoscopic ultrasound interrogation of the duplication cyst.
Disclosures:
John Hong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
J. Antonio Quiros indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Midulla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Tackett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John G. Hong, MD, J. Antonio Quiros, MD, Peter Midulla, MD, John Tackett, MD. A0607 - Colo-Colonic Intussusception Caused by a Sigmoid Duplication Cyst in a 6-Year-Old Child, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
