Back
Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
E0675 - Is Pembrolizumab Associated With Celiac Disease?
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Maria Indira Flores, MD
SBH Health System
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Maria Indira Flores, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Deepa P. Budh, MD3, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP4, Heidi Budke, MD4, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG4
1SBH Health System, Bronx, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3St. Barnabas Health System, Bronx, NY; 4Blanchard Valley Health System, Findlay, OH
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have improved the survival rate and prognosis of patients with several advanced malignancies by enhancing the immunologic system and augmenting the antitumor cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. However, their side effects are being observed more often because of the increase in their use. They are called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), such as hepatitis, colitis, and other immune reactions. We present the case of Pembrolizumab-induced Celiac disease after treatment of metastatic melanoma.
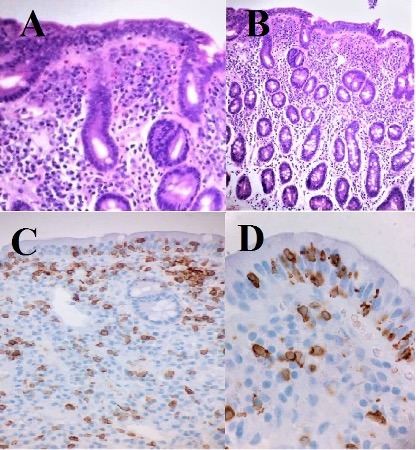
Case Description/Methods: A 49 y/o Female presented to the GI clinic for IDA, had a history of malignant melanoma diagnosed eight years ago. She presented with diffuse lymphadenopathy of the left arm and was diagnosed with malignant melanoma. Radiation therapy was initiated, and at her three months follow-up with PET-scan there was involvement of the left femur and hip and multiple nodules in abdominal and esophageal areas. This was deemed advanced metastatic malignant melanoma and was started on Pembrolizumab. After receiving this treatment for a year, she was in remission and has continued to have treatment every twelve weeks. Upper endoscopy and Colonoscopy were done to evaluate the etiology of IDA. Duodenal biopsy showed areas of inflammation of the first and second portions of the duodenum. The pathology report showed flattened villi and crypt hyperplasia; immunohistochemical showed increased CD3 + T cell lymphocytes in the surface epithelium consistent with Celiac Disease Image1. Blood tests was Positive TTG-IgA and HLA-DQ2. She was then placed on Gluten-free diet and proton pump inhibitors, showing improvement in the anemia and continues to be in remission.
Discussion: Celiac disease is an immune-mediated inflammatory disorder that affects the small bowel, triggered by the consumption of gluten. Gluten hypersensitivity leads to activation of T-cells in the lamina propia, producing mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy. Commonly resolves after withdrawal of wheat and cereals from the diet. Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that works by blocking programmed death receptor-1 (PD -1), it is used in the treatment of advanced cancer, one of them being Metastatic melanoma. However, it can cause irAEs during its use or even after. Only a few cases have been reported in the literature of pembrolizumab-induced celiac disease; We would like to emphasize the importance of a proper evaluation and follow-up of celiac disease in patients on Pembrolizumab treatment.
Disclosures:
Maria Indira Flores, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Deepa P. Budh, MD3, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP4, Heidi Budke, MD4, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG4. E0675 - Is Pembrolizumab Associated With Celiac Disease?, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1SBH Health System, Bronx, NY; 2The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3St. Barnabas Health System, Bronx, NY; 4Blanchard Valley Health System, Findlay, OH
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have improved the survival rate and prognosis of patients with several advanced malignancies by enhancing the immunologic system and augmenting the antitumor cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. However, their side effects are being observed more often because of the increase in their use. They are called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), such as hepatitis, colitis, and other immune reactions. We present the case of Pembrolizumab-induced Celiac disease after treatment of metastatic melanoma.
Case Description/Methods: A 49 y/o Female presented to the GI clinic for IDA, had a history of malignant melanoma diagnosed eight years ago. She presented with diffuse lymphadenopathy of the left arm and was diagnosed with malignant melanoma. Radiation therapy was initiated, and at her three months follow-up with PET-scan there was involvement of the left femur and hip and multiple nodules in abdominal and esophageal areas. This was deemed advanced metastatic malignant melanoma and was started on Pembrolizumab. After receiving this treatment for a year, she was in remission and has continued to have treatment every twelve weeks. Upper endoscopy and Colonoscopy were done to evaluate the etiology of IDA. Duodenal biopsy showed areas of inflammation of the first and second portions of the duodenum. The pathology report showed flattened villi and crypt hyperplasia; immunohistochemical showed increased CD3 + T cell lymphocytes in the surface epithelium consistent with Celiac Disease Image1. Blood tests was Positive TTG-IgA and HLA-DQ2. She was then placed on Gluten-free diet and proton pump inhibitors, showing improvement in the anemia and continues to be in remission.
Discussion: Celiac disease is an immune-mediated inflammatory disorder that affects the small bowel, triggered by the consumption of gluten. Gluten hypersensitivity leads to activation of T-cells in the lamina propia, producing mucosal inflammation and villous atrophy. Commonly resolves after withdrawal of wheat and cereals from the diet. Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that works by blocking programmed death receptor-1 (PD -1), it is used in the treatment of advanced cancer, one of them being Metastatic melanoma. However, it can cause irAEs during its use or even after. Only a few cases have been reported in the literature of pembrolizumab-induced celiac disease; We would like to emphasize the importance of a proper evaluation and follow-up of celiac disease in patients on Pembrolizumab treatment.

Figure: Image1 : A,B - H&E stain 40X showing flattened villi and crypt hyperplasia,
C,D - low and high power view CD3+ T cell near the surface epithelium.
C,D - low and high power view CD3+ T cell near the surface epithelium.
Disclosures:
Maria Indira Flores indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijay Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepa Budh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tonya DeVaul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heidi Budke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinaya Gaduputi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Indira Flores, MD1, Vijay Gayam, MD2, Deepa P. Budh, MD3, Tonya DeVaul, APRN-CNP4, Heidi Budke, MD4, Vinaya Gaduputi, MD, FACG4. E0675 - Is Pembrolizumab Associated With Celiac Disease?, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

