Back
Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Small Intestine
B0643 - Foreign Body Reaction Following Use of Submucosal Lifting Agent for Endoscopic Resections
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom


Sera Satoi, MD
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Sera Satoi, MD, Makoto Nishimura, MD, Kana Chin, MD, Jacques C. Beauvais, MD, Mark Schattner, MD
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
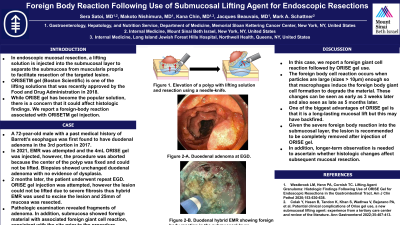
Introduction: Submucosal injection of lifting solutions is essential for both endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). In mucosal resections, a lifting solution is injected into the submucosal layer to separate the submucosa from muscularis propria to facilitate resection of the targeted lesion. ORISETM gel (Boston Scientific) is one of the lifting solutions that was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018. While ORISETM gel has become the popular solution, there is a concern that it could affect histologic findings. Here we report a foreign-body reaction associated with ORISETM gel injection.
Case Description/Methods: A 72-year-old male with a history of Barrett’s esophagus was first found to have duodenal adenoma in the 3rd portion in 2017.
4 years later the patient was found to have polypoid tissue in the 2nd portion of the duodenum. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was attempted and the tissue was lifted by submucosal injection of 4mL ORISETM gel, however, the procedure was aborted because the center of the polyp was fixed and could not be lifted. Biopsies were taken with cold forceps which showed duodenal adenoma without evidence of dysplasia. 65 days later, the patient underwent repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to remove the lesion. ORISETM gel injection was attempted, however, the lesion could not be lifted due to severe fibrosis thus hybrid EMR was used to excise the lesion and 25mm of mucosa was resected.
Pathologic examination revealed fragments of adenoma. In addition, submucosa showed foreign material with associated foreign giant cell reaction, consistent with the site prior to the procedure.
Discussion: In this case, we report a foreign giant cell reaction followed by ORISETM Gel use. The foreign body cell reaction occurs when particles are large (sizes > 10μm) enough so that macrophages induce the foreign body giant cell formation to degrade the material. These changes can be seen as early as 3 weeks later and also seen as late as 5 months later. One of the biggest advantages of ORISE TM gel is that it is a long-lasting mucosal lift but this may have backfired. Given the severe foreign body reaction into the submucosal layer, the lesion needs to be completely removed after injection of ORISE. Also, longer-term observation is needed to ascertain whether histologic changes affect subsequent mucosal resection.
Disclosures:
Sera Satoi, MD, Makoto Nishimura, MD, Kana Chin, MD, Jacques C. Beauvais, MD, Mark Schattner, MD. B0643 - Foreign Body Reaction Following Use of Submucosal Lifting Agent for Endoscopic Resections, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Introduction: Submucosal injection of lifting solutions is essential for both endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). In mucosal resections, a lifting solution is injected into the submucosal layer to separate the submucosa from muscularis propria to facilitate resection of the targeted lesion. ORISETM gel (Boston Scientific) is one of the lifting solutions that was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018. While ORISETM gel has become the popular solution, there is a concern that it could affect histologic findings. Here we report a foreign-body reaction associated with ORISETM gel injection.
Case Description/Methods: A 72-year-old male with a history of Barrett’s esophagus was first found to have duodenal adenoma in the 3rd portion in 2017.
4 years later the patient was found to have polypoid tissue in the 2nd portion of the duodenum. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was attempted and the tissue was lifted by submucosal injection of 4mL ORISETM gel, however, the procedure was aborted because the center of the polyp was fixed and could not be lifted. Biopsies were taken with cold forceps which showed duodenal adenoma without evidence of dysplasia. 65 days later, the patient underwent repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to remove the lesion. ORISETM gel injection was attempted, however, the lesion could not be lifted due to severe fibrosis thus hybrid EMR was used to excise the lesion and 25mm of mucosa was resected.
Pathologic examination revealed fragments of adenoma. In addition, submucosa showed foreign material with associated foreign giant cell reaction, consistent with the site prior to the procedure.
Discussion: In this case, we report a foreign giant cell reaction followed by ORISETM Gel use. The foreign body cell reaction occurs when particles are large (sizes > 10μm) enough so that macrophages induce the foreign body giant cell formation to degrade the material. These changes can be seen as early as 3 weeks later and also seen as late as 5 months later. One of the biggest advantages of ORISE TM gel is that it is a long-lasting mucosal lift but this may have backfired. Given the severe foreign body reaction into the submucosal layer, the lesion needs to be completely removed after injection of ORISE. Also, longer-term observation is needed to ascertain whether histologic changes affect subsequent mucosal resection.
Disclosures:
Sera Satoi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Makoto Nishimura: Boston Scientifics – Consultant. Lumendi – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Kana Chin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacques C. Beauvais indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Schattner indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sera Satoi, MD, Makoto Nishimura, MD, Kana Chin, MD, Jacques C. Beauvais, MD, Mark Schattner, MD. B0643 - Foreign Body Reaction Following Use of Submucosal Lifting Agent for Endoscopic Resections, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
