Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Liver
D0529 - Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Post Acute Liver Injury From Skullcap Supplements: An Unfortunate Case of Herbal Toxicity
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Nimish Thakral, MD
University of Kentucky
Pembroke Pines, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Nimish Thakral, MD1, Venkata Rajesh Konjeti, MD1, Jens Rosenau, MD1, Ayesha T. Jalal, MD2
1University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 2Memorial Healthcare System, Pembroke Pines, FL
Introduction: Scutellaria lateriflora, also known as Skullcap, is widely used in alternative medicine for menstrual, nervous, digestive and kidney problems. There have been rare instances of acute liver injury (ALI) attributed to its use. However, the occurrence of de-novo plasma cell hepatitis has not been reported before. We present a case of severe acute liver injury and drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis resulting from Skullcap usage.
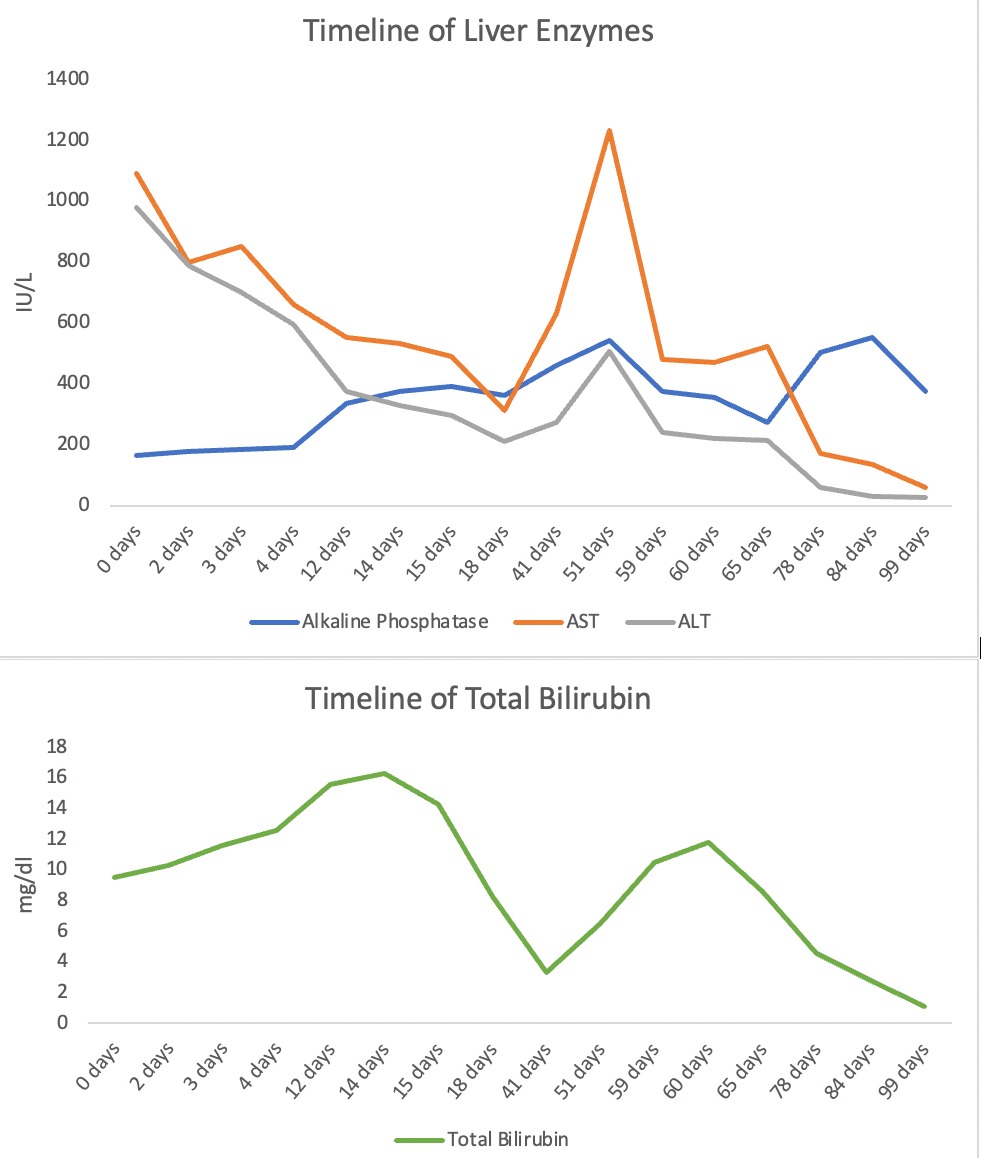
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old female, with a history of Sjogren’s disease presented with new onset jaundice. Her labs were - Alkaline Phosphatase (Alk Phos) 164 IU/L, AST 1091 IU/L, ALT 980 IU/L, Total Bilirubin (T bili) 9.5, INR 2.4. MRCP showed did not show cirrhosis or biliary obstruction. The patient’s LFTs were normal 4 months ago. She denied any history of liver disease but affirmed taking Skullcap supplements over the last month secondary to insomnia. Initial testing for causes of liver disease was negative for Hepatitis A, B, and C, CMV, EBV, and HSV. ANA was chronically positive given her history of Sjogren’s disease. IgG was elevated at 2573 mg/dl, but was thought to be secondary to ALI. Initial liver biopsy showed resolving centrilobular necrosis with predominant eosinophilic inflammation. Given downtrending LFTs over the next 72 hours, the patient was discharged with outpatient follow-up.
She was admitted a month later with worsening jaundice and acute kidney injury. Her LFTs were Alk Phos 619 IU/L, AST 1222 IU/L, ALT 540 IU/L, and T bili 6.6 mg/dl. Infectious workup was negative. Over the next few days, transaminases downtrended but the T bili continued to rise, peaking at 11.8 mg/dl. Repeat biopsy showed extensive plasma cells consistent with drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis. The patient finally did improve with resolution of jaundice. She was subsequently listed for a simultaneous liver kidney transplant but was later deactivated due to overall improvement in status.
Discussion: The toxic effects of Skullcap are thought to be mediated secondary to flavonoids present in its root. However, the contribution of adulterants cannot be excluded as there are no regulatory bodies governing herbal supplement production. To our knowledge, this is the first case of drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis secondary to Skullcap supplements.
Disclosures:
Nimish Thakral, MD1, Venkata Rajesh Konjeti, MD1, Jens Rosenau, MD1, Ayesha T. Jalal, MD2. D0529 - Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Post Acute Liver Injury From Skullcap Supplements: An Unfortunate Case of Herbal Toxicity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 2Memorial Healthcare System, Pembroke Pines, FL
Introduction: Scutellaria lateriflora, also known as Skullcap, is widely used in alternative medicine for menstrual, nervous, digestive and kidney problems. There have been rare instances of acute liver injury (ALI) attributed to its use. However, the occurrence of de-novo plasma cell hepatitis has not been reported before. We present a case of severe acute liver injury and drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis resulting from Skullcap usage.
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old female, with a history of Sjogren’s disease presented with new onset jaundice. Her labs were - Alkaline Phosphatase (Alk Phos) 164 IU/L, AST 1091 IU/L, ALT 980 IU/L, Total Bilirubin (T bili) 9.5, INR 2.4. MRCP showed did not show cirrhosis or biliary obstruction. The patient’s LFTs were normal 4 months ago. She denied any history of liver disease but affirmed taking Skullcap supplements over the last month secondary to insomnia. Initial testing for causes of liver disease was negative for Hepatitis A, B, and C, CMV, EBV, and HSV. ANA was chronically positive given her history of Sjogren’s disease. IgG was elevated at 2573 mg/dl, but was thought to be secondary to ALI. Initial liver biopsy showed resolving centrilobular necrosis with predominant eosinophilic inflammation. Given downtrending LFTs over the next 72 hours, the patient was discharged with outpatient follow-up.
She was admitted a month later with worsening jaundice and acute kidney injury. Her LFTs were Alk Phos 619 IU/L, AST 1222 IU/L, ALT 540 IU/L, and T bili 6.6 mg/dl. Infectious workup was negative. Over the next few days, transaminases downtrended but the T bili continued to rise, peaking at 11.8 mg/dl. Repeat biopsy showed extensive plasma cells consistent with drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis. The patient finally did improve with resolution of jaundice. She was subsequently listed for a simultaneous liver kidney transplant but was later deactivated due to overall improvement in status.
Discussion: The toxic effects of Skullcap are thought to be mediated secondary to flavonoids present in its root. However, the contribution of adulterants cannot be excluded as there are no regulatory bodies governing herbal supplement production. To our knowledge, this is the first case of drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis secondary to Skullcap supplements.

Figure: TImeline of Liver Function Tests.
Disclosures:
Nimish Thakral indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Rajesh Konjeti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jens Rosenau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Jalal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nimish Thakral, MD1, Venkata Rajesh Konjeti, MD1, Jens Rosenau, MD1, Ayesha T. Jalal, MD2. D0529 - Drug-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis Post Acute Liver Injury From Skullcap Supplements: An Unfortunate Case of Herbal Toxicity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
