Back


Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Liver
B0595 - Hypocalcemia-Induced Right Heart Failure: A Rare Cause of Acute Liver Failure
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Rachael Schneider, DO
Main Line Health - Lankenau Hospital
Wynnewood, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Rachael Schneider, DO1, Stefanie Gallagher, DO2, Romy Chamoun, MD2, Amanda Long, DO2, Nicole Albert, DO3, Roy Taoutel, MD2
1Main Line Health - Lankenau Hospital, Wynnewood, PA; 2Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, PA; 3MLGA, Wayne, PA
Introduction: Cardiogenic shock is an uncommon cause of acute liver failure (ALF). Hypocalcemia is a rare, but reversible cause of acute cardiomyopathy. We present the case of a patient with severe hypocalcemia after parathyroidectomy causing right ventricular (RV) failure and ALF.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with a history of primary hyperparathyroidism status post parathyroidectomy 2 months prior presented with hypoxia and confusion. On exam he was obtunded with abdominal distension and peripheral edema. Labs showed calcium 4.8 mg/dL, ionized calcium 0.63 mmol/L, INR 5.1, AST 2478 IU/L, ALT 1999 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase 304 IU/L, total bilirubin 1.6. CT abdomen noted nodular liver and cardiomegaly. He was intubated and started on IV calcium gluconate and N-acetylcysteine. Urine drug screen, acetaminophen level, salicylate level, and viral and autoimmune liver workup all unrevealing. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) showed severely decreased RV systolic function with normal LV function. Serum aminotransferases and INR normalized prior to discharge.
Discussion: In evaluating ALF, it is important to rule out unusual causes of liver injury. In addition to drug-induced and viral etiologies, other causes include ischemic injury, neoplastic infiltration, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune diseases. Treatment consists of early recognition, identifying and addressing complications, supportive care, and transplant if appropriate. In the case of our patient, the workup for the typical causes of ALF was unrevealing. He had no known underlying liver disease, suggesting an acute process. Hypocalcemia is a rare, but known reversible cause of acute dilated cardiomyopathy. As calcium plays a vital role in myocyte contractility, low levels can lead to decreased myocardial performance, cardiogenic shock, and end-organ damage including congestion and ischemia of the liver. The cases of hypocalcemic cardiomyopathy that have been reported affected the left ventricle (LV). This is likely because the oxygen requirement of the RV is lower than the LV, thus the RV is less susceptible to ischemic insults. It is important to keep a broad differential in evaluating causes of acute liver failure, including severe electrolyte disturbances causing global ischemia. Our patient’s hepatic and cardiac function quickly improved with intravenous calcium supplementation.
Mandras SA, Desai S. Right Heart Failure. StatPearls. July 2021.
Disclosures:
Rachael Schneider, DO1, Stefanie Gallagher, DO2, Romy Chamoun, MD2, Amanda Long, DO2, Nicole Albert, DO3, Roy Taoutel, MD2. B0595 - Hypocalcemia-Induced Right Heart Failure: A Rare Cause of Acute Liver Failure, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Main Line Health - Lankenau Hospital, Wynnewood, PA; 2Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, PA; 3MLGA, Wayne, PA
Introduction: Cardiogenic shock is an uncommon cause of acute liver failure (ALF). Hypocalcemia is a rare, but reversible cause of acute cardiomyopathy. We present the case of a patient with severe hypocalcemia after parathyroidectomy causing right ventricular (RV) failure and ALF.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with a history of primary hyperparathyroidism status post parathyroidectomy 2 months prior presented with hypoxia and confusion. On exam he was obtunded with abdominal distension and peripheral edema. Labs showed calcium 4.8 mg/dL, ionized calcium 0.63 mmol/L, INR 5.1, AST 2478 IU/L, ALT 1999 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase 304 IU/L, total bilirubin 1.6. CT abdomen noted nodular liver and cardiomegaly. He was intubated and started on IV calcium gluconate and N-acetylcysteine. Urine drug screen, acetaminophen level, salicylate level, and viral and autoimmune liver workup all unrevealing. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) showed severely decreased RV systolic function with normal LV function. Serum aminotransferases and INR normalized prior to discharge.
Discussion: In evaluating ALF, it is important to rule out unusual causes of liver injury. In addition to drug-induced and viral etiologies, other causes include ischemic injury, neoplastic infiltration, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune diseases. Treatment consists of early recognition, identifying and addressing complications, supportive care, and transplant if appropriate. In the case of our patient, the workup for the typical causes of ALF was unrevealing. He had no known underlying liver disease, suggesting an acute process. Hypocalcemia is a rare, but known reversible cause of acute dilated cardiomyopathy. As calcium plays a vital role in myocyte contractility, low levels can lead to decreased myocardial performance, cardiogenic shock, and end-organ damage including congestion and ischemia of the liver. The cases of hypocalcemic cardiomyopathy that have been reported affected the left ventricle (LV). This is likely because the oxygen requirement of the RV is lower than the LV, thus the RV is less susceptible to ischemic insults. It is important to keep a broad differential in evaluating causes of acute liver failure, including severe electrolyte disturbances causing global ischemia. Our patient’s hepatic and cardiac function quickly improved with intravenous calcium supplementation.
Mandras SA, Desai S. Right Heart Failure. StatPearls. July 2021.

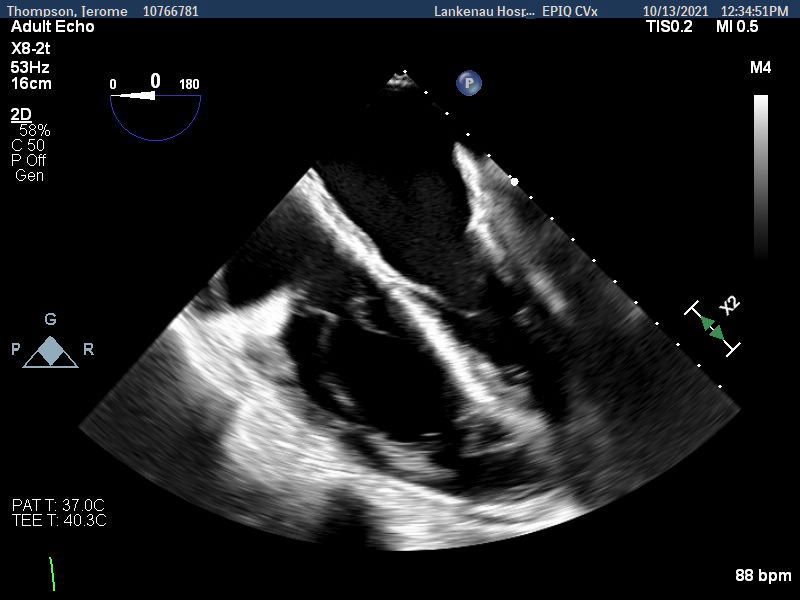
Figure: Figure 1: severely dilated and akinetic right heart, severely decreased RV function
Disclosures:
Rachael Schneider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stefanie Gallagher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Romy Chamoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanda Long indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicole Albert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Roy Taoutel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachael Schneider, DO1, Stefanie Gallagher, DO2, Romy Chamoun, MD2, Amanda Long, DO2, Nicole Albert, DO3, Roy Taoutel, MD2. B0595 - Hypocalcemia-Induced Right Heart Failure: A Rare Cause of Acute Liver Failure, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
