Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
B0065 - A Rare Case of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Biliary Ducts With Malignant Degeneration into Cholangiocarcinoma
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Paul P. Shao, MD
Stanford University
Redwood City, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Paul P. Shao, MD, Wassem Juakiem, MD, Samer P. Eldika, MD
Stanford University, Redwood City, CA
Introduction: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a mucin-producing papillary epithelial neoplasm arising from the pancreaticobiliary system. IPMN of the pancreas (P-IPMN) are common and widely recognized. Biliary tract IPMNs (BT-IPMN) are much rarer and have higher malignant transformation potential. We present a case of BT-IPMN with biliary-gastric and biliary-duodenal fistulas and malignant degeneration.
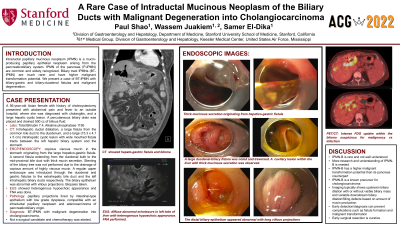
Case Description/Methods: A 56-year-old Asian female with history of cholecystectomy and hyperlipidemia presented with abdominal pain and fever to an outside hospital, where she was diagnosed with cholangitis, and a large hepatic cystic lesion. A percutaneous biliary drain was placed and drained 500 cc of bilious fluid. The patient was transferred to us for higher level of care. Her cholestasis markers were elevated with a total bilirubin of 7.4 and alkaline phosphatase of 1195. CT showed intrahepatic ductal dilatation, a large fistula from the common bile duct to the duodenum, and a large (15.3 x 4.1 x 5 cm) intrahepatic cystic lesion with wide mouthed fistula tracts between the left hepatic biliary system and the stomach. ERCP showed copious amount of viscous mucin in the stomach originating from the large hepatico-gastric fistula. A second fistula extending from the duodenal bulb to the mid-proximal bile duct was seen and the same mucinous secretion was present. Stenting of the biliary tree was not performed due to the drainage of copious amount of highly viscous mucin. A regular upper endoscope was introduced through the duodenal and gastric fistulas to the extrahepatic bile duct and the left intrahepatic biliary ducts respectively. The biliary epithelium was abnormal with villous projections. Biopsies were taken. Pathology showed papillary projections lined by intestinal-type epithelium with low grade dysplasia, compatible with an intraductal papillary neoplasm. CT-guided biopsy of the liver cystic lesion showed adenocarcinoma of pancreaticobiliary origin. She was diagnosed with BT-IPMN with malignant degeneration into cholangiocarcinoma involving much of the central liver that was not amenable for surgical resection. The patient was started on chemotherapy.
Discussion: BT-IPMNs are rare and not well understood. There is no clear guideline available. Surgical resection is the treatment of choice when discovered early. Our case highlights the high malignancy potential of BT-IPMNs and a need for their better understanding.

Disclosures:
Paul P. Shao, MD, Wassem Juakiem, MD, Samer P. Eldika, MD. B0065 - A Rare Case of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Biliary Ducts With Malignant Degeneration into Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Paul P. Shao, MD, Wassem Juakiem, MD, Samer P. Eldika, MD
Stanford University, Redwood City, CA
Introduction: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a mucin-producing papillary epithelial neoplasm arising from the pancreaticobiliary system. IPMN of the pancreas (P-IPMN) are common and widely recognized. Biliary tract IPMNs (BT-IPMN) are much rarer and have higher malignant transformation potential. We present a case of BT-IPMN with biliary-gastric and biliary-duodenal fistulas and malignant degeneration.
Case Description/Methods: A 56-year-old Asian female with history of cholecystectomy and hyperlipidemia presented with abdominal pain and fever to an outside hospital, where she was diagnosed with cholangitis, and a large hepatic cystic lesion. A percutaneous biliary drain was placed and drained 500 cc of bilious fluid. The patient was transferred to us for higher level of care. Her cholestasis markers were elevated with a total bilirubin of 7.4 and alkaline phosphatase of 1195. CT showed intrahepatic ductal dilatation, a large fistula from the common bile duct to the duodenum, and a large (15.3 x 4.1 x 5 cm) intrahepatic cystic lesion with wide mouthed fistula tracts between the left hepatic biliary system and the stomach. ERCP showed copious amount of viscous mucin in the stomach originating from the large hepatico-gastric fistula. A second fistula extending from the duodenal bulb to the mid-proximal bile duct was seen and the same mucinous secretion was present. Stenting of the biliary tree was not performed due to the drainage of copious amount of highly viscous mucin. A regular upper endoscope was introduced through the duodenal and gastric fistulas to the extrahepatic bile duct and the left intrahepatic biliary ducts respectively. The biliary epithelium was abnormal with villous projections. Biopsies were taken. Pathology showed papillary projections lined by intestinal-type epithelium with low grade dysplasia, compatible with an intraductal papillary neoplasm. CT-guided biopsy of the liver cystic lesion showed adenocarcinoma of pancreaticobiliary origin. She was diagnosed with BT-IPMN with malignant degeneration into cholangiocarcinoma involving much of the central liver that was not amenable for surgical resection. The patient was started on chemotherapy.
Discussion: BT-IPMNs are rare and not well understood. There is no clear guideline available. Surgical resection is the treatment of choice when discovered early. Our case highlights the high malignancy potential of BT-IPMNs and a need for their better understanding.

Figure: CT and ERCP findings.
Disclosures:
Paul Shao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wassem Juakiem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samer Eldika indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul P. Shao, MD, Wassem Juakiem, MD, Samer P. Eldika, MD. B0065 - A Rare Case of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Biliary Ducts With Malignant Degeneration into Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.

