Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
C0060 - A Case of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangiopathy After Cholecystectomy
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Jason J. John, MD
University of South Florida Health
Tampa, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Jason J. John, MD1, Jeffrey C. Gill, MD2
1University of South Florida Health, Tampa, FL; 2James A. Haley VA Hospital, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 (IgG4)-sclerosing cholangiopathy (IgG4-SC) is a hepato-biliary inflammatory condition that can affect any level of the biliary tree. The diagnosis remains challenging as it shares similar findings in other conditions.
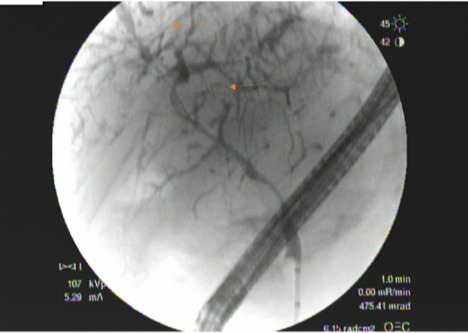
Case Description/Methods: An 83-year-old Caucasian male presented to clinic for anorexia, abdominal pain, and elevated liver function tests (LFTs). The patient had a history of cholelithiasis and was status-post cholecystectomy eight months prior, but otherwise had no history of elevated liver enzymes. Upon presentation to clinic, his AST was 205, ALT 143, and alkaline phosphatase 253, with normal bilirubin. Autoimmune work-up as well as hepatic serologies for Hepatitis A, B, and C were negative. Serum alpha fetoprotein, alpha-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin and ferritin levels were in the normal range. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed intrahepatic bile duct dilation, but normal common bile duct. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed intrahepatic dilation to 5 mm with a sclerosing cholangitis (Figure 1). Initially, there was a concern for an ischemic cholangiopathy secondary to the prior cholecystectomy, however his IgG4 returned at 1140 mg/dl, specific for IgG4-SC. The patient was started on high-dose prednisone. Repeat MRCP showed improvement of biliary ductal dilation and chronic IgG mediated pancreatic inflammation. Patient had resolution of anorexia, abdominal pain, and his liver function tests and IgG4 downtrended.
Discussion: IgG4-SC is a chronic inflammatory disease of the biliary system that typically occurs in association with other manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Most patients clinically present in their 7th or 8th decade of life and the disease has a male predominance. The presenting symptoms include jaundice, pruritis, abdominal pain, and weight loss. IgG4-SC is diagnosed via a combination of imaging, laboratory, serological, and histopathological findings. When IgG4 levels are greater than 250 mg/dl, the specificity of IgG4-SC is 90%. IgG4-SC can be differentiated from primary sclerosing cholangitis with elevated serum levels and steroid responsiveness. Rarely is a tissue diagnosis necessary. The mainstay of treatment is corticosteroids with patient response shown by normalization of LFT’s, reduction in serum IgG4 levels and improvement in imaging. Relapse can occur and is typically treated with immunomodulators.
Disclosures:
Jason J. John, MD1, Jeffrey C. Gill, MD2. C0060 - A Case of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangiopathy After Cholecystectomy, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of South Florida Health, Tampa, FL; 2James A. Haley VA Hospital, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 (IgG4)-sclerosing cholangiopathy (IgG4-SC) is a hepato-biliary inflammatory condition that can affect any level of the biliary tree. The diagnosis remains challenging as it shares similar findings in other conditions.
Case Description/Methods: An 83-year-old Caucasian male presented to clinic for anorexia, abdominal pain, and elevated liver function tests (LFTs). The patient had a history of cholelithiasis and was status-post cholecystectomy eight months prior, but otherwise had no history of elevated liver enzymes. Upon presentation to clinic, his AST was 205, ALT 143, and alkaline phosphatase 253, with normal bilirubin. Autoimmune work-up as well as hepatic serologies for Hepatitis A, B, and C were negative. Serum alpha fetoprotein, alpha-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin and ferritin levels were in the normal range. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed intrahepatic bile duct dilation, but normal common bile duct. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed intrahepatic dilation to 5 mm with a sclerosing cholangitis (Figure 1). Initially, there was a concern for an ischemic cholangiopathy secondary to the prior cholecystectomy, however his IgG4 returned at 1140 mg/dl, specific for IgG4-SC. The patient was started on high-dose prednisone. Repeat MRCP showed improvement of biliary ductal dilation and chronic IgG mediated pancreatic inflammation. Patient had resolution of anorexia, abdominal pain, and his liver function tests and IgG4 downtrended.
Discussion: IgG4-SC is a chronic inflammatory disease of the biliary system that typically occurs in association with other manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Most patients clinically present in their 7th or 8th decade of life and the disease has a male predominance. The presenting symptoms include jaundice, pruritis, abdominal pain, and weight loss. IgG4-SC is diagnosed via a combination of imaging, laboratory, serological, and histopathological findings. When IgG4 levels are greater than 250 mg/dl, the specificity of IgG4-SC is 90%. IgG4-SC can be differentiated from primary sclerosing cholangitis with elevated serum levels and steroid responsiveness. Rarely is a tissue diagnosis necessary. The mainstay of treatment is corticosteroids with patient response shown by normalization of LFT’s, reduction in serum IgG4 levels and improvement in imaging. Relapse can occur and is typically treated with immunomodulators.

Figure: Figure 1: Intrahepatic duct dilation with strictures proximally (red arrows).
Disclosures:
Jason John indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Gill indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason J. John, MD1, Jeffrey C. Gill, MD2. C0060 - A Case of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangiopathy After Cholecystectomy, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
