Back


Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
D0069 - An Unusual Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Suhail S. Sidhu, BS
Creighton University School of Medicine
Omaha, NE
Presenting Author(s)
Suhail Sidhu, BS, Sangeetha Tandalam, BS, Bryce Schutte, DO, Thamer Kassim, MD, Nicholas Dietz, MD, Sampath Poreddy, MD
Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory systemic autoimmune disease of unknown origin that can affect multiple organs. It affects the pancreatico-hepatobiliary system presenting either as sclerosing cholangitis, type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), both, or rarely presents as IgG4-related hepatopathy. We present a challenging case of a patient with IgG4-RD.
Case Description/Methods: A 43-year-old man presented with painless jaundice and diarrhea for 1 month. Physical exam was relevant for scleral icterus with a negative Murphy’s sign. Initial evaluation revealed alkaline phosphatase 237 and total bilirubin of 10.4. Diffuse intrahepatic biliary dilation with obstruction at the confluence of the common hepatic duct (CHD) was found on MRCP. Subsequent ERCP showed stenosis of the upper third of the right main bile duct. One 8.5 Fr by 15 cm transpapillary temporary stent was placed into the right hepatic duct. Biopsies showed normal ductal mucosa with no malignant cells.
Within the next month, patient experienced worsening jaundice, elevated CA-19-9 (3995), serum IgG levels (2582), and total bilirubin (6.7). Repeat ERCP showed CHD stricture. CT abdomen showed increased intrahepatic biliary ductal dilation and persistent soft tissue thickening at confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts. EUS showed normal pancreatic parenchyma and a 3cm mass at the peripheral area. Multiple biopsies were negative for cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). ERCP demonstrated nodular CHD, and biopsies of the biliary duct showed increased IgG4-positive plasma cells and an IgG4:IgG plasma cell ratio of 27%. After re-examination, it revealed an area with >20 plasma cells positive for IgG4, consistent with IgG4-related disease. The patient started on Prednisone 40mg once daily with a prolonged taper and improved significantly.
Discussion: IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis is the most common extrapancreatic manifestation of AIP type 1 presenting in >70% of patients. This case is suggestive of IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis without evidence of acute pancreatitis presenting as a hilar mass mimicking CCA. While biopsies failed to identify a neoplastic or infectious agent, it wasn’t until biopsies were stained with IgG4 revealing the etiology of the disease. It is pertinent to be aware of the GI manifestations of IgG4-RD and to consider it in the differential when addressing unrelenting symptomatic jaundice. Early confirmation of >20 plasma cells HPF in biopsy avoids unnecessary procedures and allows for early treatment.
Disclosures:
Suhail Sidhu, BS, Sangeetha Tandalam, BS, Bryce Schutte, DO, Thamer Kassim, MD, Nicholas Dietz, MD, Sampath Poreddy, MD. D0069 - An Unusual Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory systemic autoimmune disease of unknown origin that can affect multiple organs. It affects the pancreatico-hepatobiliary system presenting either as sclerosing cholangitis, type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), both, or rarely presents as IgG4-related hepatopathy. We present a challenging case of a patient with IgG4-RD.
Case Description/Methods: A 43-year-old man presented with painless jaundice and diarrhea for 1 month. Physical exam was relevant for scleral icterus with a negative Murphy’s sign. Initial evaluation revealed alkaline phosphatase 237 and total bilirubin of 10.4. Diffuse intrahepatic biliary dilation with obstruction at the confluence of the common hepatic duct (CHD) was found on MRCP. Subsequent ERCP showed stenosis of the upper third of the right main bile duct. One 8.5 Fr by 15 cm transpapillary temporary stent was placed into the right hepatic duct. Biopsies showed normal ductal mucosa with no malignant cells.
Within the next month, patient experienced worsening jaundice, elevated CA-19-9 (3995), serum IgG levels (2582), and total bilirubin (6.7). Repeat ERCP showed CHD stricture. CT abdomen showed increased intrahepatic biliary ductal dilation and persistent soft tissue thickening at confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts. EUS showed normal pancreatic parenchyma and a 3cm mass at the peripheral area. Multiple biopsies were negative for cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). ERCP demonstrated nodular CHD, and biopsies of the biliary duct showed increased IgG4-positive plasma cells and an IgG4:IgG plasma cell ratio of 27%. After re-examination, it revealed an area with >20 plasma cells positive for IgG4, consistent with IgG4-related disease. The patient started on Prednisone 40mg once daily with a prolonged taper and improved significantly.
Discussion: IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis is the most common extrapancreatic manifestation of AIP type 1 presenting in >70% of patients. This case is suggestive of IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis without evidence of acute pancreatitis presenting as a hilar mass mimicking CCA. While biopsies failed to identify a neoplastic or infectious agent, it wasn’t until biopsies were stained with IgG4 revealing the etiology of the disease. It is pertinent to be aware of the GI manifestations of IgG4-RD and to consider it in the differential when addressing unrelenting symptomatic jaundice. Early confirmation of >20 plasma cells HPF in biopsy avoids unnecessary procedures and allows for early treatment.

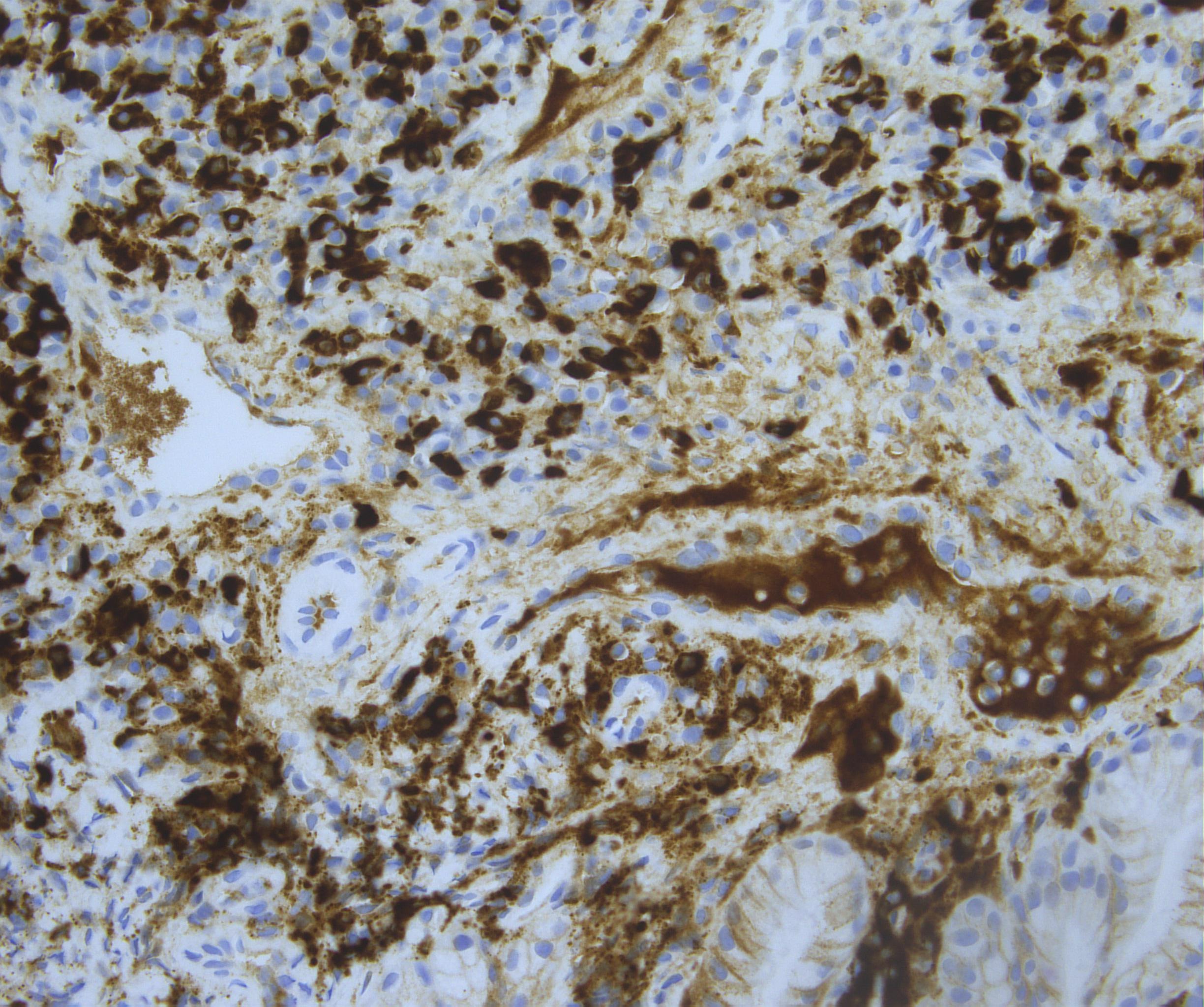
Figure: Immunohistochemical staining for IgG4 in a high power field showing markedly increased expression of IgG4 (up to 50 per high power field at 400X magnification). The upper portion of the image shows the positive plasma cells with cytoplasmic and membranous expression of IgG4
Disclosures:
Suhail Sidhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sangeetha Tandalam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bryce Schutte indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thamer Kassim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicholas Dietz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sampath Poreddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suhail Sidhu, BS, Sangeetha Tandalam, BS, Bryce Schutte, DO, Thamer Kassim, MD, Nicholas Dietz, MD, Sampath Poreddy, MD. D0069 - An Unusual Presentation of IgG4-Related Disease Mimicking Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
