Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
B0019 - EUS-Guided Portal Pressure Gradient Measurements to Diagnose Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- YR
Yeshaswini Panathur Sreenivasa Reddy, MD
University of Illinois College of Medicine at Peoria
Peoria, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Yeshaswini Panathur Sreenivasa Reddy, MD, Srinivas Puli,
University of Illinois College of Medicine at Peoria, Peoria, IL
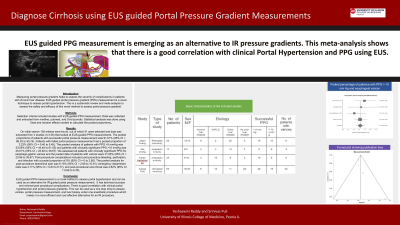
Introduction: Measuring portal pressure gradient helps to assess the severity of complications in patients with chronic liver disease. EUS guided portal pressure gradient (PPG) measurement is a novel technique to assess portal hypertension. This is a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the safety and efficacy of this novel method to assess portal pressure gradient.
Methods: Selection criteria included studies with EUS guided PPG measurement. Data was collected and extracted from medline, pubmed, and Ovid journals. Statistical analysis was done using fixed and random effects models to calculate the pooled proportions.
Results: On initial search 136 articles were found, out of which 51 were selected and data was extracted from 4 studies (n=128) that looked at EUS-guided PPG measurements. The pooled proportions of patients with successful portal pressure measurement was 91.61% (95% CI = 86.25 to 95.74). Patients with failed portal pressure measurement had a pooled proportion of 2.22% (95% CI = 0.40 to 5.45). The pooled analysis of patients with PPG >5 mmHg was 53.06% (95% CI = 44.48 to 61.55) and patients with clinically significant PPG >10 mmHg was 30.51% (95% CI = 22.92 to 38.67). We assessed all patients with clinically significant PPG for esophago-gastric varices and the pooled data of patients with varices were 31.65% (95% CI = 23.96 to 39.87). Post-procedural complications included post-procedure bleeding, perforation, and infection with a pooled proportion of 0% (95% CI = 0 to 2.85). The pooled analysis for post-procedure abdominal pain was 6.15% (95% CI = 2.68 to 10.91), emergency department visits was 3.11% (95% CI = 0.83 to 6.77), and post-procedural sore throat was 2.82% (95% CI = 0.68 to 6.35). Publication bias calculated by using the Harbord-Egger bias indicator gave a value of 1.48 (95% CI = -1.03 to 4.00, p = 0.12). The Begg-Mazumdar indicator gave Kendall's tau b value of 1 (p = 0.08).
Discussion: EUS guided PPG measurement is a novel method to assess portal hypertension and can be used as an alternative for IR guided portal pressure measurement. It has technical success and minimal post procedural complications. There is good correlation with clinical portal hypertension and portal pressure gradients. This can be used as a one stop shop to assess varices, portal pressure measurement, and liver biopsy under one anesthetic procedure which makes it a more efficient and cost effective alternative for an IR procedure.
Disclosures:
Yeshaswini Panathur Sreenivasa Reddy, MD, Srinivas Puli, . B0019 - EUS-Guided Portal Pressure Gradient Measurements to Diagnose Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Illinois College of Medicine at Peoria, Peoria, IL
Introduction: Measuring portal pressure gradient helps to assess the severity of complications in patients with chronic liver disease. EUS guided portal pressure gradient (PPG) measurement is a novel technique to assess portal hypertension. This is a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the safety and efficacy of this novel method to assess portal pressure gradient.
Methods: Selection criteria included studies with EUS guided PPG measurement. Data was collected and extracted from medline, pubmed, and Ovid journals. Statistical analysis was done using fixed and random effects models to calculate the pooled proportions.
Results: On initial search 136 articles were found, out of which 51 were selected and data was extracted from 4 studies (n=128) that looked at EUS-guided PPG measurements. The pooled proportions of patients with successful portal pressure measurement was 91.61% (95% CI = 86.25 to 95.74). Patients with failed portal pressure measurement had a pooled proportion of 2.22% (95% CI = 0.40 to 5.45). The pooled analysis of patients with PPG >5 mmHg was 53.06% (95% CI = 44.48 to 61.55) and patients with clinically significant PPG >10 mmHg was 30.51% (95% CI = 22.92 to 38.67). We assessed all patients with clinically significant PPG for esophago-gastric varices and the pooled data of patients with varices were 31.65% (95% CI = 23.96 to 39.87). Post-procedural complications included post-procedure bleeding, perforation, and infection with a pooled proportion of 0% (95% CI = 0 to 2.85). The pooled analysis for post-procedure abdominal pain was 6.15% (95% CI = 2.68 to 10.91), emergency department visits was 3.11% (95% CI = 0.83 to 6.77), and post-procedural sore throat was 2.82% (95% CI = 0.68 to 6.35). Publication bias calculated by using the Harbord-Egger bias indicator gave a value of 1.48 (95% CI = -1.03 to 4.00, p = 0.12). The Begg-Mazumdar indicator gave Kendall's tau b value of 1 (p = 0.08).
Discussion: EUS guided PPG measurement is a novel method to assess portal hypertension and can be used as an alternative for IR guided portal pressure measurement. It has technical success and minimal post procedural complications. There is good correlation with clinical portal hypertension and portal pressure gradients. This can be used as a one stop shop to assess varices, portal pressure measurement, and liver biopsy under one anesthetic procedure which makes it a more efficient and cost effective alternative for an IR procedure.
Disclosures:
Yeshaswini Panathur Sreenivasa Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srinivas Puli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yeshaswini Panathur Sreenivasa Reddy, MD, Srinivas Puli, . B0019 - EUS-Guided Portal Pressure Gradient Measurements to Diagnose Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
