Back


Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
C0008 - The Natural History of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Andrew Canakis, DO
University of Maryland Medical Center
Baltimore, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Andrew Canakis, DO1, Anusha Vittal, MD2, Smit Deliwala, MD3, Benjamin Twery, MD1, Preet Patel, MD1, Justin Canakis, DO4, Prabhleen Chahal, MD5
1University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 2National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD; 3Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI; 4George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) exhibit a wide array of clinicopathologic behavior. As such, risk stratifying these is important to prevent the progression to malignancy. Theoretically PCLs in liver transplant (LT) recipients are at increased risk of accelerated carcinogenesis in the setting of lifelong immunosuppressive medications. With improvements in surgical outcomes, LT patients are living longer and understanding the incidence and natural course of these lesions is paramount. As such we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the risk of malignant progression and outcomes of PCLs in LT recipients.
Methods: Multiple databases (PUBMED, Embase, the Cochrane Library) were searched for studies looking at PCLs in post-LT patients from inception until February 2022. Data was extracted to calculate pooled estimates and risk ratios using a random effects model. Primary outcomes were the incidence of PCLs in transplant recipients and progression to malignancy. Secondary outcomes included outcomes of those undergoing surgical resection for progression and change in size over time. There was moderate heterogeneity of our sample.
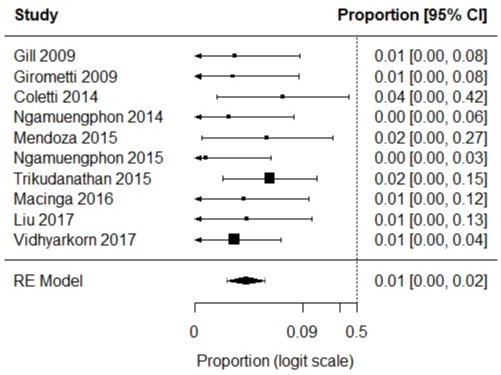
Results: 12 studies met inclusion criteria (17,862 patients with 1,411 PCLs). The pooled proportion of new PCL development in post-LT patients was 68% (95% CI, 42 – 86, I2 94%) over a follow up of 3.7±1.5 years. The relative risk of developing PCL in LT recipients compared to non-LT recipients was associated with a significant 67% reduction (RR 0.33; 95% CI, 0.14 – 0.79, I2 93.91, p = 0.01). Among 4158 patients receiving LT, 295 developed PCL and 4 of them progressed to malignancy; the pooled progression to malignancy was 1% (95% CI, 0 – 2, I2 0%) (Figure 1). LT was associated with a significant 71% reduction in relative risk of undergoing surgical resection (RR 0.29; 95% CI, 0.09 - 0.93, I2 0%, p = 0.04).
Discussion: Compared to non-transplant patients, incidental PCLs in LT patients do not carry a higher risk of malignant transformation. In the setting of immunosuppressive medication, the risk of malignant progression appears to be negligible, and these patients can be followed like non-LT patients based on guidelines. Furthermore, our findings emphasize that incidental PCLs should not preclude a LT evaluation.
Disclosures:
Andrew Canakis, DO1, Anusha Vittal, MD2, Smit Deliwala, MD3, Benjamin Twery, MD1, Preet Patel, MD1, Justin Canakis, DO4, Prabhleen Chahal, MD5. C0008 - The Natural History of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 2National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD; 3Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI; 4George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) exhibit a wide array of clinicopathologic behavior. As such, risk stratifying these is important to prevent the progression to malignancy. Theoretically PCLs in liver transplant (LT) recipients are at increased risk of accelerated carcinogenesis in the setting of lifelong immunosuppressive medications. With improvements in surgical outcomes, LT patients are living longer and understanding the incidence and natural course of these lesions is paramount. As such we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the risk of malignant progression and outcomes of PCLs in LT recipients.
Methods: Multiple databases (PUBMED, Embase, the Cochrane Library) were searched for studies looking at PCLs in post-LT patients from inception until February 2022. Data was extracted to calculate pooled estimates and risk ratios using a random effects model. Primary outcomes were the incidence of PCLs in transplant recipients and progression to malignancy. Secondary outcomes included outcomes of those undergoing surgical resection for progression and change in size over time. There was moderate heterogeneity of our sample.
Results: 12 studies met inclusion criteria (17,862 patients with 1,411 PCLs). The pooled proportion of new PCL development in post-LT patients was 68% (95% CI, 42 – 86, I2 94%) over a follow up of 3.7±1.5 years. The relative risk of developing PCL in LT recipients compared to non-LT recipients was associated with a significant 67% reduction (RR 0.33; 95% CI, 0.14 – 0.79, I2 93.91, p = 0.01). Among 4158 patients receiving LT, 295 developed PCL and 4 of them progressed to malignancy; the pooled progression to malignancy was 1% (95% CI, 0 – 2, I2 0%) (Figure 1). LT was associated with a significant 71% reduction in relative risk of undergoing surgical resection (RR 0.29; 95% CI, 0.09 - 0.93, I2 0%, p = 0.04).
Discussion: Compared to non-transplant patients, incidental PCLs in LT patients do not carry a higher risk of malignant transformation. In the setting of immunosuppressive medication, the risk of malignant progression appears to be negligible, and these patients can be followed like non-LT patients based on guidelines. Furthermore, our findings emphasize that incidental PCLs should not preclude a LT evaluation.

Figure: Individual estimates and pooled proportions of progression of pancreatic cystic lesions to malignancy in post liver transplant patients
Disclosures:
Andrew Canakis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Vittal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Smit Deliwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin Twery indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Preet Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Justin Canakis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prabhleen Chahal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant.
Andrew Canakis, DO1, Anusha Vittal, MD2, Smit Deliwala, MD3, Benjamin Twery, MD1, Preet Patel, MD1, Justin Canakis, DO4, Prabhleen Chahal, MD5. C0008 - The Natural History of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
