Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Liver
C0593 - Lifting the Veil off Weil's Disease: A Case Report of Fulminant Leptospirosis
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Vinay Jahagirdar, MBBS
University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine
Kansas City, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Vinay Jahagirdar, MBBS, Mohamed K. Ahmed, MD, Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Zubaidah Khalaf, MD, Hasan Bader, MD, Hana Hamdan, MD, Esmat Sadeddin, MD
University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO
Introduction: Leptospirosis, a zoonosis caused by the spirochete Leptospira, is acquired by contact with urine of infected animals, mainly rodents, through cuts and mucous membranes. Traditionally considered as an occupational disease affecting farmers and sewer workers, incidence through recreational exposure via freshwater activities has been increasing. It is a notifiable disease, with around 150 cases reported annually in the US.
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old homeless man presented with fever, chills, nausea, myalgias, and headache for one day. He was an active intravenous drug user and UDS was positive for methamphetamine. Temperature was 101.2 F and heart rate 115/minute. Tooth decay and track marks were noted. Abdomen was non tender. Labs showed WBC count of 14.8k, platelet count (PC) 177k, CK 1036. TEE did not show any vegetations. CT scan showed a right lung consolidation. Patient was started on Vancomycin and Piperacillin-tazobactam.
On HOD 1, patient developed watery, non-bloody diarrhea and lower limb pain. By HOD 3, PC fell to 44k, while creatinine started rising. Patient reported diffuse abdominal pain and now had scleral icterus with bilateral conjunctival congestion. Total bilirubin was 12.8. Stool studies, peripheral smear and hepatitis panel were unremarkable. Liver biopsy showed sinusoidal congestion and mild chronic inflammation within the portal tracts, with rare interface hepatitis. An infectious cause was strongly suspected in view of the bicytopenia and multi-systemic changes. Rhabdomyolysis and AKI could also be attributed to meth use.
On HOD 12, Leptospira IgM Ab returned positive. The patient received a 7-day course of oral doxycycline. Eventually, labs normalised and he was discharged on HOD 20.
Discussion: The fulminant form of leptospirosis, Weil’s disease, presents with renal failure and jaundice. Conjunctival suffusion (redness without purulent exudates) is characteristic in the initial leptospiremic phase. Hepatocellular damage and disruption of intercellular junctions leads to bilirubin elevation in the immunological phase.
Antibodies take 3-10 days to develop and so IgM serological tests must be done a week after symptom onset. PCR is very sensitive and specific in the acute phase. Microscopic agglutination test is considered the gold standard due to its high specificity. Starting treatment with empiric antibiotics early on without waiting for testing results can be lifesaving, especially in cases with a high degree of clinical suspicion.
Disclosures:
Vinay Jahagirdar, MBBS, Mohamed K. Ahmed, MD, Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Zubaidah Khalaf, MD, Hasan Bader, MD, Hana Hamdan, MD, Esmat Sadeddin, MD. C0593 - Lifting the Veil off Weil's Disease: A Case Report of Fulminant Leptospirosis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO
Introduction: Leptospirosis, a zoonosis caused by the spirochete Leptospira, is acquired by contact with urine of infected animals, mainly rodents, through cuts and mucous membranes. Traditionally considered as an occupational disease affecting farmers and sewer workers, incidence through recreational exposure via freshwater activities has been increasing. It is a notifiable disease, with around 150 cases reported annually in the US.
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old homeless man presented with fever, chills, nausea, myalgias, and headache for one day. He was an active intravenous drug user and UDS was positive for methamphetamine. Temperature was 101.2 F and heart rate 115/minute. Tooth decay and track marks were noted. Abdomen was non tender. Labs showed WBC count of 14.8k, platelet count (PC) 177k, CK 1036. TEE did not show any vegetations. CT scan showed a right lung consolidation. Patient was started on Vancomycin and Piperacillin-tazobactam.
On HOD 1, patient developed watery, non-bloody diarrhea and lower limb pain. By HOD 3, PC fell to 44k, while creatinine started rising. Patient reported diffuse abdominal pain and now had scleral icterus with bilateral conjunctival congestion. Total bilirubin was 12.8. Stool studies, peripheral smear and hepatitis panel were unremarkable. Liver biopsy showed sinusoidal congestion and mild chronic inflammation within the portal tracts, with rare interface hepatitis. An infectious cause was strongly suspected in view of the bicytopenia and multi-systemic changes. Rhabdomyolysis and AKI could also be attributed to meth use.
On HOD 12, Leptospira IgM Ab returned positive. The patient received a 7-day course of oral doxycycline. Eventually, labs normalised and he was discharged on HOD 20.
Discussion: The fulminant form of leptospirosis, Weil’s disease, presents with renal failure and jaundice. Conjunctival suffusion (redness without purulent exudates) is characteristic in the initial leptospiremic phase. Hepatocellular damage and disruption of intercellular junctions leads to bilirubin elevation in the immunological phase.
Antibodies take 3-10 days to develop and so IgM serological tests must be done a week after symptom onset. PCR is very sensitive and specific in the acute phase. Microscopic agglutination test is considered the gold standard due to its high specificity. Starting treatment with empiric antibiotics early on without waiting for testing results can be lifesaving, especially in cases with a high degree of clinical suspicion.

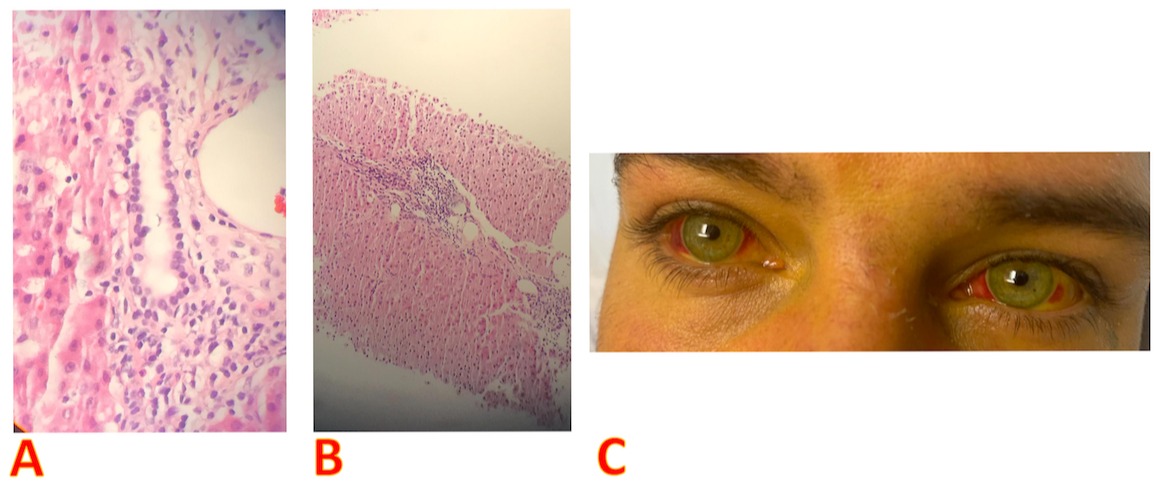
Figure: A, B: Liver biopsy showing liver parenchyma with sinusoidal congestion and mild chronic inflammation within the portal tracts consisting mainly of lymphocytes and occasional plasma cells; C: Bilateral conjunctival suffusion, characteristic of leptospirosis
Disclosures:
Vinay Jahagirdar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wael Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zubaidah Khalaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Bader indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hana Hamdan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Esmat Sadeddin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinay Jahagirdar, MBBS, Mohamed K. Ahmed, MD, Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Zubaidah Khalaf, MD, Hasan Bader, MD, Hana Hamdan, MD, Esmat Sadeddin, MD. C0593 - Lifting the Veil off Weil's Disease: A Case Report of Fulminant Leptospirosis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
