Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: GI Bleeding
C0341 - Rare Case of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Saakshi Joshi, MD
McLaren Macomb
Macomb, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Saakshi Joshi, MD1, Luis Rojas, MD2, Alexandra Davies, DO1, Samuel Gun, DO2
1McLaren Macomb, Macomb, MI; 2McLaren Macomb, Mt. Clemens, MI
Introduction: Among gastrointestinal pathologies, gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) is the most common cause of hospitalization within the United States, and consequently costing the healthcare system $5 billion.¹ Common causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding(UGIB) are gastric or duodenal ulcers, gastritis or duodenitis, and esophagitis. We present a rare case of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) extending into the duodenum causing an UGIB.
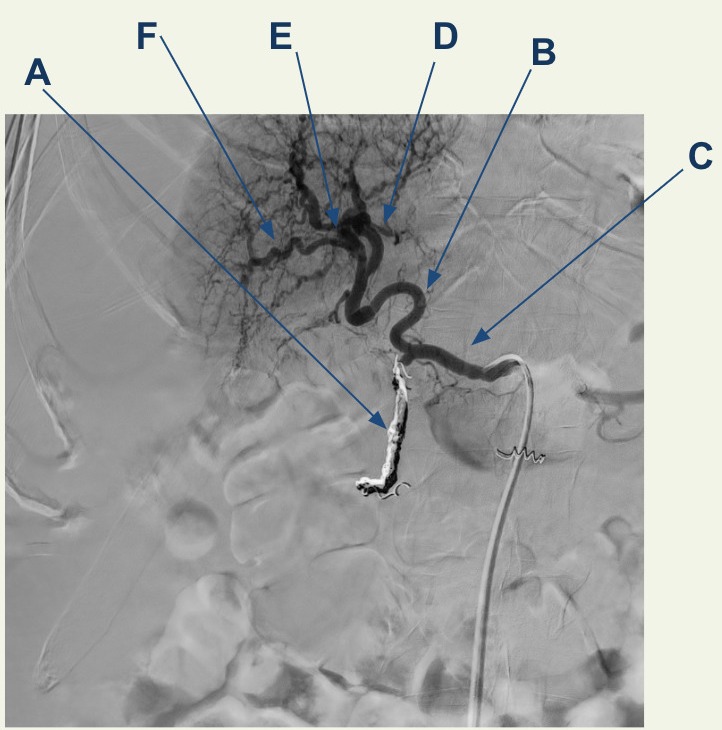
Case Description/Methods: 64 year old male with history of alcohol abuse, developed multifocal HCC and decompensated cirrhosis presents with fatigue and weakness. Additionally, patient has multiple admissions for UGIB stabilized by gastroduodenal artery embolization as seen in figure 2 after failing endoscopic treatment. At admission, patient was hypotensive at 100/57 and anemic with a hemoglobin 5.8. Computed tomography and angiogram showed a exophytic lesion supplied by the cystic artery eroding into the duodenal bulb. Band and coil embolization of the tumoral arteries arising from the cystic artery was performed as seen in Figure 1. The patient had worsening hematochezia and hemodynamic instability, and deemed inoperable. He was not a transplant candidate given his cancer burden and later expired.
Discussion: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and angioembolization play vital roles in treatment of UGIB and surgery is used as salvage therapy. EGD is used to provide diagnosis and therapy. In an acute setting the Glasgow Blatchford Score (GBS) is used for risk assessment. EGD within 24 hours is recommended for patients and within 12 hours for variceal bleeding. A combination of thermal and nonthermal coagulation, submucosal injection, and clipping can facilitate hemostasis. Contact thermal therapy, includes bipolar and unipolar cautery, allows for pressure application at the bleeding point with thermal energy for the coagulation. Non-contact thermal technique such as argon plasma coagulation uses ionized argon gas to ablate hemorrhagic tissue. Multiple nonthermal techniques including injection sclerotherapy and clipping. Injection sclerotherapy consists of injections of epinephrine, or other substances, surrounding the bleeding site with thermal therapy. Angioembolization is used for bleeding when endoscopic interventions fail. A tumor rupture is life-threatening and there are limited reports of UGIB secondary to HCC, emphasizing the importance of our case.
[1] Harrison's: Principles of Internal Medicine. 21st Ed.. United States: McGraw-Hill Education, 2022
Disclosures:
Saakshi Joshi, MD1, Luis Rojas, MD2, Alexandra Davies, DO1, Samuel Gun, DO2. C0341 - Rare Case of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary to Hepatocellular Carcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1McLaren Macomb, Macomb, MI; 2McLaren Macomb, Mt. Clemens, MI
Introduction: Among gastrointestinal pathologies, gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) is the most common cause of hospitalization within the United States, and consequently costing the healthcare system $5 billion.¹ Common causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding(UGIB) are gastric or duodenal ulcers, gastritis or duodenitis, and esophagitis. We present a rare case of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) extending into the duodenum causing an UGIB.
Case Description/Methods: 64 year old male with history of alcohol abuse, developed multifocal HCC and decompensated cirrhosis presents with fatigue and weakness. Additionally, patient has multiple admissions for UGIB stabilized by gastroduodenal artery embolization as seen in figure 2 after failing endoscopic treatment. At admission, patient was hypotensive at 100/57 and anemic with a hemoglobin 5.8. Computed tomography and angiogram showed a exophytic lesion supplied by the cystic artery eroding into the duodenal bulb. Band and coil embolization of the tumoral arteries arising from the cystic artery was performed as seen in Figure 1. The patient had worsening hematochezia and hemodynamic instability, and deemed inoperable. He was not a transplant candidate given his cancer burden and later expired.
Discussion: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and angioembolization play vital roles in treatment of UGIB and surgery is used as salvage therapy. EGD is used to provide diagnosis and therapy. In an acute setting the Glasgow Blatchford Score (GBS) is used for risk assessment. EGD within 24 hours is recommended for patients and within 12 hours for variceal bleeding. A combination of thermal and nonthermal coagulation, submucosal injection, and clipping can facilitate hemostasis. Contact thermal therapy, includes bipolar and unipolar cautery, allows for pressure application at the bleeding point with thermal energy for the coagulation. Non-contact thermal technique such as argon plasma coagulation uses ionized argon gas to ablate hemorrhagic tissue. Multiple nonthermal techniques including injection sclerotherapy and clipping. Injection sclerotherapy consists of injections of epinephrine, or other substances, surrounding the bleeding site with thermal therapy. Angioembolization is used for bleeding when endoscopic interventions fail. A tumor rupture is life-threatening and there are limited reports of UGIB secondary to HCC, emphasizing the importance of our case.
[1] Harrison's: Principles of Internal Medicine. 21st Ed.. United States: McGraw-Hill Education, 2022

Figure: A: Prior gastroduodenal artery embolization
B: Proper hepatic artery
C: Common hepatic artery
D: Left hepatic artery
E: Right hepatic artery
F: Cystic artery
B: Proper hepatic artery
C: Common hepatic artery
D: Left hepatic artery
E: Right hepatic artery
F: Cystic artery
Disclosures:
Saakshi Joshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luis Rojas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexandra Davies indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samuel Gun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saakshi Joshi, MD1, Luis Rojas, MD2, Alexandra Davies, DO1, Samuel Gun, DO2. C0341 - Rare Case of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary to Hepatocellular Carcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
