Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: IBD
C0378 - De-escalation of Combination Drug Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Adam A. Saleh, BS
Engineering Medicine at Texas A&M Health Science Center Medical School
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Adam A. Saleh, BS1, Rajdeepsingh Waghela, MD2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS2, Rachel Stading, BS3, Natalia Miroballi, BS3, Joshua Moskow, BS4, Theresa Thurston, BS4, Bincy Abraham, MD, MS, FACG5
1Engineering Medicine at Texas A&M Health Science Center Medical School, Houston, TX; 2Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 3Texas A&M Health Science Center Medical School, Houston, TX; 4Texas A&M Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 5Houston Methodist Academic Institute, Houston, TX
Introduction: There are limited data on the use of multiple biologics or small molecule drugs in combination to treat patients with inflammatory bowel disease and much less in methods for successful de-escalation of combination therapy. The aim of this study was to evaluate contributing factors to the decision to de-escalate, and successful de-escalation.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed for IBD patients who were on combination (dual biologics or biologic + small molecule) therapy and underwent de-escalation. Data was collected at both the visit at which the decision to de-escalate was made and the next follow-up visit. Data collected included patient demographics, such as age, gender, BMI, albumin, CRP, ESR, and clinical scores. At the follow-up visit, patient compliance with the de-escalation plan, and the necessity to re-escalate therapy was evaluated.
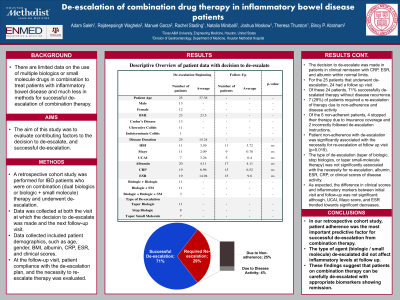
Results: Patient characteristics are outlined in table 1. The decision to de-escalate was made in patients (on average) with CRP, ESR, and albumin within normal limits. For the 25 patients that underwent de-escalation, 24 had a follow up visit. Of these patients, 71% were able to continue de-escalation with 29% requiring a re-escalation in therapy. 25% (N=6) were non-adherent with de-escalation for reasons such as insurance restrictions and incorrectly following de-escalation instructions. In one instance, a patient fully discontinued tofacitinib instead of taking the recommended taper dose. In another, the patient’s insurance company stopped covering multiple biologics and one biologic was fully discontinued as a result. Patient adherence with de-escalation was significantly associated with the necessity for re-escalation at follow up visit (p=0.019). The type of de-escalation (taper of biologic, stop biologics, or taper small-molecule therapy) was not significantly associated with the necessity for re-escalation, albumin, ESR, CRP, or clinical scores of disease activity. As expected, the difference in clinical scores and inflammatory markers between initial visit and follow-up was not significant; although, UCAI, Mayo score, and ESR trended down.
Discussion: In our retrospective cohort study, patient adherence was the most important predictive factor for successful de-escalation from combination therapy. Whether a biologic or small molecule was the agent being de-escalated did not appear to affect inflammatory levels at follow up. These findings might be limited by our sample size of 25 and thus additional studies are needed.
Disclosures:
Adam A. Saleh, BS1, Rajdeepsingh Waghela, MD2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS2, Rachel Stading, BS3, Natalia Miroballi, BS3, Joshua Moskow, BS4, Theresa Thurston, BS4, Bincy Abraham, MD, MS, FACG5. C0378 - De-escalation of Combination Drug Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Engineering Medicine at Texas A&M Health Science Center Medical School, Houston, TX; 2Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 3Texas A&M Health Science Center Medical School, Houston, TX; 4Texas A&M Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 5Houston Methodist Academic Institute, Houston, TX
Introduction: There are limited data on the use of multiple biologics or small molecule drugs in combination to treat patients with inflammatory bowel disease and much less in methods for successful de-escalation of combination therapy. The aim of this study was to evaluate contributing factors to the decision to de-escalate, and successful de-escalation.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed for IBD patients who were on combination (dual biologics or biologic + small molecule) therapy and underwent de-escalation. Data was collected at both the visit at which the decision to de-escalate was made and the next follow-up visit. Data collected included patient demographics, such as age, gender, BMI, albumin, CRP, ESR, and clinical scores. At the follow-up visit, patient compliance with the de-escalation plan, and the necessity to re-escalate therapy was evaluated.
Results: Patient characteristics are outlined in table 1. The decision to de-escalate was made in patients (on average) with CRP, ESR, and albumin within normal limits. For the 25 patients that underwent de-escalation, 24 had a follow up visit. Of these patients, 71% were able to continue de-escalation with 29% requiring a re-escalation in therapy. 25% (N=6) were non-adherent with de-escalation for reasons such as insurance restrictions and incorrectly following de-escalation instructions. In one instance, a patient fully discontinued tofacitinib instead of taking the recommended taper dose. In another, the patient’s insurance company stopped covering multiple biologics and one biologic was fully discontinued as a result. Patient adherence with de-escalation was significantly associated with the necessity for re-escalation at follow up visit (p=0.019). The type of de-escalation (taper of biologic, stop biologics, or taper small-molecule therapy) was not significantly associated with the necessity for re-escalation, albumin, ESR, CRP, or clinical scores of disease activity. As expected, the difference in clinical scores and inflammatory markers between initial visit and follow-up was not significant; although, UCAI, Mayo score, and ESR trended down.
Discussion: In our retrospective cohort study, patient adherence was the most important predictive factor for successful de-escalation from combination therapy. Whether a biologic or small molecule was the agent being de-escalated did not appear to affect inflammatory levels at follow up. These findings might be limited by our sample size of 25 and thus additional studies are needed.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table: TABLE 1. Descriptive overview of patient data with decision to de-escalate and comparison of clinical scores and inflammatory markers at follow-up. ns = non-significant.
Disclosures:
Adam Saleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajdeepsingh Waghela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manuel Garza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Stading indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natalia Miroballi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Moskow indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Theresa Thurston indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bincy Abraham: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Medtronic – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Adam A. Saleh, BS1, Rajdeepsingh Waghela, MD2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS2, Rachel Stading, BS3, Natalia Miroballi, BS3, Joshua Moskow, BS4, Theresa Thurston, BS4, Bincy Abraham, MD, MS, FACG5. C0378 - De-escalation of Combination Drug Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
