Back
Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
E0145 - Colonic Ischemia Presenting as a Near Obstructing Colonic Mass
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom
- ES
Elona Shehi, MD
Bronxcare Hospital Center
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Elona Shehi, MD1, Mohamed Farag, MD2, Harish Patel, MD, FACG3
1Bronxcare Hospital Center, Bronx, NY; 2Bronxcare, Bronx, NY; 3BronxCare Hospital Center, Bronx, NY
Introduction: Colonic malignancy is a concern in the patients presenting with rectal bleeding and noted to have colonic mass on colonoscopy. However, in elderly patients with risk factors, Colonic ischemia (CI) should be considered as a possible differential. Clinical assessment and interval Colonoscopy does change the management.
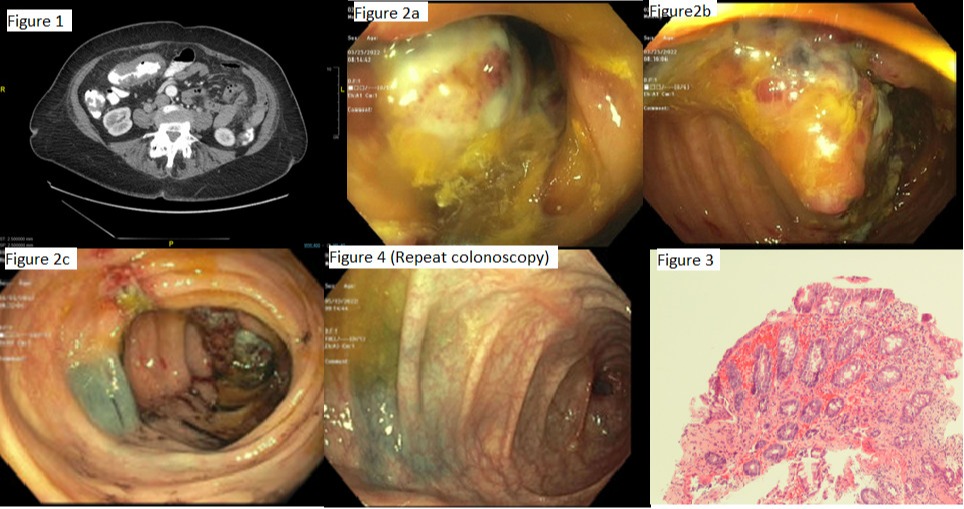
Case Description/Methods: A 78-year-old female presented with complaints of crampy lower abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. Physical exam was significant for abdominal tenderness, otherwise unremarkable. A computerized tomography of the abdomen with contrast showed mural thickening of the transverse colon with luminal narrowing (Fig. 1). Colonoscopy showed an ulcerated, semi-circular, polypoidal nearly obstructing mass, 10 cm in length and site was tattooed(Fig.2a-c). Pathology showed colonic mucosa with mild hyperplastic changes, focal ulceration, extravasated red blood cells, and glandular atrophy suggestive of ischemic induced changes (Fig 3).Carcinoembryonic antigen level was 3.9 (normal < 5.0 ng/mL). The patient was managed conservatively with bowel rest and antibiotics. A repeat colonoscopy in 8 weeks showed fully resolution of the mass adjacent to the tattoo site (Fig 4).
Discussion: Colonic ischemia occurs due to reduced colonic blood flow. Morphologic changes in CI vary with the duration and the severity of injury , from mild mucosal and submucosal edema, with or without necrosis and ulcerations , to severe ischemia causing transmural infarction. In most cases, the diagnosis of CI can be easily made on mucosal biopsies, in conjunction with the clinical, radiologic and colonoscopy findings. In rare cases, CI can appear as a mass-like lesion, mimicking a carcinoma, posing a challenge to diagnosis. Substantial submucosal edema and hemorrhage may be responsible for the mass-like appearance, which is not evident on mucosal biopsies. Due to concern for malignancy, often these patients undergo surgery. CI is a dynamic disease, with a rapid changing clinical picture. Khor at al reported resolution of the mass-like lesions in CI as early as one week, making the repeat colonoscopy a useful tool in cases where the diagnosis is not straightforward.
Disclosures:
Elona Shehi, MD1, Mohamed Farag, MD2, Harish Patel, MD, FACG3. E0145 - Colonic Ischemia Presenting as a Near Obstructing Colonic Mass, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Bronxcare Hospital Center, Bronx, NY; 2Bronxcare, Bronx, NY; 3BronxCare Hospital Center, Bronx, NY
Introduction: Colonic malignancy is a concern in the patients presenting with rectal bleeding and noted to have colonic mass on colonoscopy. However, in elderly patients with risk factors, Colonic ischemia (CI) should be considered as a possible differential. Clinical assessment and interval Colonoscopy does change the management.
Case Description/Methods: A 78-year-old female presented with complaints of crampy lower abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. Physical exam was significant for abdominal tenderness, otherwise unremarkable. A computerized tomography of the abdomen with contrast showed mural thickening of the transverse colon with luminal narrowing (Fig. 1). Colonoscopy showed an ulcerated, semi-circular, polypoidal nearly obstructing mass, 10 cm in length and site was tattooed(Fig.2a-c). Pathology showed colonic mucosa with mild hyperplastic changes, focal ulceration, extravasated red blood cells, and glandular atrophy suggestive of ischemic induced changes (Fig 3).Carcinoembryonic antigen level was 3.9 (normal < 5.0 ng/mL). The patient was managed conservatively with bowel rest and antibiotics. A repeat colonoscopy in 8 weeks showed fully resolution of the mass adjacent to the tattoo site (Fig 4).
Discussion: Colonic ischemia occurs due to reduced colonic blood flow. Morphologic changes in CI vary with the duration and the severity of injury , from mild mucosal and submucosal edema, with or without necrosis and ulcerations , to severe ischemia causing transmural infarction. In most cases, the diagnosis of CI can be easily made on mucosal biopsies, in conjunction with the clinical, radiologic and colonoscopy findings. In rare cases, CI can appear as a mass-like lesion, mimicking a carcinoma, posing a challenge to diagnosis. Substantial submucosal edema and hemorrhage may be responsible for the mass-like appearance, which is not evident on mucosal biopsies. Due to concern for malignancy, often these patients undergo surgery. CI is a dynamic disease, with a rapid changing clinical picture. Khor at al reported resolution of the mass-like lesions in CI as early as one week, making the repeat colonoscopy a useful tool in cases where the diagnosis is not straightforward.

Figure: Fig 1- Wall thickening and luminal narrowing on CT; Fig 2a/2b nearly obstructing mass on colonoscopy; Fig 3 Pathology; Fig 4 - Prior tattooed area with complete resolution of the colonic mass on repeat colonoscopy 8 weeks later
Disclosures:
Elona Shehi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Farag indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harish Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elona Shehi, MD1, Mohamed Farag, MD2, Harish Patel, MD, FACG3. E0145 - Colonic Ischemia Presenting as a Near Obstructing Colonic Mass, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
