Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Esophagus
D0218 - Dysphagia From a Pyogenic Granuloma: Could It Be?
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Bassam Hossain, DO, MPH
UHS WIlson Hospital
Vestal, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Bassam Hossain, DO, MPH1, Sumair Ahmad, MD, MPH2
1UHS WIlson Hospital, Vestal, NY; 2Great Lakes Gastroenterology, Mentor, OH
Introduction: Pyogenic granuloma is a benign inflammatory vascular lesion, mainly found in the oral mucosa and skin. Of the few cases of pyogenic granuloma within the gastrointestinal tract that have been reported, the esophagus was the main site in these cases. These patients were diagnosed with pyogenic granuloma after they underwent upper endoscopy and biopsy. Endoscopic resection is a favorable treatment option for esophageal pyogenic granuloma. We are presenting an interesting and rare case of a patient with a history of EoE who developed an esophageal pyogenic granuloma.
Case Description/Methods: A 63 year old female with a prior history of reported EoE, abnormal LFTs, presents to the Endoscopy unit after being referred for a diagnostic EGD due to having dysphagia symptoms. Patient undergoes transoral Upper Endoscopy with a cold biopsy of the esophagus/GEJ lesion and stomach. Patient is found to have an inflammatory appearing raised polypoid lesion, 6mm in size at the GEJ, superficial exudate, structurally, likely the cause of intermittent mild dysphagia symptoms. Cold biopsy is taken of the lesion for a histopath evaluation. Patient was recommended to follow up pathology of the lesion at GI clinic and repeat EGD in 6-8 weeks with BID dosing of PPI therapy to minimize reflux esophagitis. EUS of lesion or endoscopic removal can be Considered after biopsy results. The biopsy at the GE junction resulted in a pyogenic granuloma. Patient subsequently underwent an Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with endoscopic mucosal resection of esophageal nodule, 7 mm nodule in the lower esophagus at the
GE junction. The Endoscopic ultrasound showed the nodule being heterogenous arising from the mucosa and penetrating into the submucosa. There was no involvement of the muscularis propria. . Patient was discharged after having a successful procedure.
Discussion: Pyogenic granulomas are a form of hemangioma and commonly occur in the oral cavity and skin. GI pyogenic granulomas are reported in the literature with fewer than 10 cases found in the esophagus. This report presents a 63 year old patient with EoE who developed a pyogenic granuloma of the esophagus, likely secondary to trauma from severe acid-reflux with her history of EoE. Mainstay treatment for pyogenic granulomas is endoscopic resection; however, removal of potential traumatic factors is also important such as food allergies.
Disclosures:
Bassam Hossain, DO, MPH1, Sumair Ahmad, MD, MPH2. D0218 - Dysphagia From a Pyogenic Granuloma: Could It Be?, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UHS WIlson Hospital, Vestal, NY; 2Great Lakes Gastroenterology, Mentor, OH
Introduction: Pyogenic granuloma is a benign inflammatory vascular lesion, mainly found in the oral mucosa and skin. Of the few cases of pyogenic granuloma within the gastrointestinal tract that have been reported, the esophagus was the main site in these cases. These patients were diagnosed with pyogenic granuloma after they underwent upper endoscopy and biopsy. Endoscopic resection is a favorable treatment option for esophageal pyogenic granuloma. We are presenting an interesting and rare case of a patient with a history of EoE who developed an esophageal pyogenic granuloma.
Case Description/Methods: A 63 year old female with a prior history of reported EoE, abnormal LFTs, presents to the Endoscopy unit after being referred for a diagnostic EGD due to having dysphagia symptoms. Patient undergoes transoral Upper Endoscopy with a cold biopsy of the esophagus/GEJ lesion and stomach. Patient is found to have an inflammatory appearing raised polypoid lesion, 6mm in size at the GEJ, superficial exudate, structurally, likely the cause of intermittent mild dysphagia symptoms. Cold biopsy is taken of the lesion for a histopath evaluation. Patient was recommended to follow up pathology of the lesion at GI clinic and repeat EGD in 6-8 weeks with BID dosing of PPI therapy to minimize reflux esophagitis. EUS of lesion or endoscopic removal can be Considered after biopsy results. The biopsy at the GE junction resulted in a pyogenic granuloma. Patient subsequently underwent an Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with endoscopic mucosal resection of esophageal nodule, 7 mm nodule in the lower esophagus at the
GE junction. The Endoscopic ultrasound showed the nodule being heterogenous arising from the mucosa and penetrating into the submucosa. There was no involvement of the muscularis propria. . Patient was discharged after having a successful procedure.
Discussion: Pyogenic granulomas are a form of hemangioma and commonly occur in the oral cavity and skin. GI pyogenic granulomas are reported in the literature with fewer than 10 cases found in the esophagus. This report presents a 63 year old patient with EoE who developed a pyogenic granuloma of the esophagus, likely secondary to trauma from severe acid-reflux with her history of EoE. Mainstay treatment for pyogenic granulomas is endoscopic resection; however, removal of potential traumatic factors is also important such as food allergies.

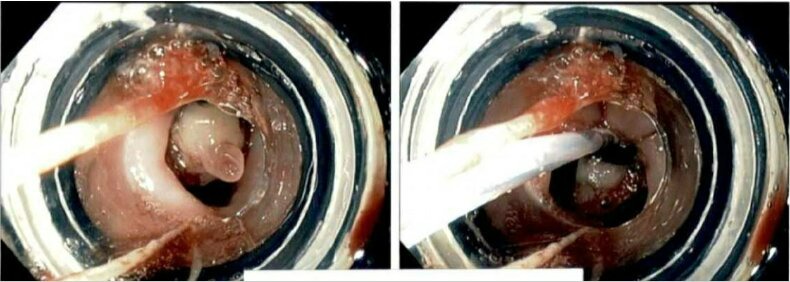
Figure: 7 mm nodule in the lower esophagus at the
GE junction. This was resected with endoscopic mucosal resection
after the endoscopic ultrasound. This was banded with one band
with Duette device.
GE junction. This was resected with endoscopic mucosal resection
after the endoscopic ultrasound. This was banded with one band
with Duette device.
Disclosures:
Bassam Hossain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumair Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bassam Hossain, DO, MPH1, Sumair Ahmad, MD, MPH2. D0218 - Dysphagia From a Pyogenic Granuloma: Could It Be?, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
