Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Esophagus
C0250 - A Case of Heterotropic Pancreatic Tissue at the Gastroesophageal Junction
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- VP
Vikas Pabby, MD, MPH
UCLA
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Vikas Pabby, MD, MPH, Sepehr Hamidi, MD
UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: We report a rare case of heterotropic pancreas located at the GE junction which was incidentally discovered during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
Heterotropic pancreas (HP) (pancreatic rest or ectopic pancreas) is a congenital anomaly in which there is ectopic pancreatic tissue indicating that it is separate from the main pancreatic gland, and does not have any continuity (anatomic, vascular, or ductal) with the main pancreatic gland. HP is generally found in the stomach, duodenum, or proximal jejunum. The prevalence of HP is believed to be 0.55 to 13.7% on autopsy. It is uncommon to find HP in the esophagus with nineteen cases being reported in literature it is rare to find HP at the GE junction with only six cases being reported in literature.
Case Description/Methods: A 45-year-old male presented for chronic heartburn. On EGD, distal to the gastroesophageal (GE) junction there was a 2 cm nodule that was biopsied and removed by a hot snare. In the gastric antrum, there was gastritis characterized by erythema. The duodenum appeared normal. Pathology from the GE junction nodule was consistent with heterotropic pancreatic tissue. The gastric biopsies were consistent with chronic active gastritis.
Discussion: Pancreatic rest is a submucosal nodule where pancreatic tissue is developed and commonly found in the upper small intestine or stomach. The pathogenesis for HP is not known. Nearly all pancreatic rests have no symptoms. It can be incidentally found through surgery or endoscopy. HP may still function in a similar manner as the main pancreatic gland and may secrete enzyme rich serous fluid, proteolytic enzymes causing a local inflammatory response, in which case there may be symptoms as a result.
When present at the GE junction, symptoms that have been reported in literature include dysphagia due to mass effect, symptoms of heartburn, or epigastric pain. The endoscopic appears is usually a well-circumscribed submucosal lesion commonly with central “umbilication” covered by normal mucosa. Surface biopsies may be non-diagnostic due to sampling of overlying mucosa. The final diagnosis is based on histology of the endoscopically or surgically resected specimen. Endoscopic ultrasound with fine needle aspiration of the lesion may also be utilized for diagnosis. The symptoms of heartburn present in our patient may have been contributed to by the incidentally found HP.
Disclosures:
Vikas Pabby, MD, MPH, Sepehr Hamidi, MD. C0250 - A Case of Heterotropic Pancreatic Tissue at the Gastroesophageal Junction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: We report a rare case of heterotropic pancreas located at the GE junction which was incidentally discovered during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
Heterotropic pancreas (HP) (pancreatic rest or ectopic pancreas) is a congenital anomaly in which there is ectopic pancreatic tissue indicating that it is separate from the main pancreatic gland, and does not have any continuity (anatomic, vascular, or ductal) with the main pancreatic gland. HP is generally found in the stomach, duodenum, or proximal jejunum. The prevalence of HP is believed to be 0.55 to 13.7% on autopsy. It is uncommon to find HP in the esophagus with nineteen cases being reported in literature it is rare to find HP at the GE junction with only six cases being reported in literature.
Case Description/Methods: A 45-year-old male presented for chronic heartburn. On EGD, distal to the gastroesophageal (GE) junction there was a 2 cm nodule that was biopsied and removed by a hot snare. In the gastric antrum, there was gastritis characterized by erythema. The duodenum appeared normal. Pathology from the GE junction nodule was consistent with heterotropic pancreatic tissue. The gastric biopsies were consistent with chronic active gastritis.
Discussion: Pancreatic rest is a submucosal nodule where pancreatic tissue is developed and commonly found in the upper small intestine or stomach. The pathogenesis for HP is not known. Nearly all pancreatic rests have no symptoms. It can be incidentally found through surgery or endoscopy. HP may still function in a similar manner as the main pancreatic gland and may secrete enzyme rich serous fluid, proteolytic enzymes causing a local inflammatory response, in which case there may be symptoms as a result.
When present at the GE junction, symptoms that have been reported in literature include dysphagia due to mass effect, symptoms of heartburn, or epigastric pain. The endoscopic appears is usually a well-circumscribed submucosal lesion commonly with central “umbilication” covered by normal mucosa. Surface biopsies may be non-diagnostic due to sampling of overlying mucosa. The final diagnosis is based on histology of the endoscopically or surgically resected specimen. Endoscopic ultrasound with fine needle aspiration of the lesion may also be utilized for diagnosis. The symptoms of heartburn present in our patient may have been contributed to by the incidentally found HP.

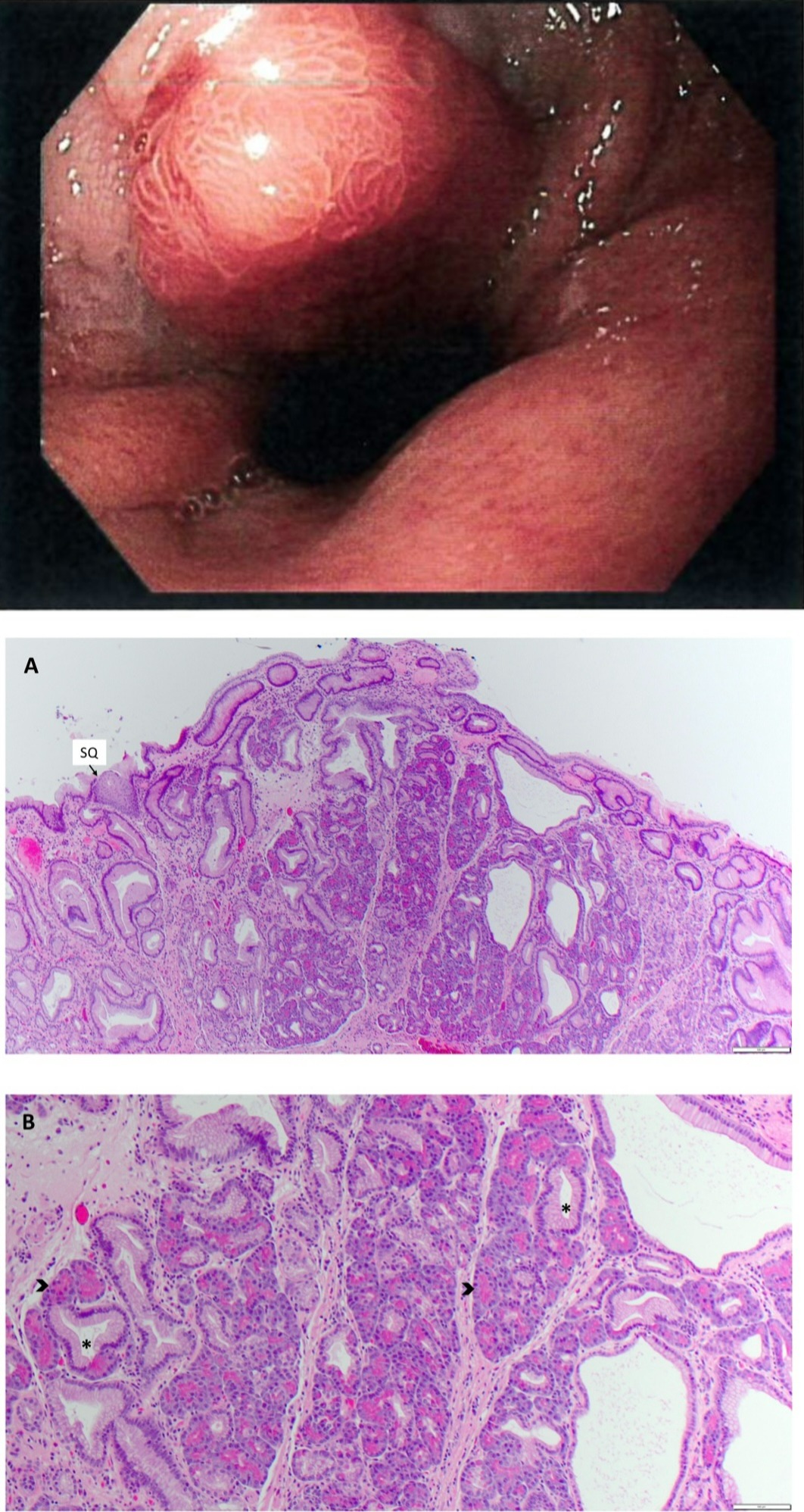
Figure: Gross Image: EGD showing GE junction with two centimeter nodule.
Pathology Image A: Pancreatic heterotopia/metaplasia is the lobular structure within the lamina propria; a small focus of esophageal squamous epithelium (SQ) is seen (hematoxylin and eosin stain, (x40).
Pathology Image B: Pancreatic acinar cells (arrowhead) have deeply eosinophilic granules and ductal cells have pale cytoplasm (x100).
Pathology Image A: Pancreatic heterotopia/metaplasia is the lobular structure within the lamina propria; a small focus of esophageal squamous epithelium (SQ) is seen (hematoxylin and eosin stain, (x40).
Pathology Image B: Pancreatic acinar cells (arrowhead) have deeply eosinophilic granules and ductal cells have pale cytoplasm (x100).
Disclosures:
Vikas Pabby indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sepehr Hamidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikas Pabby, MD, MPH, Sepehr Hamidi, MD. C0250 - A Case of Heterotropic Pancreatic Tissue at the Gastroesophageal Junction, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
