Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Small Intestine
D0650 - Pembrolizumab-Induced Ulcerative Duodenitis Treatment Successfully Treated With Prednisone
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Khola Qamar, MD
Dartmouth-Hitchcock Putnam Physicians
Bennington, VT
Presenting Author(s)
Khola Qamar, MD1, Abhinav Tiwari, MD2
1Dartmouth-Hitchcock Putnam Physicians, Bennington, VT; 2Sacred Heart Medical Center at RiverBend, Springfield, OR
Introduction: Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) inhibitors belong to a category of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and have been used to treat melanoma, lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma Hodgkin's lymphoma, and gastric cancer. Among gastrointestinal adverse events, colitis occurs most frequently, while gastritis is of rare occurrence as only handful of cases have been reported. Here, we present a unique case of isolated ulcerative duodenitis associated with PD-L1 uses successfully treated with steroid.
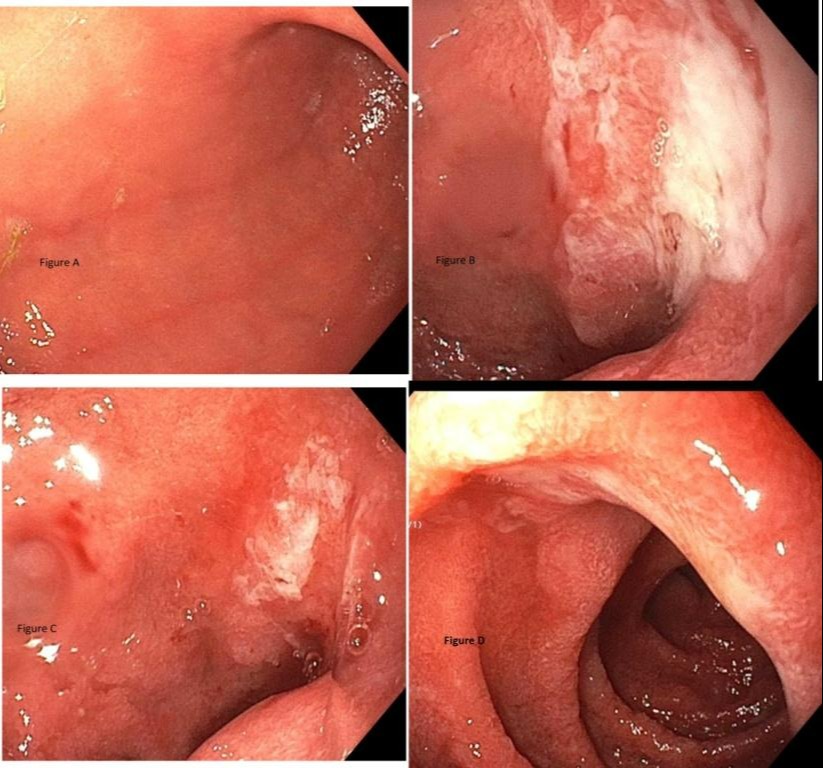
Case Description/Methods: 57-year-old female with PMH of malignant melanoma with osseous metastasis treated with Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for 8 months, last dose received 1 month prior to presentation. She presented with 10-day history of acute onset nausea, non-bilious vomiting, and LUQ pain. There was no history of NSAID use. Workup including CBC, LFTs, contrast enhanced CT abdomen was unremarkable. EGD revealed multiple superficial duodenal ulcers (see figure) in the bulb and 2nd part with background of mucosal inflammation. Biopsies showed marked active duodenitis with villous atrophy, cellular atrophy, cryptitis, crypt abscess and crypt dropout consistent with medication induced injury. She was started on 1 mg/kg (60 mg), tapered by 10 mg/week. Her symptoms resolved by end of 1 week of treatment.
Discussion: There have been less than 20 cases of PD-L1 associated upper GI adverse events reported in literature. EGD findings have been variable including normal, mild gastritis, gastric erosions, hemorrhagic gastritis, atrophy, and ulceration. Our case is unique as the patient had isolated duodenal findings. The exact mechanism of injury is unknown, although several mechanisms of tissue injury due to self‐reactive CD8‐positive T cells and plasma antibody‐mediated autoantibody production from CD4‐positive T cells have been proposed. Our patient responded well with tapering dose of prednisone, however few refractory cases required treatment with anti‐tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‐α antibody, infliximab. It is imperative to carefully examine the duodenum including 2nd/3rd part when excluding ICI related upper GI adverse effects.
Disclosures:
Khola Qamar, MD1, Abhinav Tiwari, MD2. D0650 - Pembrolizumab-Induced Ulcerative Duodenitis Treatment Successfully Treated With Prednisone, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Dartmouth-Hitchcock Putnam Physicians, Bennington, VT; 2Sacred Heart Medical Center at RiverBend, Springfield, OR
Introduction: Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) inhibitors belong to a category of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and have been used to treat melanoma, lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma Hodgkin's lymphoma, and gastric cancer. Among gastrointestinal adverse events, colitis occurs most frequently, while gastritis is of rare occurrence as only handful of cases have been reported. Here, we present a unique case of isolated ulcerative duodenitis associated with PD-L1 uses successfully treated with steroid.
Case Description/Methods: 57-year-old female with PMH of malignant melanoma with osseous metastasis treated with Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for 8 months, last dose received 1 month prior to presentation. She presented with 10-day history of acute onset nausea, non-bilious vomiting, and LUQ pain. There was no history of NSAID use. Workup including CBC, LFTs, contrast enhanced CT abdomen was unremarkable. EGD revealed multiple superficial duodenal ulcers (see figure) in the bulb and 2nd part with background of mucosal inflammation. Biopsies showed marked active duodenitis with villous atrophy, cellular atrophy, cryptitis, crypt abscess and crypt dropout consistent with medication induced injury. She was started on 1 mg/kg (60 mg), tapered by 10 mg/week. Her symptoms resolved by end of 1 week of treatment.
Discussion: There have been less than 20 cases of PD-L1 associated upper GI adverse events reported in literature. EGD findings have been variable including normal, mild gastritis, gastric erosions, hemorrhagic gastritis, atrophy, and ulceration. Our case is unique as the patient had isolated duodenal findings. The exact mechanism of injury is unknown, although several mechanisms of tissue injury due to self‐reactive CD8‐positive T cells and plasma antibody‐mediated autoantibody production from CD4‐positive T cells have been proposed. Our patient responded well with tapering dose of prednisone, however few refractory cases required treatment with anti‐tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‐α antibody, infliximab. It is imperative to carefully examine the duodenum including 2nd/3rd part when excluding ICI related upper GI adverse effects.

Figure: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showing stomach (fig A), ulcerated mucosa in duodenal bulb (fig B and C) and in 2nd part of duodenum (fig D)
Disclosures:
Khola Qamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhinav Tiwari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khola Qamar, MD1, Abhinav Tiwari, MD2. D0650 - Pembrolizumab-Induced Ulcerative Duodenitis Treatment Successfully Treated With Prednisone, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
