Back
Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
E0703 - Tissue Is the Issue: A Rare Case of Collagenous Gastritis
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Idrees Suliman, MD
Mountain Vista Medical Center
Mesa, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Preeyanka Sundar, MD1, Suma Harsha Kosuru, MBBS1, Idrees Suliman, MD2, Sara Ancello, DO1
1Midwestern University, Mesa, AZ; 2Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ
Introduction: Collagenous gastritis (CG), collagenous sprue, and collagenous colitis are rare forms of collagenous gastroenteritides marked by subepithelial collagen deposition of more than 10mm and inflammatory infiltrate in the lamina propria. CG was first identified in 1989. It's a rare disease, with just 100 cases reported so far. Here, we present a distinct case of collagenous gastritis.
Case Description/Methods: 52-year-old female with no chronic medical conditions presented with symptoms of mild reflux, epigastric pain, and intermittent diarrhea up to 5 times per day. She had sporadic Ibuprofen use for headaches. Her mother was diagnosed with lupus and a half-sister with a history of mixed connective tissue disorder. Initial upper endoscopy revealed grade B esophagitis and gastritis, biopsies showed CG. Colonoscopy with random biopsies showed no evidence of collagenous colitis. She was treated with high dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and repeat endoscopy in 4 weeks with biopsies via Sydney protocol was performed. Additional blood work was normal including normal thyroid panel, celiac screen (anti-transglutaminase IgA: < 1.0 U/ml, IgA: 2.34 g/L) and IgG4 titer (0.27 g/L.) Repeat EGD with biopsies per Sydney protocol confirmed CG in all gastric quadrants, except fundus. After stopping NSAIDs and continuing on PPI, her symptoms resolved with a plan for surveillance endoscopy in 6 months.
Discussion: In our patient, the diagnosis of CG led to further investigations to rule out possible associated autoimmune diseases. The occasional ibuprofen may have been contributory, but the repeat biopsies on the second endoscopy confirmed the presence of CG despite cessation. The only contributing factor in her case is positive family history. There are very few cases reported in the literature with the possible association of lupus with CG. This distinctive case of CG is an important contribution to the limited pool of existing cases as the patient herself did not have any preexisting allergic or autoimmune conditions and it appears that this process occurred idiopathically. Given the rarity of the condition and limited literature available, we emphasize the importance of delineated medical guidelines for appropriate screening and surveillance.
Disclosures:
Preeyanka Sundar, MD1, Suma Harsha Kosuru, MBBS1, Idrees Suliman, MD2, Sara Ancello, DO1. E0703 - Tissue Is the Issue: A Rare Case of Collagenous Gastritis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Midwestern University, Mesa, AZ; 2Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ
Introduction: Collagenous gastritis (CG), collagenous sprue, and collagenous colitis are rare forms of collagenous gastroenteritides marked by subepithelial collagen deposition of more than 10mm and inflammatory infiltrate in the lamina propria. CG was first identified in 1989. It's a rare disease, with just 100 cases reported so far. Here, we present a distinct case of collagenous gastritis.
Case Description/Methods: 52-year-old female with no chronic medical conditions presented with symptoms of mild reflux, epigastric pain, and intermittent diarrhea up to 5 times per day. She had sporadic Ibuprofen use for headaches. Her mother was diagnosed with lupus and a half-sister with a history of mixed connective tissue disorder. Initial upper endoscopy revealed grade B esophagitis and gastritis, biopsies showed CG. Colonoscopy with random biopsies showed no evidence of collagenous colitis. She was treated with high dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and repeat endoscopy in 4 weeks with biopsies via Sydney protocol was performed. Additional blood work was normal including normal thyroid panel, celiac screen (anti-transglutaminase IgA: < 1.0 U/ml, IgA: 2.34 g/L) and IgG4 titer (0.27 g/L.) Repeat EGD with biopsies per Sydney protocol confirmed CG in all gastric quadrants, except fundus. After stopping NSAIDs and continuing on PPI, her symptoms resolved with a plan for surveillance endoscopy in 6 months.
Discussion: In our patient, the diagnosis of CG led to further investigations to rule out possible associated autoimmune diseases. The occasional ibuprofen may have been contributory, but the repeat biopsies on the second endoscopy confirmed the presence of CG despite cessation. The only contributing factor in her case is positive family history. There are very few cases reported in the literature with the possible association of lupus with CG. This distinctive case of CG is an important contribution to the limited pool of existing cases as the patient herself did not have any preexisting allergic or autoimmune conditions and it appears that this process occurred idiopathically. Given the rarity of the condition and limited literature available, we emphasize the importance of delineated medical guidelines for appropriate screening and surveillance.

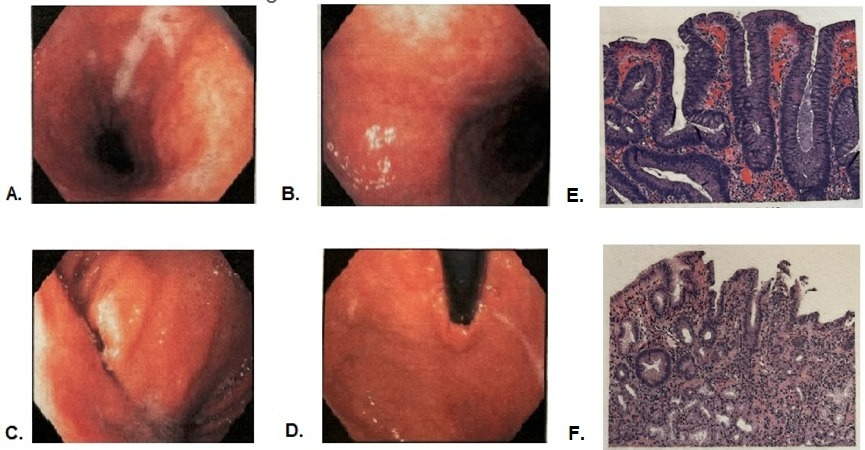
Figure: Figure 1: Endoscopic appearance of collagenous gastritis. A, B. body, C. Antrum D. fundus ; E,F: Histology of collagenous gastritis characterized by thickening of sub epithelial basement membrane accompanied by diffuse superficial lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates and surface epithelial degeneration
| COLLAGENOUS GASTRITIS (CG) - characterized by marked sub epithelial collagen deposition with associated inflammatory infiltrate. |
| EPIDEMIOLOGY - Female Preponderance - All age groups but primarily affects adults. |
| ETIOLOGY - The etiology is unknown - Stancu et al. outlined three pathogenic mechanisms that may lead to collagen deposition in cases of CG: (1) Chronic inflammation (2) Fibroblast sheath abnormality (3) Leakage of plasma proteins and fibrinogen |
| ASSOCIATIONS - intestinal and autoimmune disorders, including celiac disease. collagenous enteritis, collagenous colitis, sjogren syndrome, SLE, juvenile arthritis, RA, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Grave's disease, Diabetes mellitus type 1, and CVID. - Medications such as Olmesartan, Venlafaxine |
| SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS - epigastric and or abdominal pain, anemia , gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, perforated ulcer, weight loss, abdominal distension, fatigue, dyspepsia, retrosternal pain, constipation and dysphagia. |
| DIAGNOSIS - EGD with biopsy |
| TREATMENT - Anti-secretory agents including PPIs, and H2 receptor antagonists, steroids, iron supplementation and hypoallergenic diets have been tried with limited success. - Other treatment modalities , such as sucralfate, mesalazine, bismuth subsalicylate, furazolidone, sulfasalazine, azathioprine, and parenteral nutrition have also been tested. |
Table: Summary of Collagenous gastritis (CG)
Disclosures:
Preeyanka Sundar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suma Harsha Kosuru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Idrees Suliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Ancello indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Preeyanka Sundar, MD1, Suma Harsha Kosuru, MBBS1, Idrees Suliman, MD2, Sara Ancello, DO1. E0703 - Tissue Is the Issue: A Rare Case of Collagenous Gastritis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
