Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Colon
D0162 - Breast Cancer With Metastasis to Colon: A Case Report
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- BH
Benjamin Heriford, DO
UT Health San Antonio
San Antonio, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Benjamin Heriford, DO1, Mahesh Gajendran, MD, MPH2, Chandraprakash Umapathy, MD3, Eric Smith, MD4
1UT Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 2UTHSCSA, San Antonio, TX; 3University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 4BSW- Round Rock, Round Rock, TX
Introduction: The most common sites of metastases in breast cancer include bone, liver and lung. Gastrointestinal tract is a less common site for metastases in breast cancer. A PubMed literature review from 2015 to 2020 revealed only 32 cases of gastrointestinal metastases of breast cancer origin.1 Metastasis to the colon was seen in 28% of these cases with an average interval time to diagnosis of 9.43 years. In the case below, we present an uncommon case of a patient complaining of diarrhea and found to have ER+, HER2- metastases to ascending colon.
Case Description/Methods: Patient is a 56-year-old woman with history of ER+, HER2- invasive lobular carcinoma of the left breast diagnosed in 2009 and peritoneal carcinomatosis since 2017, who underwent diagnostic colonoscopy for chronic diarrhea. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen showed an area of thickening near the ileocecal junction measuring 6.5 cm, concerning for possible intraluminal mass. Colonoscopy showed mild stenosis in the proximal and distal ascending colon. Biopsies from the ascending colon were positive for ER+, HER2- metastatic carcinoma. This prompted a change in her chemotherapy regimen to Eribulin, designed to target metastatic breast cancer. After altering her chemotherapy regimen, CT imaging showed improvement in the thickening of ascending colon.
Discussion: Metastatic breast cancer involving the gastrointestinal tract is uncommon and is often underestimated. Metastases to the stomach and small bowel are more frequent than colonic involvement. Lobular type of breast carcinoma is the most common histological type that metastasizes to the colon. Previous studies have suggested that the presence of hormone receptors may facilitate gastrointestinal spread. The use of immunohistochemistry staining was vital in differentiating metastatic disease from a primary colonic cancer. For a correct diagnosis, deep biopsy should be performed as endoscopic diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer can be difficult when the biopsy samples are too superficial. A better knowledge of gastrointestinal metastases from primary breast carcinoma is warranted because appropriate management may result in longer survival.
1Fu JX, Zou YN, Long-Li, Wang XJ. Widespread Metastasis to the Stomach 10 Years After Primary Breast Cancer: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(48)
Disclosures:
Benjamin Heriford, DO1, Mahesh Gajendran, MD, MPH2, Chandraprakash Umapathy, MD3, Eric Smith, MD4. D0162 - Breast Cancer With Metastasis to Colon: A Case Report, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UT Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 2UTHSCSA, San Antonio, TX; 3University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 4BSW- Round Rock, Round Rock, TX
Introduction: The most common sites of metastases in breast cancer include bone, liver and lung. Gastrointestinal tract is a less common site for metastases in breast cancer. A PubMed literature review from 2015 to 2020 revealed only 32 cases of gastrointestinal metastases of breast cancer origin.1 Metastasis to the colon was seen in 28% of these cases with an average interval time to diagnosis of 9.43 years. In the case below, we present an uncommon case of a patient complaining of diarrhea and found to have ER+, HER2- metastases to ascending colon.
Case Description/Methods: Patient is a 56-year-old woman with history of ER+, HER2- invasive lobular carcinoma of the left breast diagnosed in 2009 and peritoneal carcinomatosis since 2017, who underwent diagnostic colonoscopy for chronic diarrhea. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen showed an area of thickening near the ileocecal junction measuring 6.5 cm, concerning for possible intraluminal mass. Colonoscopy showed mild stenosis in the proximal and distal ascending colon. Biopsies from the ascending colon were positive for ER+, HER2- metastatic carcinoma. This prompted a change in her chemotherapy regimen to Eribulin, designed to target metastatic breast cancer. After altering her chemotherapy regimen, CT imaging showed improvement in the thickening of ascending colon.
Discussion: Metastatic breast cancer involving the gastrointestinal tract is uncommon and is often underestimated. Metastases to the stomach and small bowel are more frequent than colonic involvement. Lobular type of breast carcinoma is the most common histological type that metastasizes to the colon. Previous studies have suggested that the presence of hormone receptors may facilitate gastrointestinal spread. The use of immunohistochemistry staining was vital in differentiating metastatic disease from a primary colonic cancer. For a correct diagnosis, deep biopsy should be performed as endoscopic diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer can be difficult when the biopsy samples are too superficial. A better knowledge of gastrointestinal metastases from primary breast carcinoma is warranted because appropriate management may result in longer survival.
1Fu JX, Zou YN, Long-Li, Wang XJ. Widespread Metastasis to the Stomach 10 Years After Primary Breast Cancer: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(48)

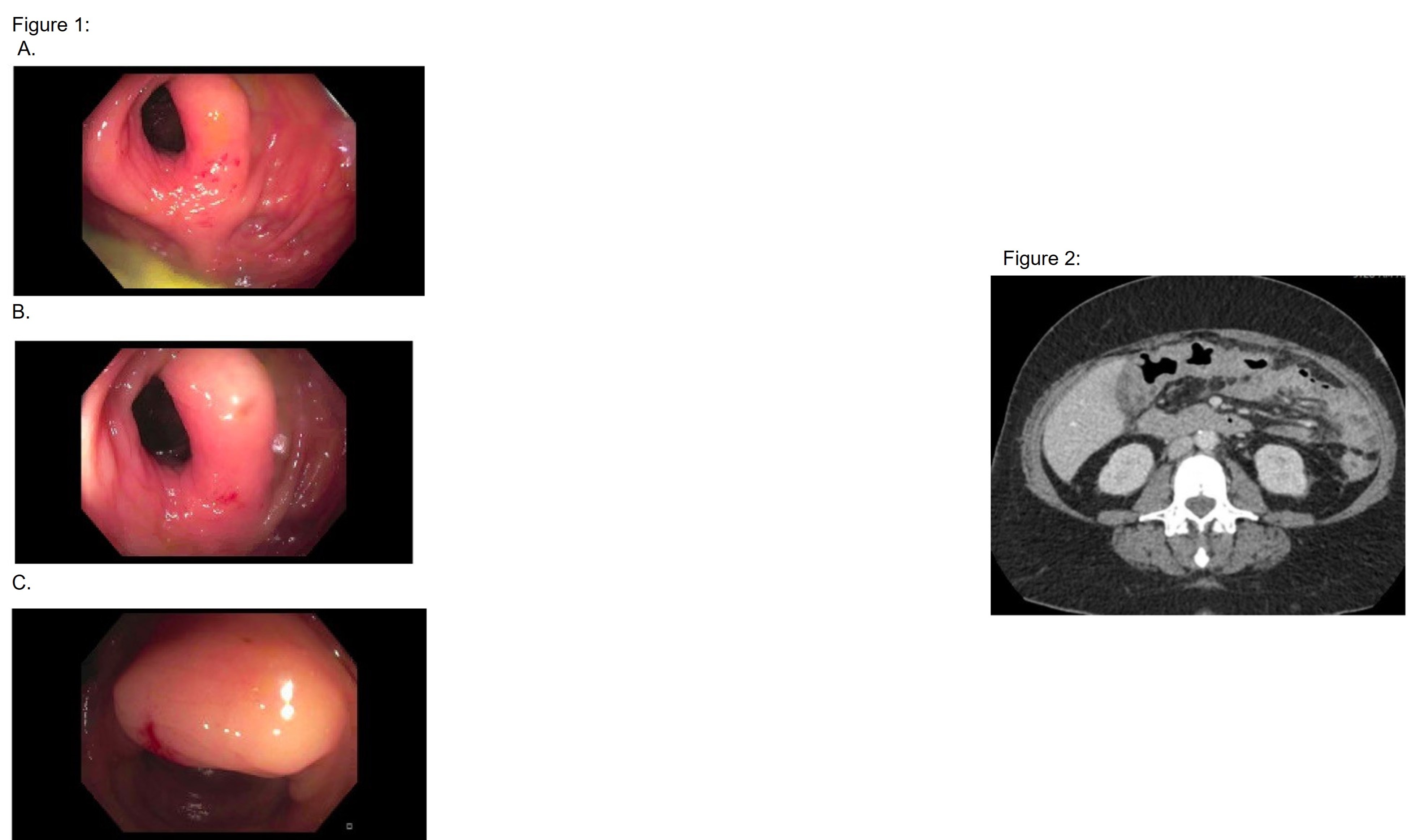
Figure: Figure 1: Image A and B demonstrate the mild stenosis in the splenic flexure from edema seen on colonoscopy. Image C demonstrates edema and nodularity of mucosa in the ascending colon.
Figure 2: Image of CT prior to colonoscopy with circumferential nodular colonic mural thickening noted at and above the level of the ileocecal junction measuring up to 6.5 cm
Figure 2: Image of CT prior to colonoscopy with circumferential nodular colonic mural thickening noted at and above the level of the ileocecal junction measuring up to 6.5 cm
Disclosures:
Benjamin Heriford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahesh Gajendran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chandraprakash Umapathy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Smith indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin Heriford, DO1, Mahesh Gajendran, MD, MPH2, Chandraprakash Umapathy, MD3, Eric Smith, MD4. D0162 - Breast Cancer With Metastasis to Colon: A Case Report, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
