Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: IBD
B0411 - Indirect Effects of Tofacitinib on Work Productivity in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Mediation Analysis Between Work Productivity and the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Laura E. Targownik, MD, MSHS
Mount Sinai Hospital, University of Toronto
Toronto, ON, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Laura Targownik, MD, MSHS1, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MSc, MACG3, Andrew G. Bushmakin, MS4, Joseph C. Cappelleri, PhD, MPH4, Elaine Tai, PharmD5, Sean Gardiner, MD6, Peter Hur, 6, Julian Panés, MD, PhD7
1Mount Sinai Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; 2Susan and Leonard Feinstein IBD Center, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Unit of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 4Pfizer Inc, Groton, CT; 5Pfizer Canada, Kirkland, PQ, Canada; 6Pfizer Inc, New York, NY; 7Formerly, Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, IDIBAPS, CIBERehd, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral small molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of UC. Tofacitinib induction treatment has been shown to improve work productivity in patients (pts) with UC. However, it is unknown whether improvements in work productivity are fully explained by changes in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) or if other factors not captured by these changes contribute.
Methods: We evaluated the interrelationship between IBDQ domains (bowel, emotional, social, and systemic) and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-UC (WPAI-UC) components (overall work productivity loss and activity impairment) among pts in the Phase 3, 8-week induction studies that evaluated tofacitinib as induction therapy for UC (OCTAVE Induction 1&2; NCT01465763; NCT01458951). A mediation model used IBDQ domains as mediators of the treatment effect on WPAI-UC components as outcomes. Work productivity loss and activity impairment can be viewed as complementary outcomes covering work and other daily activities, respectively. Analyses used all available pooled data from Week 8 in pts receiving tofacitinib/placebo.
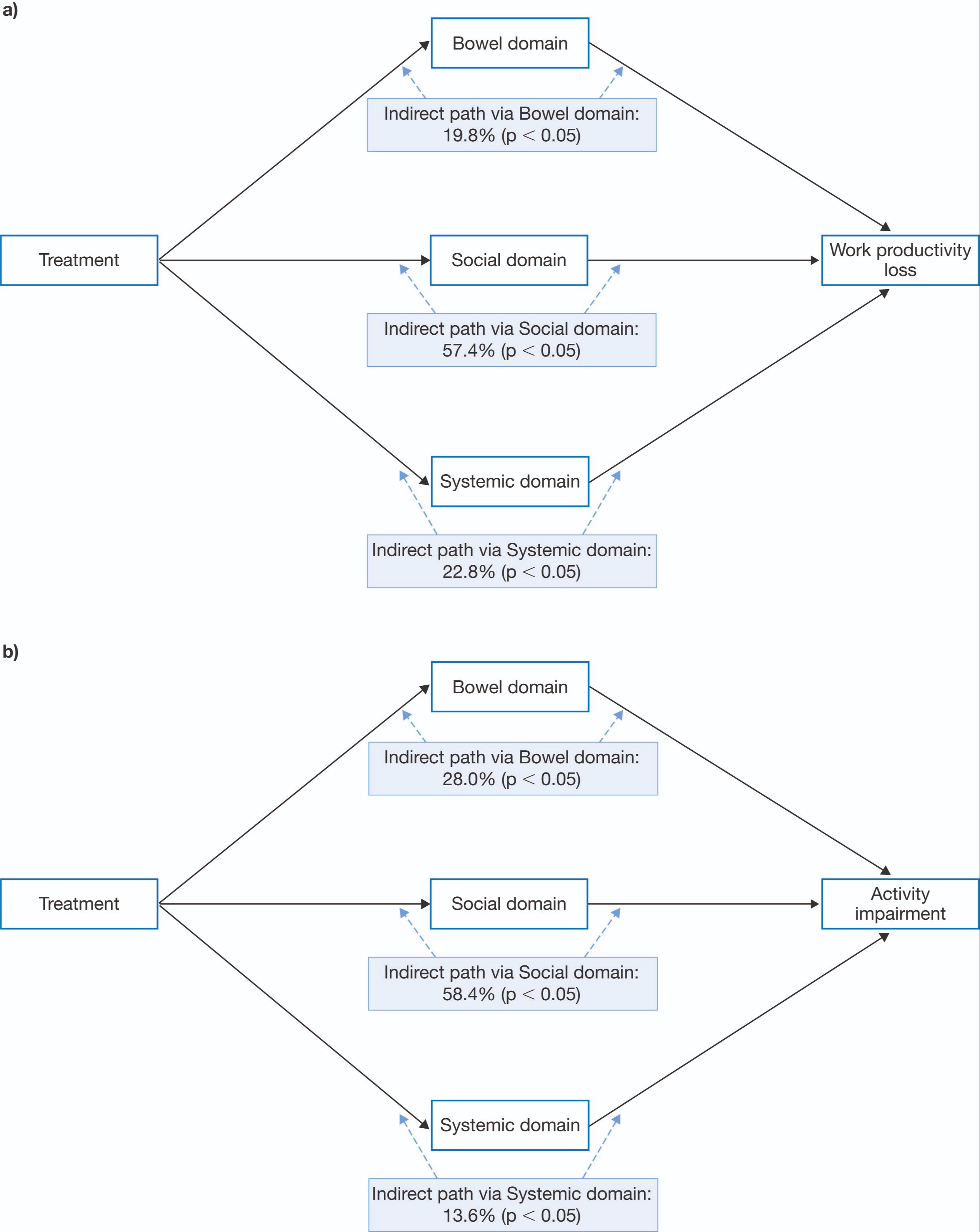
Results: There were 490 and 1,083 pts available for analysis in the models assessing work productivity loss and activity impairment, respectively. For the models evaluating work productivity loss (Figure a) and activity impairment (Figure b), the effects of tofacitinib were fully mediated via IBDQ domains; the largest effects were via the IBDQ social domain, which represented 57.4% and 58.4% of the effects of tofacitinib on work productivity loss and activity impairment, respectively (Figure a and Figure b, respectively). The impact of tofacitinib via the IBDQ emotional domain did not affect work productivity loss or activity impairment.
Discussion: This analysis suggests that the effects of tofacitinib induction therapy on work productivity loss and activity impairment in pts with UC were fully mediated via IBDQ bowel, social, and systemic domains. These findings provide insights into the interrelationship between IBDQ domains and WPAI-UC and may help inform healthcare providers on the impact of UC therapies on pts' work and leisure activities.
Disclosures:
Laura Targownik, MD, MSHS1, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MSc, MACG3, Andrew G. Bushmakin, MS4, Joseph C. Cappelleri, PhD, MPH4, Elaine Tai, PharmD5, Sean Gardiner, MD6, Peter Hur, 6, Julian Panés, MD, PhD7. B0411 - Indirect Effects of Tofacitinib on Work Productivity in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Mediation Analysis Between Work Productivity and the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mount Sinai Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; 2Susan and Leonard Feinstein IBD Center, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Unit of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 4Pfizer Inc, Groton, CT; 5Pfizer Canada, Kirkland, PQ, Canada; 6Pfizer Inc, New York, NY; 7Formerly, Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, IDIBAPS, CIBERehd, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral small molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of UC. Tofacitinib induction treatment has been shown to improve work productivity in patients (pts) with UC. However, it is unknown whether improvements in work productivity are fully explained by changes in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) or if other factors not captured by these changes contribute.
Methods: We evaluated the interrelationship between IBDQ domains (bowel, emotional, social, and systemic) and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-UC (WPAI-UC) components (overall work productivity loss and activity impairment) among pts in the Phase 3, 8-week induction studies that evaluated tofacitinib as induction therapy for UC (OCTAVE Induction 1&2; NCT01465763; NCT01458951). A mediation model used IBDQ domains as mediators of the treatment effect on WPAI-UC components as outcomes. Work productivity loss and activity impairment can be viewed as complementary outcomes covering work and other daily activities, respectively. Analyses used all available pooled data from Week 8 in pts receiving tofacitinib/placebo.
Results: There were 490 and 1,083 pts available for analysis in the models assessing work productivity loss and activity impairment, respectively. For the models evaluating work productivity loss (Figure a) and activity impairment (Figure b), the effects of tofacitinib were fully mediated via IBDQ domains; the largest effects were via the IBDQ social domain, which represented 57.4% and 58.4% of the effects of tofacitinib on work productivity loss and activity impairment, respectively (Figure a and Figure b, respectively). The impact of tofacitinib via the IBDQ emotional domain did not affect work productivity loss or activity impairment.
Discussion: This analysis suggests that the effects of tofacitinib induction therapy on work productivity loss and activity impairment in pts with UC were fully mediated via IBDQ bowel, social, and systemic domains. These findings provide insights into the interrelationship between IBDQ domains and WPAI-UC and may help inform healthcare providers on the impact of UC therapies on pts' work and leisure activities.

Figure: Figure. Summary of indirect (mediated through IBDQ domains) effects of tofacitinib vs placebo on the a) work productivity loss and b) activity impairment WPAI-UC components as a percentage of the total treatment effect.
The WPAI-UC is a self-administered six-item questionnaire that generates four metrics: absenteeism (work time missed), presenteeism (impairment whilst working), productivity loss (overall work impairment from the combination of absenteeism and presenteeism), and activity impairment (non-work activity impairment). WPAI-UC component scores are expressed as percentages, with a higher percentage indicating greater impairment and less productivity.
The IBDQ evaluates disease-related quality of life by 32 items over four domains: bowel (total domain score ranges from 10 to 70), emotional (total domain score ranges from 12 to 84), social (total domain score ranges from 5 to 35), and systemic (total domain score ranges from 5 to 35). For the total score (ranges from 32 to 224) and each domain, a higher score indicates a better quality of life.
IBDQ, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; WPAI-UC, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-Ulcerative Colitis
The WPAI-UC is a self-administered six-item questionnaire that generates four metrics: absenteeism (work time missed), presenteeism (impairment whilst working), productivity loss (overall work impairment from the combination of absenteeism and presenteeism), and activity impairment (non-work activity impairment). WPAI-UC component scores are expressed as percentages, with a higher percentage indicating greater impairment and less productivity.
The IBDQ evaluates disease-related quality of life by 32 items over four domains: bowel (total domain score ranges from 10 to 70), emotional (total domain score ranges from 12 to 84), social (total domain score ranges from 5 to 35), and systemic (total domain score ranges from 5 to 35). For the total score (ranges from 32 to 224) and each domain, a higher score indicates a better quality of life.
IBDQ, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; WPAI-UC, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-Ulcerative Colitis
Disclosures:
Laura Targownik: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gilead Sciences – Grant/Research Support. JAMP – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Marla Dubinsky: AbbVie – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genetech – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Trellus Health – Shareholder. UCB – Consultant.
Flavio Steinwurz: AbbVie – Consultant, Speaker fees. Amgen – Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speaker fees. Eurofarma – Consultant, Speaker fees. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Speaker fees. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Speaker fees. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sandoz – Consultant, Speaker fees. Takeda – Consultant, Speaker fees. UCB – Consultant, Speaker fees.
Andrew Bushmakin: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Stock Options.
Joseph Cappelleri: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Stock Options.
Elaine Tai: Pfizer Canada – Employee, Stock Options.
Sean Gardiner: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Peter Hur: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Stock Options.
Julian Panés: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support, Personal fees. Arena – Personal fees. Athos – Personal fees. Boehringer Ingelheim – Personal fees. Celgene – Personal fees. Celltrion – Personal fees. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Personal fees. Galapagos – Personal fees. Genentech/Roche – Personal fees. GSK – Personal fees. Immunic – Personal fees. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Personal fees. Mirum – Personal fees. Morphic – Personal fees. Nestlé – Personal fees. Origo – Personal fees. Pandion – Personal fees. Pfizer Inc – Grant/Research Support, Personal fees. Progenity – Personal fees. Takeda – Personal fees. Theravance Biopharma – Personal fees. Wassermann – Personal fees.
Laura Targownik, MD, MSHS1, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MSc, MACG3, Andrew G. Bushmakin, MS4, Joseph C. Cappelleri, PhD, MPH4, Elaine Tai, PharmD5, Sean Gardiner, MD6, Peter Hur, 6, Julian Panés, MD, PhD7. B0411 - Indirect Effects of Tofacitinib on Work Productivity in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Mediation Analysis Between Work Productivity and the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
