Back

Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
Category: Small Intestine
E0650 - MEN2B-Associated Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- PG
Patricia Garcia, MD
Bridgeport Hospital, Yale New Haven Health
Bridgeport, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Patricia Garcia, MD1, Darrick K. Li, MD, PhD2, Leonel Rodriguez, MD2, Jill K. Deutsch, MD, MA2
1Bridgeport Hospital, Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by medullary thyroid cancer and pheochromocytoma. Gastrointestinal (GI) involvement, if present, is often observed with onset at birth or shortly thereafter. GI symptoms may manifest as constipation that can progress to megacolon while involvement of other portions of the GI tract are less commonly reported. We report a case of MEN2B who presented with progressive gastrointestinal symptoms and was found to have chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO).
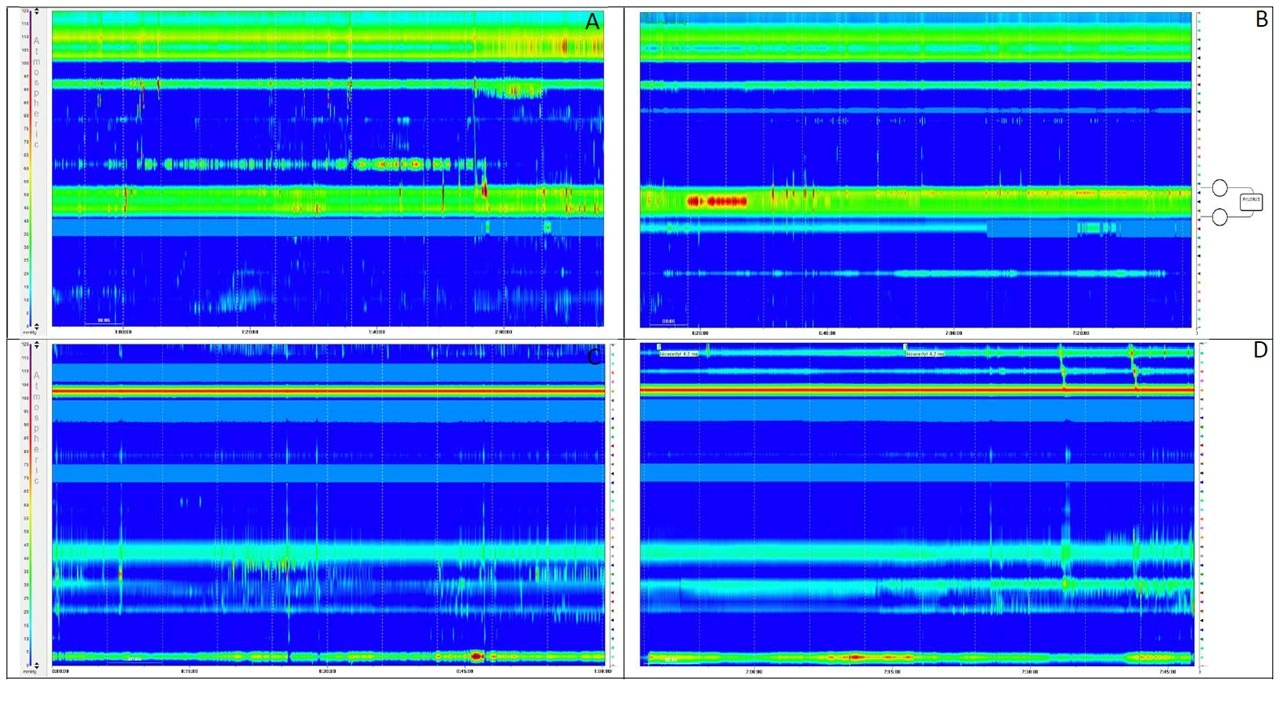
Case Description/Methods: A 23-year-old female with past medical history of MEN2B presented to our clinic for evaluation of abdominal pain, bloating, and loose stools. Since childhood, the patient had chronic abdominal distension and intermittent episodes of abdominal pain and distension. 8 months prior to presentation, her symptoms became increasingly severe and required several hospitalizations for IV hydration. Her symptoms continued to progress and became associated with significant weight loss, nausea, and anorexia, at which time she was seen in our clinic. On physical examination, her vital signs were stable, and she was in no acute distress. Examination notable for a thin female (BMI 16) with a distended, tympanic abdomen with hyperactive bowel sounds and diffuse tenderness. Laboratory findings and infectious workup were largely unremarkable. CT imaging showed marked distension of the entire colon as well as the small bowel without definite transition point. She underwent a bidirectional endoscopy which was notable for a normal upper endoscopy, gross dilation of the colon, and no stricture in the terminal ileum. Antroduodenal manometry and colonic manometry (Figure 1) performed at the time of endoscopy were consistent with CIPO of neuropathic origin. She was started on prucalopride 2 mg daily with significant improvement of her symptoms.
Discussion: We present an unusual case of MEN2B-associated gastrointestinal involvement manifesting as CIPO which suggests that small intestinal dysmotility may need to be considered in the workup and management of gastrointestinal symptoms in MEN2B patients. While gastrointestinal involvement in MEN2B classically presents with a pseudo-Hirschprung’s type megacolon, this case also demonstrates that identification of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, particularly in young patients, should also prompt workup for MEN2B.
Disclosures:
Patricia Garcia, MD1, Darrick K. Li, MD, PhD2, Leonel Rodriguez, MD2, Jill K. Deutsch, MD, MA2. E0650 - MEN2B-Associated Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Patricia Garcia, MD1, Darrick K. Li, MD, PhD2, Leonel Rodriguez, MD2, Jill K. Deutsch, MD, MA2
1Bridgeport Hospital, Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by medullary thyroid cancer and pheochromocytoma. Gastrointestinal (GI) involvement, if present, is often observed with onset at birth or shortly thereafter. GI symptoms may manifest as constipation that can progress to megacolon while involvement of other portions of the GI tract are less commonly reported. We report a case of MEN2B who presented with progressive gastrointestinal symptoms and was found to have chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO).
Case Description/Methods: A 23-year-old female with past medical history of MEN2B presented to our clinic for evaluation of abdominal pain, bloating, and loose stools. Since childhood, the patient had chronic abdominal distension and intermittent episodes of abdominal pain and distension. 8 months prior to presentation, her symptoms became increasingly severe and required several hospitalizations for IV hydration. Her symptoms continued to progress and became associated with significant weight loss, nausea, and anorexia, at which time she was seen in our clinic. On physical examination, her vital signs were stable, and she was in no acute distress. Examination notable for a thin female (BMI 16) with a distended, tympanic abdomen with hyperactive bowel sounds and diffuse tenderness. Laboratory findings and infectious workup were largely unremarkable. CT imaging showed marked distension of the entire colon as well as the small bowel without definite transition point. She underwent a bidirectional endoscopy which was notable for a normal upper endoscopy, gross dilation of the colon, and no stricture in the terminal ileum. Antroduodenal manometry and colonic manometry (Figure 1) performed at the time of endoscopy were consistent with CIPO of neuropathic origin. She was started on prucalopride 2 mg daily with significant improvement of her symptoms.
Discussion: We present an unusual case of MEN2B-associated gastrointestinal involvement manifesting as CIPO which suggests that small intestinal dysmotility may need to be considered in the workup and management of gastrointestinal symptoms in MEN2B patients. While gastrointestinal involvement in MEN2B classically presents with a pseudo-Hirschprung’s type megacolon, this case also demonstrates that identification of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, particularly in young patients, should also prompt workup for MEN2B.

Figure: Antroduodenal manometry with notable absence of MMCIII in the fasted state (panel A), and lack of stimulation in response to octreotide (panel B) suggestive of neuropathic CIPO and consistent with the presumed pathology of diffuse intestinal ganglioneuromatosis. Colon manometry revealed no high-amplitude phasic contractions (panel C) with a non-propagating response isolated to the proximal 10-15cm of the right colon to bisacodyl stimulation (panel D).
Disclosures:
Patricia Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Darrick Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leonel Rodriguez: Abbott – Speakers Bureau. IHS – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Jill Deutsch: GI Supply – Key Opinion Leader.
Patricia Garcia, MD1, Darrick K. Li, MD, PhD2, Leonel Rodriguez, MD2, Jill K. Deutsch, MD, MA2. E0650 - MEN2B-Associated Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

