Back
Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
E0034 - Acellular Is Not Always Benign: A Case of Primary Pancreatic Sarcoma
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Idrees Suliman, MD
Mountain Vista Medical Center
Mesa, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Idrees Suliman, MD1, Paresh Sojitra, MD2, Preeyanka Sundar, MD2, Kaivan Patel, BS2, Spogmai R. Khan, MD1, Tushar Gohel, MD2
1Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ; 2Midwestern University, Mesa, AZ
Introduction: Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms (PCN) are encountered more frequently given the more widespread usage of cross sectional imaging. Primary pancreatic sarcomas represent 0.1% of all pancreatic malignancies and tend to be aggressive and have a poor prognosis.
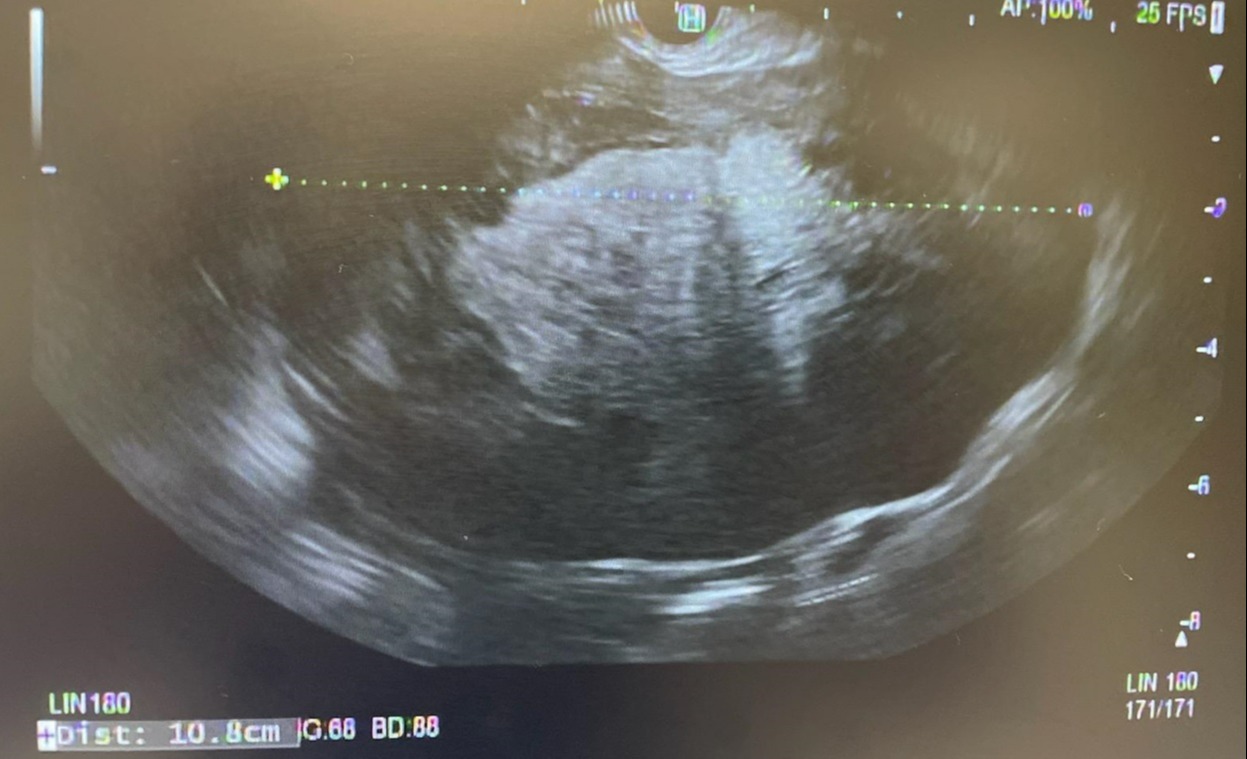
Case Description/Methods: A 74 yo F w/ PMHx significant for HLD presented to ER with persistent nausea and vomiting of two days duration. She became concerned when she was unable to tolerate oral diet and decided to seek medical attention. There was no abdominal pain. Her only medication was atorvastatin. No family history of malignancy. Social history yielded occasional alcohol use (1-2/year) and no smoking. She was independent and ROS was unremarkable. Her PE was unremarkable with no abdominal tenderness. CXR and CBC were unremarkable. CMP was significant for a mildly elevated bilirubin 1.3. Given the fact that she was unable to tolerate PO she was admitted for further evaluation and supportive management. Due to unresolving symptoms she underwent a CT scan with IV contrast. It was significant for a 10.4 x 9.1 x 7.2cm cystic lesion centered in the root of the jejunal mesentery. The pancreatic body and tail were displaced and the main pancreatic duct appeared normal. The origin was unclear. MRI with and without contrast could not delineate the origin of the cyst either. AFP and CEA were unremarkable. EUS was undertaken and was significant for a large 10cmx8cm complex cyst in the pancreatic body. The cyst was heterogenous and had a solid component (90%). The bile ducts and pancreatic ducts were normal in caliber. There was no lymphadenopathy. A 22g needle was used to aspirate 1.5mL of fluid. Grossly the fluid was thin and serous appearing. Intraoperative microscopic review showed an acellular fluid with blood only. The patient improved with supportive management and was discharged home. Pathology subsequently showed high grade spindle cells positive for MDM2 with patchy SMA staining. They were negative for S100, SOX10, and CD117. This is consistent with a high-grade sarcoma however the specimen has been sent to a tertiary care center for a second opinion. The patient is currently awaiting oncology input but is systemically well
Discussion: It is of vital importance that large cystic lesions in close proximity to the pancreas be evaluated urgently with EUS. While intraoperative FNA results are helpful, what can appear benign can in fact be a highly aggressive tumor. Primary pancreatic sarcomas are a rare but important consideration of PCN.
Disclosures:
Idrees Suliman, MD1, Paresh Sojitra, MD2, Preeyanka Sundar, MD2, Kaivan Patel, BS2, Spogmai R. Khan, MD1, Tushar Gohel, MD2. E0034 - Acellular Is Not Always Benign: A Case of Primary Pancreatic Sarcoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ; 2Midwestern University, Mesa, AZ
Introduction: Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms (PCN) are encountered more frequently given the more widespread usage of cross sectional imaging. Primary pancreatic sarcomas represent 0.1% of all pancreatic malignancies and tend to be aggressive and have a poor prognosis.
Case Description/Methods: A 74 yo F w/ PMHx significant for HLD presented to ER with persistent nausea and vomiting of two days duration. She became concerned when she was unable to tolerate oral diet and decided to seek medical attention. There was no abdominal pain. Her only medication was atorvastatin. No family history of malignancy. Social history yielded occasional alcohol use (1-2/year) and no smoking. She was independent and ROS was unremarkable. Her PE was unremarkable with no abdominal tenderness. CXR and CBC were unremarkable. CMP was significant for a mildly elevated bilirubin 1.3. Given the fact that she was unable to tolerate PO she was admitted for further evaluation and supportive management. Due to unresolving symptoms she underwent a CT scan with IV contrast. It was significant for a 10.4 x 9.1 x 7.2cm cystic lesion centered in the root of the jejunal mesentery. The pancreatic body and tail were displaced and the main pancreatic duct appeared normal. The origin was unclear. MRI with and without contrast could not delineate the origin of the cyst either. AFP and CEA were unremarkable. EUS was undertaken and was significant for a large 10cmx8cm complex cyst in the pancreatic body. The cyst was heterogenous and had a solid component (90%). The bile ducts and pancreatic ducts were normal in caliber. There was no lymphadenopathy. A 22g needle was used to aspirate 1.5mL of fluid. Grossly the fluid was thin and serous appearing. Intraoperative microscopic review showed an acellular fluid with blood only. The patient improved with supportive management and was discharged home. Pathology subsequently showed high grade spindle cells positive for MDM2 with patchy SMA staining. They were negative for S100, SOX10, and CD117. This is consistent with a high-grade sarcoma however the specimen has been sent to a tertiary care center for a second opinion. The patient is currently awaiting oncology input but is systemically well
Discussion: It is of vital importance that large cystic lesions in close proximity to the pancreas be evaluated urgently with EUS. While intraoperative FNA results are helpful, what can appear benign can in fact be a highly aggressive tumor. Primary pancreatic sarcomas are a rare but important consideration of PCN.

Figure: EUS imaging of pancreatic complex cyst
Disclosures:
Idrees Suliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paresh Sojitra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Preeyanka Sundar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kaivan Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Spogmai Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tushar Gohel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Idrees Suliman, MD1, Paresh Sojitra, MD2, Preeyanka Sundar, MD2, Kaivan Patel, BS2, Spogmai R. Khan, MD1, Tushar Gohel, MD2. E0034 - Acellular Is Not Always Benign: A Case of Primary Pancreatic Sarcoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
