Back
Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
D0064 - Pancreatic Hepatoid Carcinoma: A Very Rare and Intriguing Entity
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Yasir Ahmed, MD
United Health Services Hospital
Binghamton, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Yasir Ahmed, MD1, Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Fahad Malik, MD2, Daniel Chin, MD1, Ali Khan, MD1, Ali Marhaba, MD3
1United Health Services Hospital, Binghamton, NY; 2United Health Services Hospital, Binghamtom, NY; 3UHS, Johnson City, NY
Introduction: Hepatoid carcinoma (HC) is a rare tumor with features morphologically and immunohistochemically like focal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HC is extremely rare in pancreas compared to other organs with less than 50 cases reported in the literature so far.
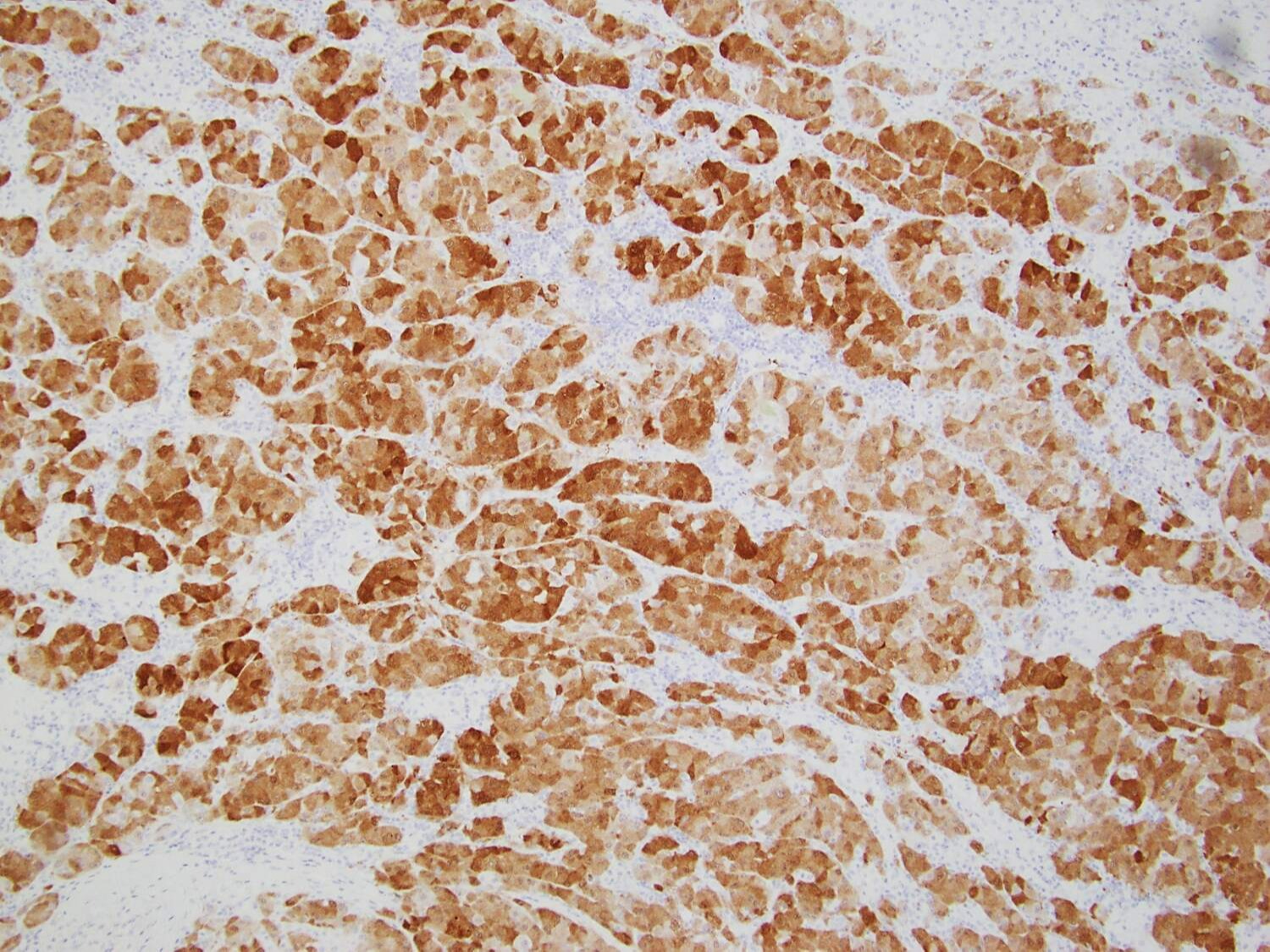
Case Description/Methods: 67-year-old male with compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C, was evaluated for gradual weight loss and poor appetite. Abdominal ultrasound (US) showed a pancreatic head mass only and a cirrhotic liver. Computed tomography scan of the abdomen & pelvis with contrast revealed a 10.1 cm pancreatic head mass and another mixed attenuation 4.18 cm mass in lateral right hepatic lobe suggesting a metastatic neoplastic disease. CA 19-9 levels were normal, and Alfa Fetoprotein (AFP) levels were significantly elevated. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the mass via endoscopic US was initially reported as pancreatic adenocarcinoma. An excisional supraclavicular lymph node biopsy had features consistent with metastatic hepatoid (hepatocellular) carcinoma. Additional immunohistochemical staining and evaluation by pathologists of the pancreatic FNA sample confirmed a hepatoid (hepatocellular) carcinoma. The neoplastic cells were strongly positive for Cam 5.2, Hep par-1, arginase-1, glypican-3, villin, beta-catenin and SMAD-4. The patient was started on atezolizumab and bevacizumab therapy.
Discussion: The theories proposed to explain pathogenesis of pancreatic hepatoid carcinoma (PHS) are a) pancreas has ectopic liver tissue where an HC originates b) the pancreatic cells transdifferentiate into hepatocytes and c) there may be activation of the genes controlling hepatic differentiation of pancreatic cells during carcinogenesis, which are normally suppressed.
Four histological subtypes are noticed on a review of 41 cases: purely HCC-like morphology, with neuroendocrine differentiation, and with acinar or glandular differentiation.
Serum AFP levels are mostly elevated and used as a marker to determine the success of therapy. Hep Par-1 is thought to be the most sensitive among all the markers.
Prognosis is difficult to predict and there is no consensus on preferred chemotherapy due to limited data. Surgical resection is the preferred treatment option.
PHC should be considered in the differential diagnosis pancreatic tumors. This case will add valuable information to the limited literature on PHC.
Disclosures:
Yasir Ahmed, MD1, Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Fahad Malik, MD2, Daniel Chin, MD1, Ali Khan, MD1, Ali Marhaba, MD3. D0064 - Pancreatic Hepatoid Carcinoma: A Very Rare and Intriguing Entity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1United Health Services Hospital, Binghamton, NY; 2United Health Services Hospital, Binghamtom, NY; 3UHS, Johnson City, NY
Introduction: Hepatoid carcinoma (HC) is a rare tumor with features morphologically and immunohistochemically like focal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HC is extremely rare in pancreas compared to other organs with less than 50 cases reported in the literature so far.
Case Description/Methods: 67-year-old male with compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C, was evaluated for gradual weight loss and poor appetite. Abdominal ultrasound (US) showed a pancreatic head mass only and a cirrhotic liver. Computed tomography scan of the abdomen & pelvis with contrast revealed a 10.1 cm pancreatic head mass and another mixed attenuation 4.18 cm mass in lateral right hepatic lobe suggesting a metastatic neoplastic disease. CA 19-9 levels were normal, and Alfa Fetoprotein (AFP) levels were significantly elevated. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the mass via endoscopic US was initially reported as pancreatic adenocarcinoma. An excisional supraclavicular lymph node biopsy had features consistent with metastatic hepatoid (hepatocellular) carcinoma. Additional immunohistochemical staining and evaluation by pathologists of the pancreatic FNA sample confirmed a hepatoid (hepatocellular) carcinoma. The neoplastic cells were strongly positive for Cam 5.2, Hep par-1, arginase-1, glypican-3, villin, beta-catenin and SMAD-4. The patient was started on atezolizumab and bevacizumab therapy.
Discussion: The theories proposed to explain pathogenesis of pancreatic hepatoid carcinoma (PHS) are a) pancreas has ectopic liver tissue where an HC originates b) the pancreatic cells transdifferentiate into hepatocytes and c) there may be activation of the genes controlling hepatic differentiation of pancreatic cells during carcinogenesis, which are normally suppressed.
Four histological subtypes are noticed on a review of 41 cases: purely HCC-like morphology, with neuroendocrine differentiation, and with acinar or glandular differentiation.
Serum AFP levels are mostly elevated and used as a marker to determine the success of therapy. Hep Par-1 is thought to be the most sensitive among all the markers.
Prognosis is difficult to predict and there is no consensus on preferred chemotherapy due to limited data. Surgical resection is the preferred treatment option.
PHC should be considered in the differential diagnosis pancreatic tumors. This case will add valuable information to the limited literature on PHC.

Figure: Arginase-1 stain positive
Disclosures:
Yasir Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Sakhawat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fahad Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Chin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Marhaba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasir Ahmed, MD1, Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Fahad Malik, MD2, Daniel Chin, MD1, Ali Khan, MD1, Ali Marhaba, MD3. D0064 - Pancreatic Hepatoid Carcinoma: A Very Rare and Intriguing Entity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

