Back


Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Esophagus
D0230 - Esophagobronchial Fistula After a Laparoscopic Partial Fundoplication, Mimicking as Empyema
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Jessie Wang, MD
St. Joseph's Medical Center
Stockton, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Solomon O. Badejoko, MD, MPH1, Jessie Wang, MD1, Paul E. Formaker, MS2, Mojolaoluwa Balogun, MS2, Arshi Jha, DO1, Jessica B. Madej, MD1, Mariam Akinwale, MD1, Kolade Olabode, MD, MPH3, Nso Nso, MD, MPH4, Raphael Ezeagu, MD, MPH5, Gurtej Malhi, MD1
1St. Joseph's Medical Center, Stockton, CA; 2Tuoro University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Vallejo, CA; 3College of Public Health, Kent State University, Kent, OH; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens Hospital Center, Astoria, NY; 5Ballad Health, Johnson City, TN
Introduction: Laparoscopic fundoplication is often indicated in cases of paraesophageal hiatal hernia (HH) and chronic GERD that are refractory to medical management. Esophagobronchial (EB) fistula is a rare postoperative complication of fundoplication and is very challenging to diagnose and manage. We present an uncommon case of EB fistula, eventually managed with esophageal stent placement.[1]
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old female with a history of paraesophageal HH and chronic GERD symptoms refractory to medical management underwent HH repair with laparoscopic 270-degree fundoplication. Her postoperative outpatient course was complicated by presumed aspiration pneumonia and was treated. She presented 2 weeks post-procedure with persistent left-sided pleuritic chest pain, cough, and dyspnea which progressively got worse since discharge. Labs showed WBC 26 cells/mm3, CRP 37mg/L. Chest CT scan showed loculated empyema (16 x 12 x 13 cm) in the left lung base, small gas/fluid collection (1x1 cm) posterior to the distal esophagus, and compressive atelectasis. She received piperacillin and metronidazole. Thoracotomy and empyema drainage were performed.
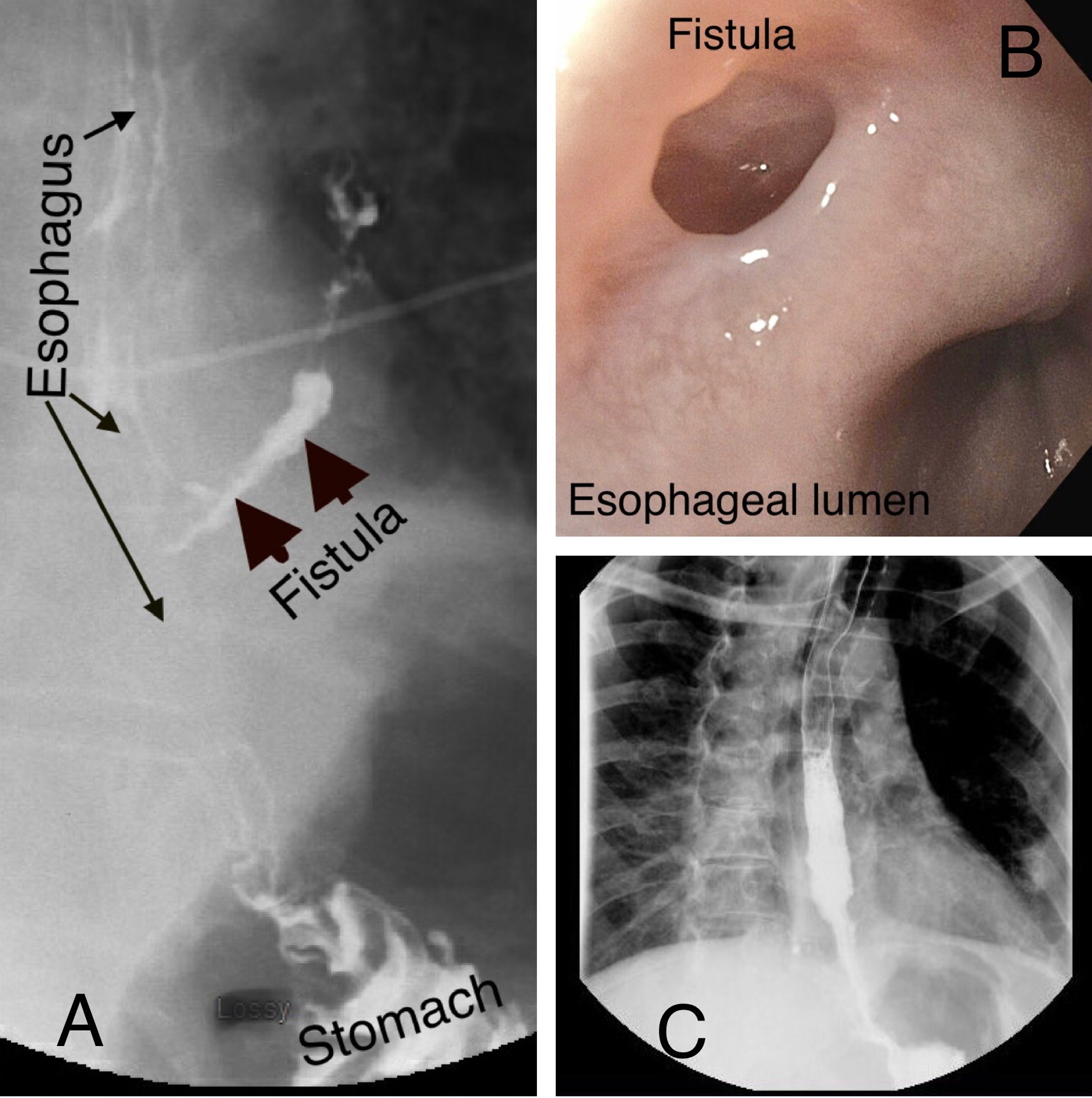
An Esophagoscopy revealed a small fistulous opening in the distal esophagus (5-6mm in size), about 4cm proximal to the GE junction. An 18mm x 10cm fully covered Wallflex Boston Scientific esophageal stent was deployed, with the distal end below the GE junction. To prevent migration, it was secured using the Apollo Endo Stitch device. The patient was safely discharged home on Pantoprazole. The chest tube was removed and she was discharged home. On follow-up 3 months later, she had no recurrent pneumonia, cough, chest pain, or fever. A repeat endoscopy with the removal of the esophageal stent was performed. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy, the fistulous opening appeared to have closed. Post-procedure gastrograffin esophagram demonstrated no leak. She continued to do well 2 months post-removal of the esophageal stent.
Discussion: This case report highlights a rare complication of the EB fistula that has been associated with a HH repair and fundoplication. A high clinical index of suspicion, early diagnosis, and management are needed in patients who develop recurrent cough and pneumonia with empyema soon after partial fundoplication. These patients can be successfully managed by placement of fully covered esophageal stent insertion along with drainage of empyema if present with chest tube insertion.
Disclosures:
Solomon O. Badejoko, MD, MPH1, Jessie Wang, MD1, Paul E. Formaker, MS2, Mojolaoluwa Balogun, MS2, Arshi Jha, DO1, Jessica B. Madej, MD1, Mariam Akinwale, MD1, Kolade Olabode, MD, MPH3, Nso Nso, MD, MPH4, Raphael Ezeagu, MD, MPH5, Gurtej Malhi, MD1. D0230 - Esophagobronchial Fistula After a Laparoscopic Partial Fundoplication, Mimicking as Empyema, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1St. Joseph's Medical Center, Stockton, CA; 2Tuoro University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Vallejo, CA; 3College of Public Health, Kent State University, Kent, OH; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens Hospital Center, Astoria, NY; 5Ballad Health, Johnson City, TN
Introduction: Laparoscopic fundoplication is often indicated in cases of paraesophageal hiatal hernia (HH) and chronic GERD that are refractory to medical management. Esophagobronchial (EB) fistula is a rare postoperative complication of fundoplication and is very challenging to diagnose and manage. We present an uncommon case of EB fistula, eventually managed with esophageal stent placement.[1]
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old female with a history of paraesophageal HH and chronic GERD symptoms refractory to medical management underwent HH repair with laparoscopic 270-degree fundoplication. Her postoperative outpatient course was complicated by presumed aspiration pneumonia and was treated. She presented 2 weeks post-procedure with persistent left-sided pleuritic chest pain, cough, and dyspnea which progressively got worse since discharge. Labs showed WBC 26 cells/mm3, CRP 37mg/L. Chest CT scan showed loculated empyema (16 x 12 x 13 cm) in the left lung base, small gas/fluid collection (1x1 cm) posterior to the distal esophagus, and compressive atelectasis. She received piperacillin and metronidazole. Thoracotomy and empyema drainage were performed.
An Esophagoscopy revealed a small fistulous opening in the distal esophagus (5-6mm in size), about 4cm proximal to the GE junction. An 18mm x 10cm fully covered Wallflex Boston Scientific esophageal stent was deployed, with the distal end below the GE junction. To prevent migration, it was secured using the Apollo Endo Stitch device. The patient was safely discharged home on Pantoprazole. The chest tube was removed and she was discharged home. On follow-up 3 months later, she had no recurrent pneumonia, cough, chest pain, or fever. A repeat endoscopy with the removal of the esophageal stent was performed. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy, the fistulous opening appeared to have closed. Post-procedure gastrograffin esophagram demonstrated no leak. She continued to do well 2 months post-removal of the esophageal stent.
Discussion: This case report highlights a rare complication of the EB fistula that has been associated with a HH repair and fundoplication. A high clinical index of suspicion, early diagnosis, and management are needed in patients who develop recurrent cough and pneumonia with empyema soon after partial fundoplication. These patients can be successfully managed by placement of fully covered esophageal stent insertion along with drainage of empyema if present with chest tube insertion.

Figure: Esophagobronchial fistula (A and B); Gastrograffin esophagram performed 3 months after the esophageal stent placement (C)
Disclosures:
Solomon Badejoko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessie Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Formaker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mojolaoluwa Balogun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arshi Jha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessica Madej indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mariam Akinwale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kolade Olabode indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nso Nso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raphael Ezeagu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurtej Malhi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Solomon O. Badejoko, MD, MPH1, Jessie Wang, MD1, Paul E. Formaker, MS2, Mojolaoluwa Balogun, MS2, Arshi Jha, DO1, Jessica B. Madej, MD1, Mariam Akinwale, MD1, Kolade Olabode, MD, MPH3, Nso Nso, MD, MPH4, Raphael Ezeagu, MD, MPH5, Gurtej Malhi, MD1. D0230 - Esophagobronchial Fistula After a Laparoscopic Partial Fundoplication, Mimicking as Empyema, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
