Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Liver
D0527 - Autoimmune Hepatitis Triggered by Acute Liver Failure Caused by Hepatitis A
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- SG
Subhash Garikipati, MD
Louisiana State University
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Subhash Garikipati, MD1, Hajra Channa, MD2, Hrishikesh Samant, MD3
1Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 2Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Shreveport, LA; 3Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease with autoantibodies and elevated serum globulin levels that can present either as acute or chronic hepatitis. It has been theorized that autoimmune hepatitis is unveiled when there is an environmental trigger in a genetically predisposed individual. There has been some evidence that various viruses can be a trigger as well. This is a patient who developed autoimmune hepatitis shortly after an episode of hepatitis A.
Case Description/Methods: A 37-year-old female with no medical history was previously hospitalized with acute liver failure secondary to acute hepatitis A in a restaurant-related outbreak. She recovered after a four-day hospital stay and liver enzymes normalized after three months from > 7000 U/L. After another three months, she presented with complaints of dark-colored urine, right-sided abdominal pain, bilateral pedal edema, and fatigue and was also found to have elevated liver enzymes (AST 1612 U/L, ALT 1347 U/L). Viral hepatitis labs were negative. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) and anti-liver-kidney microsome (anti-LK) antibodies were negative but anti-smooth muscle antibody (ASMA) was 1:80 and IgG was 3893. A liver biopsy performed revealed chronic moderately active hepatitis with abundant plasma cells and stage 2 fibrosis which combined with lab findings was suggestive of autoimmune hepatitis. Prednisone 20 mg every day was started and liver enzymes normalized in three weeks. At that time, azathioprine was started and prednisone was weaned off.
Discussion: The exact pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis is not clear but it appears that environmental triggers can cause the disease in genetically susceptible patients. It is thought to be a molecular interaction between the antigen, the major histocompatibility complex, and the T cell receptor which forms a complex. Triggers can include viruses, herbs, and immunizations. The major autoantibodies involved in autoimmune hepatitis include ANA, anti-LK, ASMA, and anti-mitochondrial antibody. The goal of therapy is to suppress the immune system and often starts prednisone plus/minus azathioprine which can help reduce the doses of steroids required. This often leads to remission, at which point prednisone can be tapered and maintenance doses of azathioprine can be used.
Disclosures:
Subhash Garikipati, MD1, Hajra Channa, MD2, Hrishikesh Samant, MD3. D0527 - Autoimmune Hepatitis Triggered by Acute Liver Failure Caused by Hepatitis A, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 2Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Shreveport, LA; 3Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease with autoantibodies and elevated serum globulin levels that can present either as acute or chronic hepatitis. It has been theorized that autoimmune hepatitis is unveiled when there is an environmental trigger in a genetically predisposed individual. There has been some evidence that various viruses can be a trigger as well. This is a patient who developed autoimmune hepatitis shortly after an episode of hepatitis A.
Case Description/Methods: A 37-year-old female with no medical history was previously hospitalized with acute liver failure secondary to acute hepatitis A in a restaurant-related outbreak. She recovered after a four-day hospital stay and liver enzymes normalized after three months from > 7000 U/L. After another three months, she presented with complaints of dark-colored urine, right-sided abdominal pain, bilateral pedal edema, and fatigue and was also found to have elevated liver enzymes (AST 1612 U/L, ALT 1347 U/L). Viral hepatitis labs were negative. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) and anti-liver-kidney microsome (anti-LK) antibodies were negative but anti-smooth muscle antibody (ASMA) was 1:80 and IgG was 3893. A liver biopsy performed revealed chronic moderately active hepatitis with abundant plasma cells and stage 2 fibrosis which combined with lab findings was suggestive of autoimmune hepatitis. Prednisone 20 mg every day was started and liver enzymes normalized in three weeks. At that time, azathioprine was started and prednisone was weaned off.
Discussion: The exact pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis is not clear but it appears that environmental triggers can cause the disease in genetically susceptible patients. It is thought to be a molecular interaction between the antigen, the major histocompatibility complex, and the T cell receptor which forms a complex. Triggers can include viruses, herbs, and immunizations. The major autoantibodies involved in autoimmune hepatitis include ANA, anti-LK, ASMA, and anti-mitochondrial antibody. The goal of therapy is to suppress the immune system and often starts prednisone plus/minus azathioprine which can help reduce the doses of steroids required. This often leads to remission, at which point prednisone can be tapered and maintenance doses of azathioprine can be used.

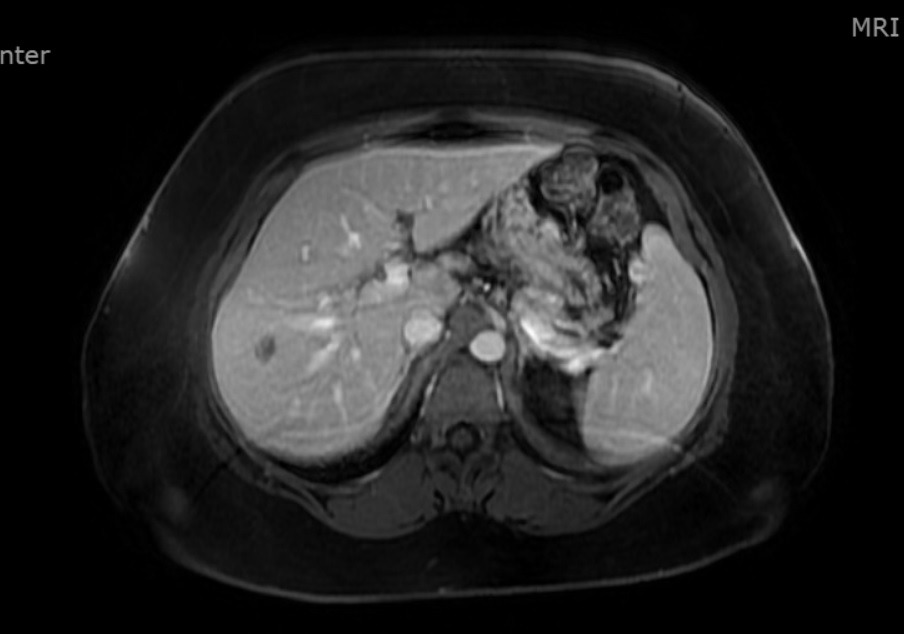
Figure: MRI showing hepatomegaly and a lesion in the right hepatic lobe consistent with benign hemangioma
Disclosures:
Subhash Garikipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hajra Channa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hrishikesh Samant indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Subhash Garikipati, MD1, Hajra Channa, MD2, Hrishikesh Samant, MD3. D0527 - Autoimmune Hepatitis Triggered by Acute Liver Failure Caused by Hepatitis A, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
