Back


Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: General Endoscopy
C0287 - Overnight Split Dosing With 1L Polyethylene Glycol + Ascorbic Acid Bowel Preparation Delivers High Levels of High-Quality Cleansing for Colonoscopy: A Sub-Analysis of a Large Real-World Study
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- CA
Cátia Arieira, MD
Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira
Guimarães, Braga, Portugal
Presenting Author(s)
Cátia Arieira, MD1, José Cotter, MD1, Ricardo Gorjão, MD2, Vicente Lorenzo-Zúñiga, MD3, Miguel A. Pantaleón Sánchez, MD4, David Carral Martínez, MD5, Fernándo Sábado, MD6, Elena Pérez Arellano, MD7, Blas J. Gómez Rodríguez, MD8, Antonio López Cano, MD9, Salvador Machlab, MD10, Jose M. Esteban López-Jamar, MD11, Sarbelio Rodriguez, MD12, Juha Halonen, PhD13, Fatma Akriche, MD13, Carmen Turbí Disla, MD14
1Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira, Guimarães, Braga, Portugal; 2Hospital CUF Descobertas, Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal; 3Hospital HM Sant Jordi, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; 4Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; 5Hospital San Rafael, A Coruña, Galicia, Spain; 6Consorcio Hospitalario Provincial de Castelló, Valencia, Comunidad Valenciana, Spain; 7Hospital La Zarzuela, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 8Hospital Quirón Salud Sagrado Corazón, Sevilla, Andalucia, Spain; 9Hospital Doctor López Cano, Cádiz, Andalucia, Spain; 10Parc Taulı́ Hospital Universitari & Institut d’Investigació i Innovació Parc Taulı́ I3PT, Sabadell, Catalonia, Spain; 11Hospital Universitario Clínico San Carlos, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 12Hospital Ruber Juan Bravo, European University of Madrid, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 13Norgine, Medical Affairs, Harefield, England, United Kingdom; 14Norgine, Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Introduction: Clinical guidelines recommend evening/morning split dosing for routine colonoscopy procedures. Overnight split dosing with 1 liter polyethylene glycol + ascorbic acid (1L PEG+ASC) has demonstrated strong cleansing performance in clinical trials. Here we report a sub-analysis from the largest real-world study to date of 1L PEG+ASC, evaluating patients who received this split dosing regimen.
Methods: An observational, multicenter, retrospective study evaluated the medical records of colonoscopy outpatients between July 2019 and September 2021 at 12 centers in Spain and Portugal. Eligible adults (aged ≥18 years) had a screening, surveillance, or diagnostic colonoscopy after an evening/morning (split dose) or same-day regimen of 1L PEG+ASC. Bowel cleansing was assessed by site endoscopists using the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS). Segmental BBPS scores of 3 defined high-quality cleansing. High adherence was defined as consumption of ≥75% of each dose and safety was assessed based on registered adverse events (AEs). BBPS scores were compared between time to colonoscopy groups with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
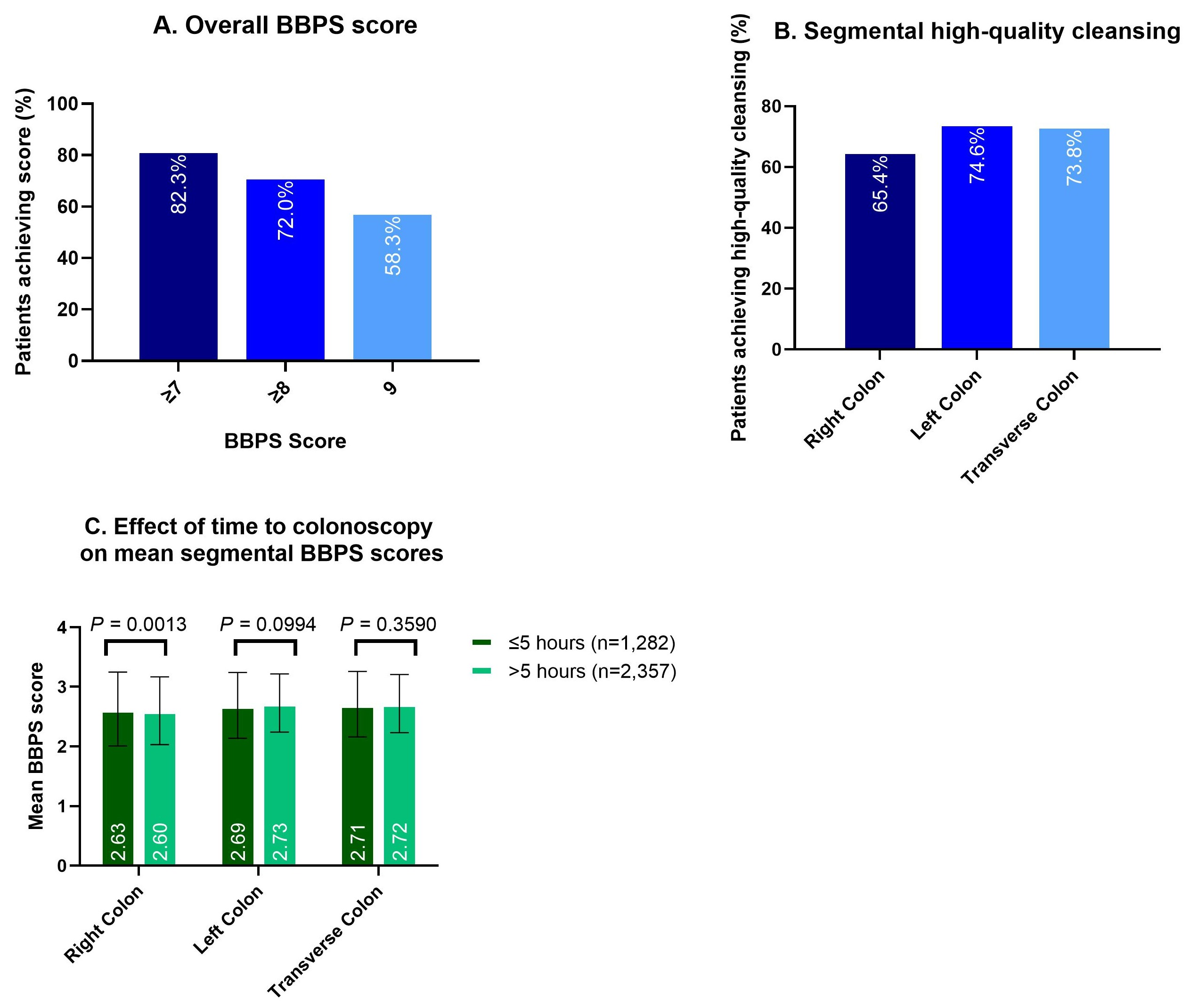
Results: A total of 13,169 patients from the 12 centers were enrolled in the study, of which 4,316 received a split-dosing regimen and were included in this analysis. In the split-dose group, 48.0% of patients were male, mean (SD) age was 58.1 ± 13.4 years, and 33.4% were ≥65 years old. An overall BBPS score of 9 was attained in 58.3% of patients (Figure 1A). High rates of BBPS 3 were observed in all segments (Figure 1B). There was no effect of time lapse to colonoscopy on segmental cleansing in the transversal and left colon (Figure 1C). Only 1.6% of colonoscopies were incomplete, 0.39% due to poor preparation. Overall, 3.9% (95% CI: 3.4%–4.6%) of patients experienced an AE. The main AEs were nausea (2.4%), vomiting (1.2%), and abdominal pain (0.4%). Adherence was high at 97.6% of those 1,834 patients who reported volume intake.
Discussion: Results from this analysis show that overnight split dosing with 1L PEG+ASC delivered an excellent overall and segmental bowel cleansing quality in real-world settings.
Disclosures:
Cátia Arieira, MD1, José Cotter, MD1, Ricardo Gorjão, MD2, Vicente Lorenzo-Zúñiga, MD3, Miguel A. Pantaleón Sánchez, MD4, David Carral Martínez, MD5, Fernándo Sábado, MD6, Elena Pérez Arellano, MD7, Blas J. Gómez Rodríguez, MD8, Antonio López Cano, MD9, Salvador Machlab, MD10, Jose M. Esteban López-Jamar, MD11, Sarbelio Rodriguez, MD12, Juha Halonen, PhD13, Fatma Akriche, MD13, Carmen Turbí Disla, MD14. C0287 - Overnight Split Dosing With 1L Polyethylene Glycol + Ascorbic Acid Bowel Preparation Delivers High Levels of High-Quality Cleansing for Colonoscopy: A Sub-Analysis of a Large Real-World Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira, Guimarães, Braga, Portugal; 2Hospital CUF Descobertas, Lisbon, Lisboa, Portugal; 3Hospital HM Sant Jordi, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; 4Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; 5Hospital San Rafael, A Coruña, Galicia, Spain; 6Consorcio Hospitalario Provincial de Castelló, Valencia, Comunidad Valenciana, Spain; 7Hospital La Zarzuela, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 8Hospital Quirón Salud Sagrado Corazón, Sevilla, Andalucia, Spain; 9Hospital Doctor López Cano, Cádiz, Andalucia, Spain; 10Parc Taulı́ Hospital Universitari & Institut d’Investigació i Innovació Parc Taulı́ I3PT, Sabadell, Catalonia, Spain; 11Hospital Universitario Clínico San Carlos, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 12Hospital Ruber Juan Bravo, European University of Madrid, Madrid, Madrid, Spain; 13Norgine, Medical Affairs, Harefield, England, United Kingdom; 14Norgine, Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Introduction: Clinical guidelines recommend evening/morning split dosing for routine colonoscopy procedures. Overnight split dosing with 1 liter polyethylene glycol + ascorbic acid (1L PEG+ASC) has demonstrated strong cleansing performance in clinical trials. Here we report a sub-analysis from the largest real-world study to date of 1L PEG+ASC, evaluating patients who received this split dosing regimen.
Methods: An observational, multicenter, retrospective study evaluated the medical records of colonoscopy outpatients between July 2019 and September 2021 at 12 centers in Spain and Portugal. Eligible adults (aged ≥18 years) had a screening, surveillance, or diagnostic colonoscopy after an evening/morning (split dose) or same-day regimen of 1L PEG+ASC. Bowel cleansing was assessed by site endoscopists using the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS). Segmental BBPS scores of 3 defined high-quality cleansing. High adherence was defined as consumption of ≥75% of each dose and safety was assessed based on registered adverse events (AEs). BBPS scores were compared between time to colonoscopy groups with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
Results: A total of 13,169 patients from the 12 centers were enrolled in the study, of which 4,316 received a split-dosing regimen and were included in this analysis. In the split-dose group, 48.0% of patients were male, mean (SD) age was 58.1 ± 13.4 years, and 33.4% were ≥65 years old. An overall BBPS score of 9 was attained in 58.3% of patients (Figure 1A). High rates of BBPS 3 were observed in all segments (Figure 1B). There was no effect of time lapse to colonoscopy on segmental cleansing in the transversal and left colon (Figure 1C). Only 1.6% of colonoscopies were incomplete, 0.39% due to poor preparation. Overall, 3.9% (95% CI: 3.4%–4.6%) of patients experienced an AE. The main AEs were nausea (2.4%), vomiting (1.2%), and abdominal pain (0.4%). Adherence was high at 97.6% of those 1,834 patients who reported volume intake.
Discussion: Results from this analysis show that overnight split dosing with 1L PEG+ASC delivered an excellent overall and segmental bowel cleansing quality in real-world settings.

Figure: Figure 1. Bowel cleansing performance of split dose 1L PEG+ASC: (A) Rates of overall colon high-quality cleansing (BBPS score >6); (B) Rates of segmental high-quality cleansing (BBPS score 3); (C) Effect of time to colonoscopy on mean segmental BBPS scores.
Disclosures:
Cátia Arieira indicated no relevant financial relationships.
José Cotter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ricardo Gorjão indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vicente Lorenzo-Zúñiga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Pantaleón Sánchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Carral Martínez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fernándo Sábado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elena Pérez Arellano: Norgine – Honoraria for speaking.
Blas J. Gómez Rodríguez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antonio López Cano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salvador Machlab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose M. Esteban López-Jamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarbelio Rodriguez: Norgine – Honoraria for speaking.
Juha Halonen: Norgine – Employee.
Fatma Akriche: Norgine – Employee.
Carmen Turbí Disla: Norgine – Employee.
Cátia Arieira, MD1, José Cotter, MD1, Ricardo Gorjão, MD2, Vicente Lorenzo-Zúñiga, MD3, Miguel A. Pantaleón Sánchez, MD4, David Carral Martínez, MD5, Fernándo Sábado, MD6, Elena Pérez Arellano, MD7, Blas J. Gómez Rodríguez, MD8, Antonio López Cano, MD9, Salvador Machlab, MD10, Jose M. Esteban López-Jamar, MD11, Sarbelio Rodriguez, MD12, Juha Halonen, PhD13, Fatma Akriche, MD13, Carmen Turbí Disla, MD14. C0287 - Overnight Split Dosing With 1L Polyethylene Glycol + Ascorbic Acid Bowel Preparation Delivers High Levels of High-Quality Cleansing for Colonoscopy: A Sub-Analysis of a Large Real-World Study, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
