Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Small Intestine
C0646 - Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma: Two Distinct Presentations of a Rare Disease Entity
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- NP
Nikisha Pandya, MD
Coney Island Hospital
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Nikisha Pandya, MD, Nitin Pendyala, MD, Mohammad Choudhry, MD, Michael Bernstein, MD
Coney Island Hospital, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Follicular Lymphoma (FL), a B cell neoplasm, is the second most common type of nodal NHL with frequent duodenal involvement mostly presenting with non-specific abdominal pain. Primary Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (PGINHL) is a rare entity accounting for 2% of all small intestinal malignancies. Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma (DFL) only accounts for 1 to 6% of PGINHL. We present two cases of DFL with variable symptoms.
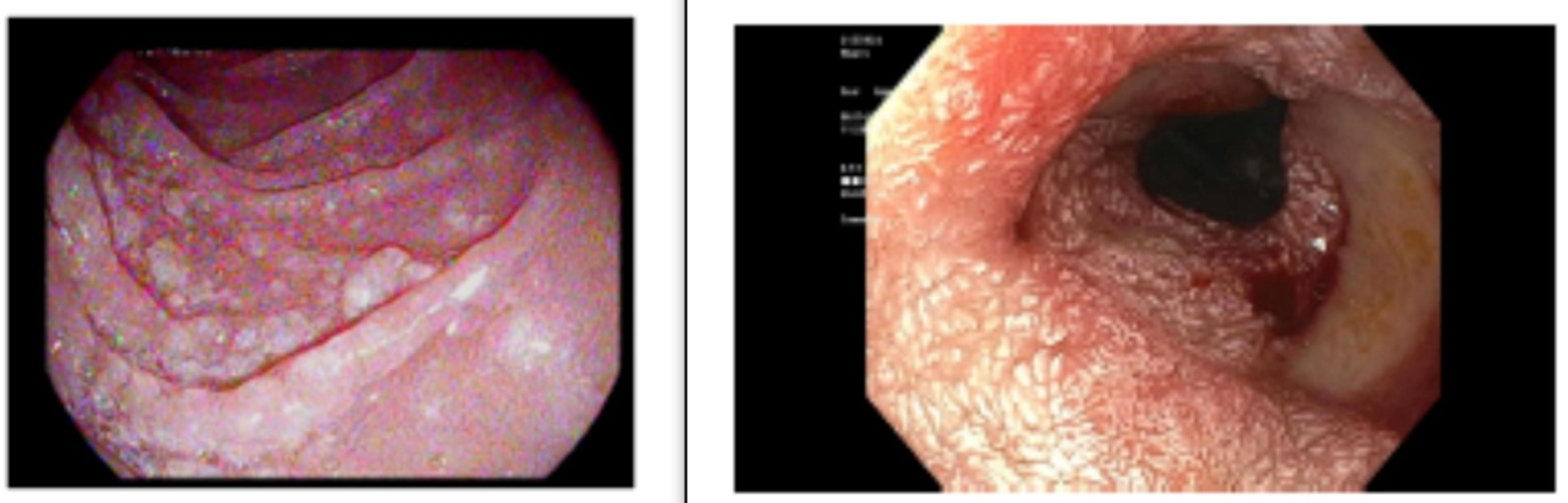
Case Description/Methods: Case 1: A 58-year-old female presented with nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, and 60-pound weight loss over one year. She denied any fever, night sweats, family history of malignancy and had a normal upper and lower endoscopy 5 years ago. EGD showed nodular mucosa in the 2nd portion of the duodenum confirmed to be low-grade FL on biopsy. Metastatic workup showed stage 4 lymphoma. There was no evidence of bulky lymphadenopathy and diagnosis of DFL was made. Patient finished 6 cycles of R-CHOP therapy due to concern for recurrent/residual DFL and currently remains indolent.
Case 2: A 41-year-old male presented with coffee-ground emesis, melena, and 10 lbs weight loss over a month in absence of NSAID use. He also had fever, palpitations, and diaphoresis. Patient’s grandfather had colon cancer and the mother had non-Hodgkin lymphoma and breast cancer. EGD and colonoscopy 9 months prior to presentation showed erosive gastritis and tubular adenoma, respectively. Repeat EGD showed abnormal duodenal mucosa with an area of oozing at the site of the biopsy. Pathology report supported the diagnosis of low-grade DFL. Metastatic workup showed a mediastinal mass, a large 7.7x 4.9x7 cm mesenteric nodal mass, and a 5.8 cm x 5.9 cm duodenal mass involving the head of the pancreas. The patient moved to Iowa for further workup.
Discussion: DFL is an extremely rare PGINHL with an indolent course and good prognosis. DFL has unique features in that immunohistochemically it is similar to nodal FL, however, gene expression analysis groups it closer to MALT lymphoma, and thus, treatment options are heterogeneous with no established guidelines. ‘Wait and Watch’ strategy is often implemented in patients with low-grade disease, however, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy have also been explored. Treatment of DFL with antibiotics owing to its similarity to and association with MALT lymphoma and H. pylori respectively has had mixed results. The two cases described above highlight heterogeneous presentation, dyspepsia, and upper GI bleed, of a rare malignancy - DFL.
Disclosures:
Nikisha Pandya, MD, Nitin Pendyala, MD, Mohammad Choudhry, MD, Michael Bernstein, MD. C0646 - Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma: Two Distinct Presentations of a Rare Disease Entity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Coney Island Hospital, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Follicular Lymphoma (FL), a B cell neoplasm, is the second most common type of nodal NHL with frequent duodenal involvement mostly presenting with non-specific abdominal pain. Primary Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (PGINHL) is a rare entity accounting for 2% of all small intestinal malignancies. Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma (DFL) only accounts for 1 to 6% of PGINHL. We present two cases of DFL with variable symptoms.
Case Description/Methods: Case 1: A 58-year-old female presented with nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, and 60-pound weight loss over one year. She denied any fever, night sweats, family history of malignancy and had a normal upper and lower endoscopy 5 years ago. EGD showed nodular mucosa in the 2nd portion of the duodenum confirmed to be low-grade FL on biopsy. Metastatic workup showed stage 4 lymphoma. There was no evidence of bulky lymphadenopathy and diagnosis of DFL was made. Patient finished 6 cycles of R-CHOP therapy due to concern for recurrent/residual DFL and currently remains indolent.
Case 2: A 41-year-old male presented with coffee-ground emesis, melena, and 10 lbs weight loss over a month in absence of NSAID use. He also had fever, palpitations, and diaphoresis. Patient’s grandfather had colon cancer and the mother had non-Hodgkin lymphoma and breast cancer. EGD and colonoscopy 9 months prior to presentation showed erosive gastritis and tubular adenoma, respectively. Repeat EGD showed abnormal duodenal mucosa with an area of oozing at the site of the biopsy. Pathology report supported the diagnosis of low-grade DFL. Metastatic workup showed a mediastinal mass, a large 7.7x 4.9x7 cm mesenteric nodal mass, and a 5.8 cm x 5.9 cm duodenal mass involving the head of the pancreas. The patient moved to Iowa for further workup.
Discussion: DFL is an extremely rare PGINHL with an indolent course and good prognosis. DFL has unique features in that immunohistochemically it is similar to nodal FL, however, gene expression analysis groups it closer to MALT lymphoma, and thus, treatment options are heterogeneous with no established guidelines. ‘Wait and Watch’ strategy is often implemented in patients with low-grade disease, however, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy have also been explored. Treatment of DFL with antibiotics owing to its similarity to and association with MALT lymphoma and H. pylori respectively has had mixed results. The two cases described above highlight heterogeneous presentation, dyspepsia, and upper GI bleed, of a rare malignancy - DFL.

Figure: The image on the left shows whitish nodular mucosa in the second portion of the duodenum in Case 1. The image on the right shows abnormal duodenal mucosa in Case 2.
Disclosures:
Nikisha Pandya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nitin Pendyala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Choudhry indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Bernstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikisha Pandya, MD, Nitin Pendyala, MD, Mohammad Choudhry, MD, Michael Bernstein, MD. C0646 - Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma: Two Distinct Presentations of a Rare Disease Entity, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
