Back
Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
C0145 - Case of Metastatic Breast Cancer Resembling Hyperplastic Polyps
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Abhinav Tiwari, MD
Sacred Heart Medical Center at RiverBend
Springfield, OR
Presenting Author(s)
Abhinav Tiwari, MD1, Khola Qamar, MD2
1Sacred Heart Medical Center at RiverBend, Springfield, OR; 2Dartmouth-Hitchcock Putnam Physicians, Bennington, VT
Introduction: Breast cancer is most common malignancy in woman worldwide. Metastasis to the gastrointestinal tract (GI) is relatively rare occurring in only 3 % cases. Herein, we report a case of breast cancer metastasis localized only to the GI mucosa in the form of mucosal polyps which resembled typical hyperplastic polyps.
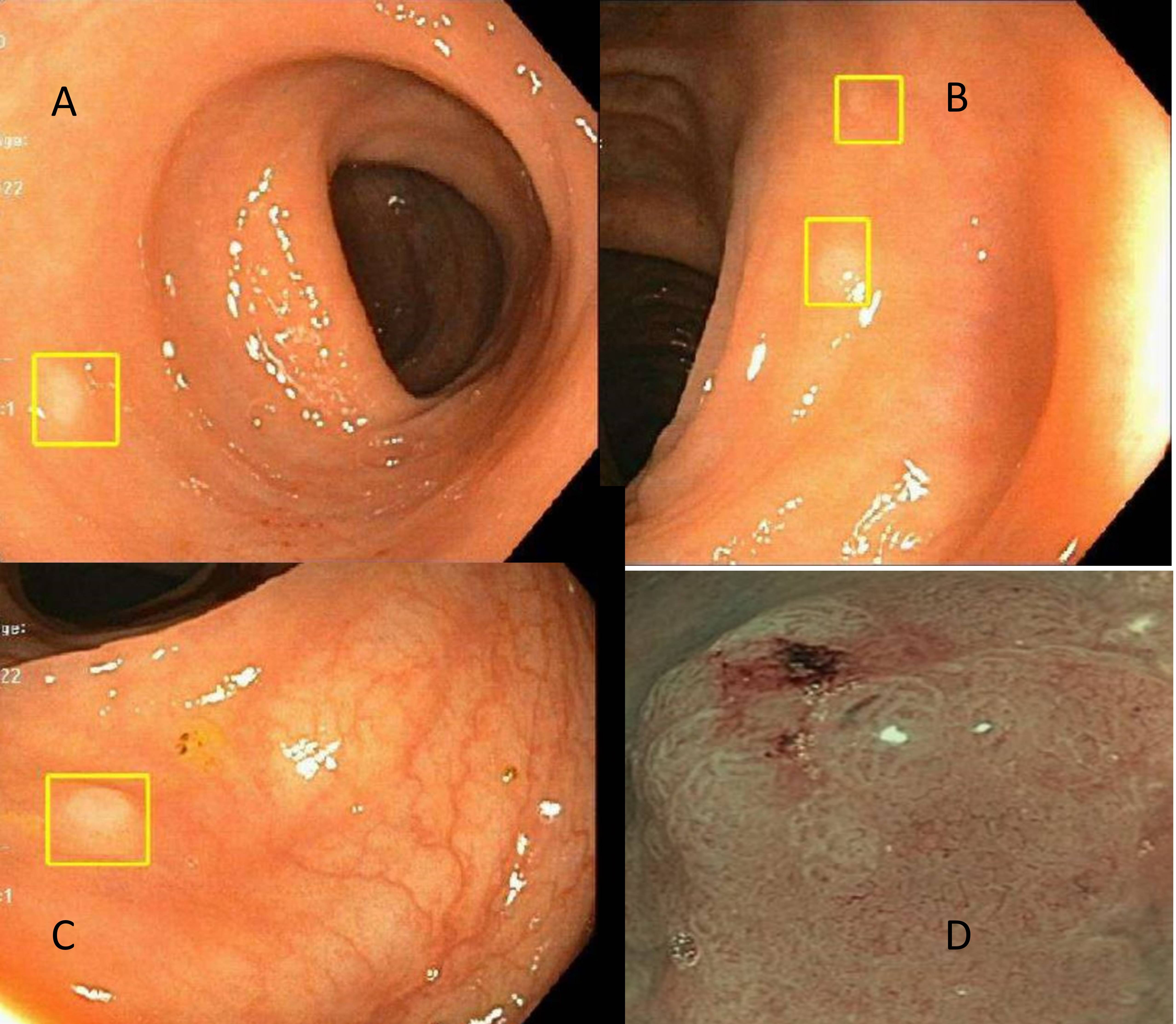
Case Description/Methods: 59-year-old female with history of pT2N2aM0, stage IIIA grade 2 invasive lobular carcinoma of the right breast status post mastectomy and axillary lymph-node dissection (showing 5/6 lymph node positive) along with adjuvant chemotherapy with Adriamycin, Cytoxan followed by weekly Taxol and radiation therapy. She had recent normal Computerized tomography and PET scan without any recurrent disease. She was referred for Iron deficiency anemia with hemoglobin 9.5 g/dL along with microcytosis and low ferritin measuring 4 g/L in absence of any overt bleeding. She underwent diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy. Former was unremarkable but colonoscopy showed multiple 3-4 mm sessile polyps scattered through the colon. On Narrow band imaging (NBI), these polyps had irregular pit pattern. Multiple targeted biopsies were taken from there lesions that revealed metastatic lobular adenocarcinoma from breast primary. She had discussion with oncologist to restart chemotherapy.
Discussion: Breast cancer frequently metastasizes to the bones, lungs, CNS, and liver, whereas metastasis GI tract is rare, occurring only in 3.4% of patients. Breast cancer metastasis to the GI can be asymptomatic or can present as nonspecific symptoms, such as abdominal pain, anemia, bleeding, diarrhea, weight loss or bowel obstruction. Radiological imaging can miss early lesions as seen in this case. On colonoscopy, the breast cancer metastases present as diffuse thickening of the colonic wall or as ulcerated or polypoid lesions. Colonic metastasis in the form of multiple sessile diminutive polyps scattered thought the colon is rarely reported in the literature. It is important to utilize NBI to evaluate pit pattern as any aberrancy may be indicative of non-hyperplasic nature of these otherwise hyperplastic appearing polyps on white light.
Disclosures:
Abhinav Tiwari, MD1, Khola Qamar, MD2. C0145 - Case of Metastatic Breast Cancer Resembling Hyperplastic Polyps, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sacred Heart Medical Center at RiverBend, Springfield, OR; 2Dartmouth-Hitchcock Putnam Physicians, Bennington, VT
Introduction: Breast cancer is most common malignancy in woman worldwide. Metastasis to the gastrointestinal tract (GI) is relatively rare occurring in only 3 % cases. Herein, we report a case of breast cancer metastasis localized only to the GI mucosa in the form of mucosal polyps which resembled typical hyperplastic polyps.
Case Description/Methods: 59-year-old female with history of pT2N2aM0, stage IIIA grade 2 invasive lobular carcinoma of the right breast status post mastectomy and axillary lymph-node dissection (showing 5/6 lymph node positive) along with adjuvant chemotherapy with Adriamycin, Cytoxan followed by weekly Taxol and radiation therapy. She had recent normal Computerized tomography and PET scan without any recurrent disease. She was referred for Iron deficiency anemia with hemoglobin 9.5 g/dL along with microcytosis and low ferritin measuring 4 g/L in absence of any overt bleeding. She underwent diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy. Former was unremarkable but colonoscopy showed multiple 3-4 mm sessile polyps scattered through the colon. On Narrow band imaging (NBI), these polyps had irregular pit pattern. Multiple targeted biopsies were taken from there lesions that revealed metastatic lobular adenocarcinoma from breast primary. She had discussion with oncologist to restart chemotherapy.
Discussion: Breast cancer frequently metastasizes to the bones, lungs, CNS, and liver, whereas metastasis GI tract is rare, occurring only in 3.4% of patients. Breast cancer metastasis to the GI can be asymptomatic or can present as nonspecific symptoms, such as abdominal pain, anemia, bleeding, diarrhea, weight loss or bowel obstruction. Radiological imaging can miss early lesions as seen in this case. On colonoscopy, the breast cancer metastases present as diffuse thickening of the colonic wall or as ulcerated or polypoid lesions. Colonic metastasis in the form of multiple sessile diminutive polyps scattered thought the colon is rarely reported in the literature. It is important to utilize NBI to evaluate pit pattern as any aberrancy may be indicative of non-hyperplasic nature of these otherwise hyperplastic appearing polyps on white light.

Figure: Colonoscopy showing hyperplastic appearing polyps in the colon (fig A to C) and irregular pit pattern under NBI (fig D)
Disclosures:
Abhinav Tiwari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khola Qamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhinav Tiwari, MD1, Khola Qamar, MD2. C0145 - Case of Metastatic Breast Cancer Resembling Hyperplastic Polyps, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
