Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Small Intestine
B0650 - Asymptomatic Multiple Lymphomatous Polyposis: An Atypical Presentation of Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Navkiran Randhawa, DO
Franciscan Health
Olympia Fields, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Navkiran Randhawa, DO, Ahamed Khalyfa, DO, Mahnoor Khan, DO, Rida Aslam, DO, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO
Franciscan Health, Olympia Fields, IL
Introduction: Multiple lymphomatous polyposis (MLP) is a rare type of mantle cell lymphoma that affects the GI tract. Patients with MLP generally present with generalized GI symptoms including abdominal pain and imaging, including endoscopy, can be unrevealing. We present an unusual case of a patient without GI symptoms who was found to have MLP affecting areas of the duodenum, colon, and rectum.
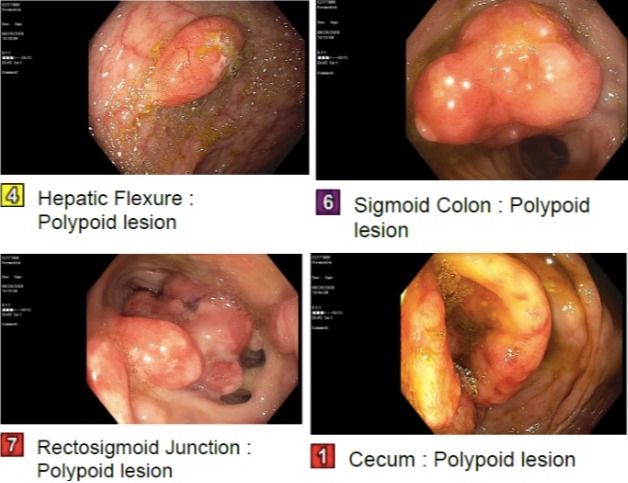
Case Description/Methods: We present a 71-year-old female with a past medical history of IBS, previous diverticulitis s/p sigmoidectomy, history of transverse myelitis and DM who presented to the hospital with progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 6 weeks. She denied any B-symptoms (fevers, night sweats, weight loss). Subsequent labs did not identify any abnormalities. CTA chest revealed a large right pleural effusion and significant lymphadenopathy in the axilla and supraclavicular regions bilaterally. A thoracentesis was performed which revealed cytology consistent with MCL. A CT abdomen/pelvis demonstrated a mass in the pylorus and duodenal bulb and a questionable mass in the sigmoid colon. A bidirectional endoscopy was performed which showed polypoid lesions in the duodenum, hepatic flexure,sigmoid colon, recto-sigmoid colon. Biopsy of the polyps revealed mantle cell lymphoma . PET scan showed lymphadenopathy in the axillary, mediastinal, hilar, retroperitoneal regions, splenomegaly, and FDG avidity in the gastrocolic ligament. The patient was initially treated with r-AraC chemotherapy regimen and was later transitioned to Bendamustine/Rituximab regimen. She also had a bone marrow biopsy which showed normocellular marrow and was scheduled to receive bone marrow transplant.
Discussion: MLP is an extremely rare phenomenon and is characteristically seen in patients with MCL. It is characterized by numerous GI polypoid lesions involving different areas in the gastrointestinal tract. Common clinical symptoms reported for patients with MPL include weight loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and intestinal malabsorption. Some cases have even reported chylous ascites and intestinal obstruction secondary to intussusception. This case highlights a unique clinical presentation of shortness of breath and a rare endoscopic finding of MLP to diagnose MCL. As MPL has a poor prognosis, early detection and treatment is imperative. In summary, we report an unusual patient with high-risk MCL who had asymptomatic MLP identified only at staging bidirectional endoscopy.
Disclosures:
Navkiran Randhawa, DO, Ahamed Khalyfa, DO, Mahnoor Khan, DO, Rida Aslam, DO, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO. B0650 - Asymptomatic Multiple Lymphomatous Polyposis: An Atypical Presentation of Mantle Cell Lymphoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Franciscan Health, Olympia Fields, IL
Introduction: Multiple lymphomatous polyposis (MLP) is a rare type of mantle cell lymphoma that affects the GI tract. Patients with MLP generally present with generalized GI symptoms including abdominal pain and imaging, including endoscopy, can be unrevealing. We present an unusual case of a patient without GI symptoms who was found to have MLP affecting areas of the duodenum, colon, and rectum.
Case Description/Methods: We present a 71-year-old female with a past medical history of IBS, previous diverticulitis s/p sigmoidectomy, history of transverse myelitis and DM who presented to the hospital with progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 6 weeks. She denied any B-symptoms (fevers, night sweats, weight loss). Subsequent labs did not identify any abnormalities. CTA chest revealed a large right pleural effusion and significant lymphadenopathy in the axilla and supraclavicular regions bilaterally. A thoracentesis was performed which revealed cytology consistent with MCL. A CT abdomen/pelvis demonstrated a mass in the pylorus and duodenal bulb and a questionable mass in the sigmoid colon. A bidirectional endoscopy was performed which showed polypoid lesions in the duodenum, hepatic flexure,sigmoid colon, recto-sigmoid colon. Biopsy of the polyps revealed mantle cell lymphoma . PET scan showed lymphadenopathy in the axillary, mediastinal, hilar, retroperitoneal regions, splenomegaly, and FDG avidity in the gastrocolic ligament. The patient was initially treated with r-AraC chemotherapy regimen and was later transitioned to Bendamustine/Rituximab regimen. She also had a bone marrow biopsy which showed normocellular marrow and was scheduled to receive bone marrow transplant.
Discussion: MLP is an extremely rare phenomenon and is characteristically seen in patients with MCL. It is characterized by numerous GI polypoid lesions involving different areas in the gastrointestinal tract. Common clinical symptoms reported for patients with MPL include weight loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and intestinal malabsorption. Some cases have even reported chylous ascites and intestinal obstruction secondary to intussusception. This case highlights a unique clinical presentation of shortness of breath and a rare endoscopic finding of MLP to diagnose MCL. As MPL has a poor prognosis, early detection and treatment is imperative. In summary, we report an unusual patient with high-risk MCL who had asymptomatic MLP identified only at staging bidirectional endoscopy.

Figure: A bidirectional endoscopy was performed which showed polypoid lesions in the duodenum, hepatic flexure,sigmoid colon, recto-sigmoid colon.
Disclosures:
Navkiran Randhawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahamed Khalyfa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahnoor Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rida Aslam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tilemahos Spyratos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navkiran Randhawa, DO, Ahamed Khalyfa, DO, Mahnoor Khan, DO, Rida Aslam, DO, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO. B0650 - Asymptomatic Multiple Lymphomatous Polyposis: An Atypical Presentation of Mantle Cell Lymphoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
