Back


Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: GI Bleeding
D0335 - Iododerma Associated Hemorrhagic Shock
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Luke Townsend, MD
Ochsner Clinic Foundation
New Orleans, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Luke Townsend, MD, Mohammad T. Sultan, DO, MS, Austin Thomas, MD
Ochsner Clinic Foundation, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Iodinated contrast media (ICM) is used in the evaluation of patients for an array of medical maladies and administered more than 75 million times per year worldwide. Reactions are relatively uncommon, most involve cutaneous manifestations when present (1). Iododerma is a rare neutrophilic dermatosis secondary to ICM(1-3). Extracutaneous manifestations include conjunctivitis, salivary gland swelling and respiratory compromise (1). We present a case of Iododerma associated hemorrhagic shock.
Case Description/Methods: 71-year-old female presented for GI bleeding. EGD with pharyngeal edema, tongue swelling, 6 mm ulcer in oropharynx, normal appearing mucosa throughout with no active bleed or stigmata. Colonoscopy notable for a few polyps, diverticulosis, no active bleed identified. Push enteroscopy without bleeding to proximal jejunum and repeat colonoscopy revealed blood in the colon with clots at the ileocecum. Angiogram followed with embolization of a branch of the SMA supplying terminal ileum. Despite intervention bleeding continued. Repeat angiogram without active bleed. After angiograms, patient developed severe tongue swelling and was intubated for airway protection.
Patient noted to have multiple nodular skin lesions, bullous facial and extremity lesions, and oral ulcers. ANA + (1:1280) serology noted. Started on steroids and Rhematology, Dermatology consulted. Skin biopsy resulted focal papillary dermal edema, superficial to mid dermal neutrophilic and histiocytic infiltrate surrounding vacuolated/ haloed structures containing variably sized acellular structures consistent with iododerma. GI blood loss and hemorrhagic shock persisted. EGD on day 10 and 15 showed progressive ulceration throughout the GI tract involving the posterior oropharynx, duodenum and proximal jejunum refractory to bipolar cautery. Small intestine biopsies showed active enteritis associated with ulceration. Findings nonspecific but concerning for sequela related to iododerma. Evaluated by general surgery, given diffuse sources of GI bleeding, not a surgical candidate. Required 36 units of PRBC’s, 23 units of platelets and 8 units of FFP. Palliative care consulted and a transition to comfort care was agreed upon.
Discussion: Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media are infrequent, iododerma is a potentially serious complication. Understanding of its GI manifestations is unclear. Management of GI bleeding in iododerma is challenging given limits in use of IR procedures that are critical in these situations.
Disclosures:
Luke Townsend, MD, Mohammad T. Sultan, DO, MS, Austin Thomas, MD. D0335 - Iododerma Associated Hemorrhagic Shock, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Ochsner Clinic Foundation, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Iodinated contrast media (ICM) is used in the evaluation of patients for an array of medical maladies and administered more than 75 million times per year worldwide. Reactions are relatively uncommon, most involve cutaneous manifestations when present (1). Iododerma is a rare neutrophilic dermatosis secondary to ICM(1-3). Extracutaneous manifestations include conjunctivitis, salivary gland swelling and respiratory compromise (1). We present a case of Iododerma associated hemorrhagic shock.
Case Description/Methods: 71-year-old female presented for GI bleeding. EGD with pharyngeal edema, tongue swelling, 6 mm ulcer in oropharynx, normal appearing mucosa throughout with no active bleed or stigmata. Colonoscopy notable for a few polyps, diverticulosis, no active bleed identified. Push enteroscopy without bleeding to proximal jejunum and repeat colonoscopy revealed blood in the colon with clots at the ileocecum. Angiogram followed with embolization of a branch of the SMA supplying terminal ileum. Despite intervention bleeding continued. Repeat angiogram without active bleed. After angiograms, patient developed severe tongue swelling and was intubated for airway protection.
Patient noted to have multiple nodular skin lesions, bullous facial and extremity lesions, and oral ulcers. ANA + (1:1280) serology noted. Started on steroids and Rhematology, Dermatology consulted. Skin biopsy resulted focal papillary dermal edema, superficial to mid dermal neutrophilic and histiocytic infiltrate surrounding vacuolated/ haloed structures containing variably sized acellular structures consistent with iododerma. GI blood loss and hemorrhagic shock persisted. EGD on day 10 and 15 showed progressive ulceration throughout the GI tract involving the posterior oropharynx, duodenum and proximal jejunum refractory to bipolar cautery. Small intestine biopsies showed active enteritis associated with ulceration. Findings nonspecific but concerning for sequela related to iododerma. Evaluated by general surgery, given diffuse sources of GI bleeding, not a surgical candidate. Required 36 units of PRBC’s, 23 units of platelets and 8 units of FFP. Palliative care consulted and a transition to comfort care was agreed upon.
Discussion: Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media are infrequent, iododerma is a potentially serious complication. Understanding of its GI manifestations is unclear. Management of GI bleeding in iododerma is challenging given limits in use of IR procedures that are critical in these situations.

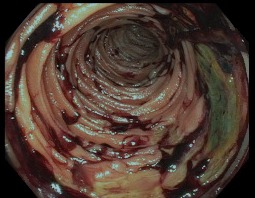
Figure: Duodenum with multiple progressive ulcerations
Disclosures:
Luke Townsend indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Sultan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Austin Thomas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luke Townsend, MD, Mohammad T. Sultan, DO, MS, Austin Thomas, MD. D0335 - Iododerma Associated Hemorrhagic Shock, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
