Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Liver
B0614 - Autoimmune Hepatitis-Like Syndrome After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Tzu-Yu Liu, MD
Brown University Warren Alpert School of Medicine
Presenting Author(s)
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD, Thomas Sepe, MD
Brown University Warren Alpert School of Medicine, Providence, RI
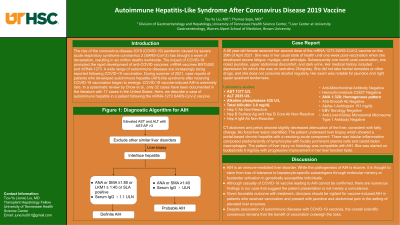
Introduction: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has brought a wave of devastation, resulting in six million deaths worldwide. This has prompted the rapid development of anti-COVID vaccines: mRNA vaccines BNTb262 and mRNA-1273. A wide range of autoimmune diseases are increasingly being reported following COVID-19 vaccination. We describe a rare case of autoimmune hepatitis-like syndrome following the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Case Description/Methods: A 56 year-old female received her second dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine on the 29th of April 2021. One week post-vaccination, she developed severe fatigue, myalgia, and arthralgia. Subsequently, she noted jaundice, upper abdominal discomfort, and dark urine one month post-vaccination. She had a history of depression for which she was on sertraline 25mg/day. She did not use herbal remedies or alcohol. On examination, she was jaundiced with mild right upper quadrant tenderness. Laboratory results were markedly abnormal: AST of 1377 U/L, ALT of 2035 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 435 U/L, and bilirubin of 3.8 mg/dL. Further investigation showed a positive 1:320 anti-nuclear antibody. Serology for viral hepatitis and Epstein-Barr virus were negative. Ceruloplasmin and ɑ1-antitrypsin levels were normal. Anti-smooth muscle antibody, anti-liver-kidney microsomal microsome type 1 antibody, and anti-mitochondrial antibody were negative. Abdominal ultrasound showed hepatic steatosis without cholelithiasis or biliary dilatation. A liver biopsy revealed portal, peri-portal, and lobular inflammation consisting of lymphocytic infiltrates, focally prominent plasma cells, and ceroid-laden macrophages. The pathology was compatible with AIH. The patient was started on budesonide 9 mg/day with improvement in liver function tests.
Discussion: Although 5.16 billion people have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine globally, COVID-19 vaccine-induced AIH remains extremely rare with only 32 cases documented in the literature. While the causality of the vaccine leading to AIH is not established, the absence of hepatotoxic agents, negative viral serology, supportive histology, and response to treatment in our case suggest the association is not a mere coincidence. Clinicians should be vigilant for vaccine-induced AIH in patients who received vaccination and present with jaundice and abdominal pain in the setting of elevated liver enzymes.
Disclosures:
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD, Thomas Sepe, MD. B0614 - Autoimmune Hepatitis-Like Syndrome After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Brown University Warren Alpert School of Medicine, Providence, RI
Introduction: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has brought a wave of devastation, resulting in six million deaths worldwide. This has prompted the rapid development of anti-COVID vaccines: mRNA vaccines BNTb262 and mRNA-1273. A wide range of autoimmune diseases are increasingly being reported following COVID-19 vaccination. We describe a rare case of autoimmune hepatitis-like syndrome following the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Case Description/Methods: A 56 year-old female received her second dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine on the 29th of April 2021. One week post-vaccination, she developed severe fatigue, myalgia, and arthralgia. Subsequently, she noted jaundice, upper abdominal discomfort, and dark urine one month post-vaccination. She had a history of depression for which she was on sertraline 25mg/day. She did not use herbal remedies or alcohol. On examination, she was jaundiced with mild right upper quadrant tenderness. Laboratory results were markedly abnormal: AST of 1377 U/L, ALT of 2035 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 435 U/L, and bilirubin of 3.8 mg/dL. Further investigation showed a positive 1:320 anti-nuclear antibody. Serology for viral hepatitis and Epstein-Barr virus were negative. Ceruloplasmin and ɑ1-antitrypsin levels were normal. Anti-smooth muscle antibody, anti-liver-kidney microsomal microsome type 1 antibody, and anti-mitochondrial antibody were negative. Abdominal ultrasound showed hepatic steatosis without cholelithiasis or biliary dilatation. A liver biopsy revealed portal, peri-portal, and lobular inflammation consisting of lymphocytic infiltrates, focally prominent plasma cells, and ceroid-laden macrophages. The pathology was compatible with AIH. The patient was started on budesonide 9 mg/day with improvement in liver function tests.
Discussion: Although 5.16 billion people have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine globally, COVID-19 vaccine-induced AIH remains extremely rare with only 32 cases documented in the literature. While the causality of the vaccine leading to AIH is not established, the absence of hepatotoxic agents, negative viral serology, supportive histology, and response to treatment in our case suggest the association is not a mere coincidence. Clinicians should be vigilant for vaccine-induced AIH in patients who received vaccination and present with jaundice and abdominal pain in the setting of elevated liver enzymes.
Disclosures:
Tzu-Yu Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Sepe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tzu-Yu Liu, MD, Thomas Sepe, MD. B0614 - Autoimmune Hepatitis-Like Syndrome After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
