Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Liver
B0561 - Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma - A Mimicker of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Michael Meyers, MD
Mercy Health Grand Rapids/Michigan State University Internal Medicine Residency Program
Grand Rapids, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Meyers, MD
Mercy Health Grand Rapids/Michigan State University Internal Medicine Residency Program, Grand Rapids, MI
Introduction: Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung (HAL) is a rare lung carcinoma that resembles hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver (HCC) on histology. Immunohistochemical staining distinguishes the two. We present a case of HAL in which treatment targeting HCC achieved significant response.
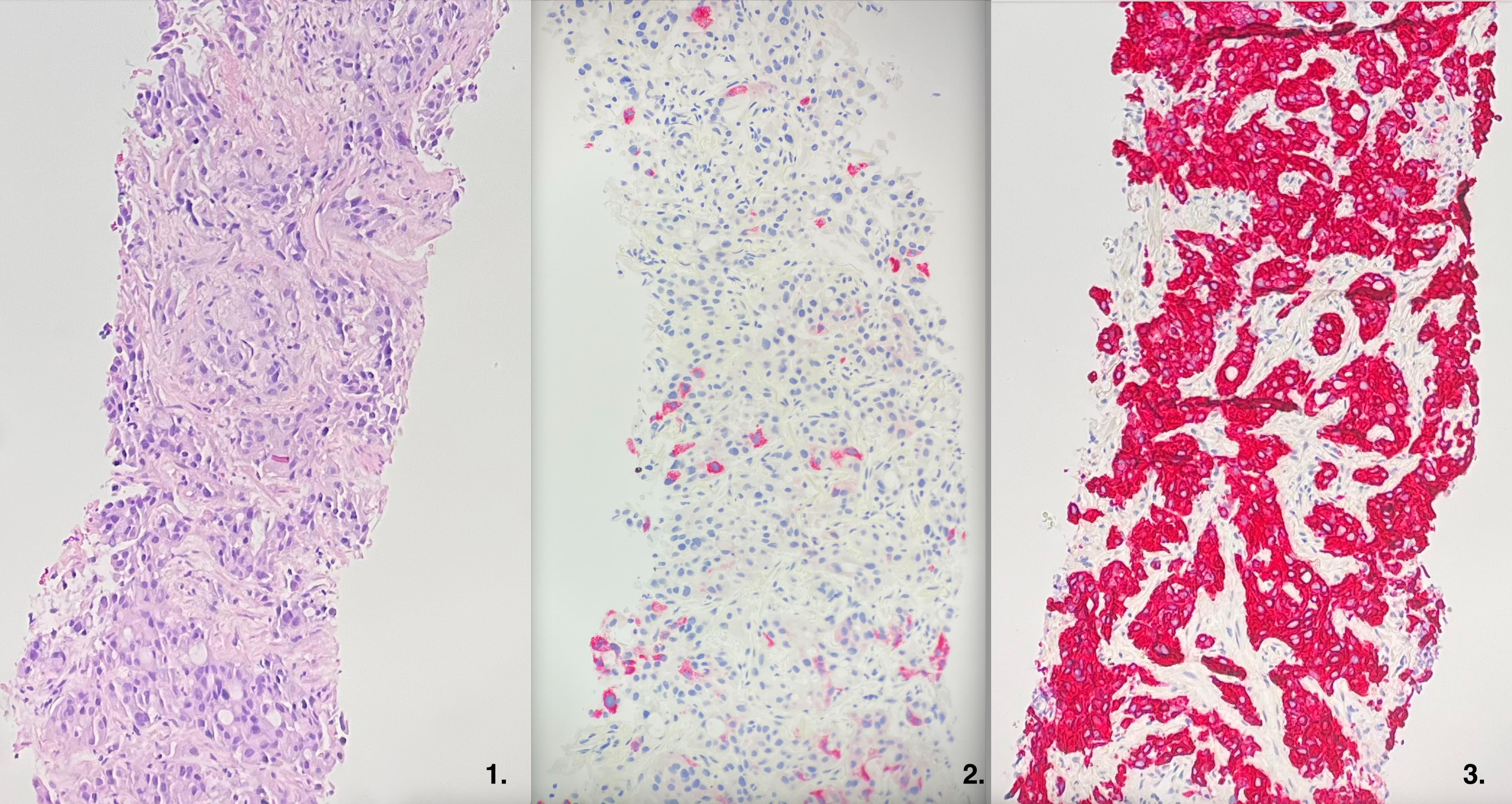
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old male with a history of tobacco use presented with pathologic weight loss. CT scan revealed a 31mm lung nodule with mediastinal adenopathy in addition to a 10mm liver lesion. Core needle biopsy of the pulmonary nodule was performed. Histology showed a poorly-differentiated carcinoma comprising polygonal cells containing eccentrically located nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with cells arranged in solid nests, resembling HCC.(Image 1) Treatment with atezolizumab and bevacizumab was initiated. However, given the patient’s lack of risk factors for HCC, further pathology analysis was requested. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for Hep-Par, consistent with HCC.(Image 2) However, strong diffuse positivity for cytokeratin-7 favored lung as the primary site of the tumor.(Image 3) This led to a change in the diagnosis from HCC to HAL. Two cycles of immunotherapy led to a significant reduction in tumor burden. After two additional months of therapy, new onset back pain led to the discovery of spinal metastases. Treatment was changed to carboplatin and Taxol, but the patient only received one cycle before his decline and passing.
Discussion: This case highlights a unique pathology to be considered when histology suggests HCC. HAL resembles HCC histologically; in both there are cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in sheet-like portions. Immunohistochemical staining differentiates between the two. While Hep-Par stains are positive in both, only cytokeratin-7 stains are positive in HAL.i
The prognosis for HAL is poor. Partial disease response has been reported with platinum-based chemotherapy.ii This case is unique in that there was a significant response to atezolizumab and bevacizumab, which was first chosen to target HCC.
i Grossman K, Beasley MB, Braman SS. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: Review of a rare form of lung cancer. Respir Med. 2016;119:175-179. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2016.09.003
ii Gavrancic T, Park YH. A novel approach using sorafenib in alpha fetoprotein-producing hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2015;13(4):387-391. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2015.0054
Disclosures:
Michael Meyers, MD. B0561 - Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma - A Mimicker of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mercy Health Grand Rapids/Michigan State University Internal Medicine Residency Program, Grand Rapids, MI
Introduction: Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung (HAL) is a rare lung carcinoma that resembles hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver (HCC) on histology. Immunohistochemical staining distinguishes the two. We present a case of HAL in which treatment targeting HCC achieved significant response.
Case Description/Methods: A 69-year-old male with a history of tobacco use presented with pathologic weight loss. CT scan revealed a 31mm lung nodule with mediastinal adenopathy in addition to a 10mm liver lesion. Core needle biopsy of the pulmonary nodule was performed. Histology showed a poorly-differentiated carcinoma comprising polygonal cells containing eccentrically located nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with cells arranged in solid nests, resembling HCC.(Image 1) Treatment with atezolizumab and bevacizumab was initiated. However, given the patient’s lack of risk factors for HCC, further pathology analysis was requested. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for Hep-Par, consistent with HCC.(Image 2) However, strong diffuse positivity for cytokeratin-7 favored lung as the primary site of the tumor.(Image 3) This led to a change in the diagnosis from HCC to HAL. Two cycles of immunotherapy led to a significant reduction in tumor burden. After two additional months of therapy, new onset back pain led to the discovery of spinal metastases. Treatment was changed to carboplatin and Taxol, but the patient only received one cycle before his decline and passing.
Discussion: This case highlights a unique pathology to be considered when histology suggests HCC. HAL resembles HCC histologically; in both there are cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in sheet-like portions. Immunohistochemical staining differentiates between the two. While Hep-Par stains are positive in both, only cytokeratin-7 stains are positive in HAL.i
The prognosis for HAL is poor. Partial disease response has been reported with platinum-based chemotherapy.ii This case is unique in that there was a significant response to atezolizumab and bevacizumab, which was first chosen to target HCC.
i Grossman K, Beasley MB, Braman SS. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: Review of a rare form of lung cancer. Respir Med. 2016;119:175-179. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2016.09.003
ii Gavrancic T, Park YH. A novel approach using sorafenib in alpha fetoprotein-producing hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2015;13(4):387-391. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2015.0054

Figure: 1. Haematoxylin and eosin stain showing poorly differentiated polygonal cells containing eccentrically located nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with cells arranged in solid nests. 2. Hep-par stain positivity suggestive of hepatocellular carcinoma. 3. Cytokeratin-7 stain diffusely positive favoring lung as the primary tumor site.
Disclosures:
Michael Meyers indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Meyers, MD. B0561 - Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma - A Mimicker of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
