Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Stomach
D0687 - Impact of Anxiety and Depression Treatment on Symptom Severity and Quality of Life in Patients With Gastroparesis
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Simone A. Jarrett, MD
Albert Einstein Medical Center
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Simone A. Jarrett, MD1, Krystal Mills, MD2, Jabez K. Beazer, MD3, Kingsley Njoku, MD2, Ryan Alevy, BS2, Allan Joseph, MD4, Danny Alevy, 5, Kevin Lo, MD1, Zurab Azmaiparashvili, MD6, Julia Liu, MD, MS7, Jennifer Christie, MD8
1Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 2Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 3Morehouse Internal Medicine GME, Atlanta, GA; 4MoreHouse University, Atlanta, GA; 5University of Georgia, Atlanta, GA; 6Einstein Medical Center, Paoli, PA; 7Morehouse School of Medicine, Decatur, GA; 8Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: The association between symptoms of gastroparesis and treatment of concomitant anxiety or depression remains understudied.
Methods: Eligible patients identified from review of ICD codes associated with gastroparesis and anxiety or depression from our hospital underwent structured telephone interviews. The PAGI-SYM scale– which characterizes the severity of gastrointestinal symptoms and PAGI-QOL – which examines the impact of symptoms to quality of life were utilized to assess patient outcomes. Scores vary from 0 (none or absent) to 5 (very severe). A total score for each questionnaire was computed. Spearman rank correlation was used to determine associations between PAGI scores and treatment follow up and compliance for anxiety and depression which was patient reported. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
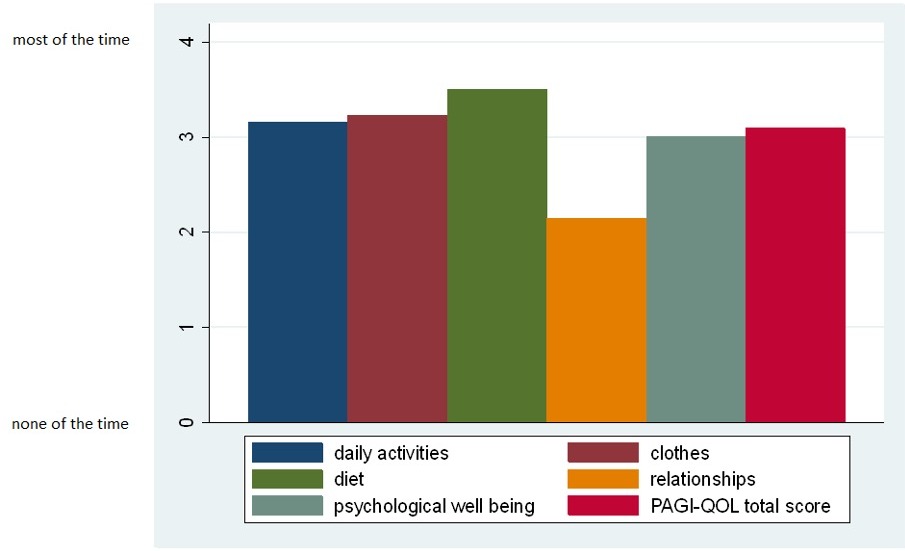
Results: 33 patients were included for analysis. The mean age was 48.4±10.6 and 88% were female. 70% were African American while 24% were Caucasian. 91% were diagnosed with depression, 9% had anxiety alone while 67% had both. More than half followed up with a psychiatrist (53%) with 82% taking medications for their anxiety or depression. However, only 55% of the patients were compliant with their psychiatric medications. Based on the PAGI-SYM score, postprandial fullness, bloating and upper abdominal pain were within the 3 range (affected a good bit of time) while the rest of the symptoms were reported as < 3. The mean total PAGI-SYM score was 3.1±1.3. Most of the PAGI-QOL scale scores were also within the 3 range and the most affected scale was diet (3.5±1.3) while the least affected was relationships (2.2±1.7). The mean total PAGI-QOL score was 3.1±1.2 (see Figure 1). There was a significant positive correlation between PAGI-QOL scores and PAGI-SYM (Rho:0.52, p=0.006) with higher symptom scores associated with greater negative effects on quality of life. However, there were no significant correlations between PAGI-QOL and PAGI-SYM scores with patients receiving treatment for psychiatric illness, medication compliance, and follow-up with a psychiatrist in our cohort.
Discussion: Gastrointestinal symptoms in patient with gastroparesis negatively impact on quality of life, however there were no significant correlations between symptom severity or QOL and psychiatrist follow up, treatment, or medication use for anxiety or depression in this patient cohort. Additional studies involving larger cohorts are needed.
Disclosures:
Simone A. Jarrett, MD1, Krystal Mills, MD2, Jabez K. Beazer, MD3, Kingsley Njoku, MD2, Ryan Alevy, BS2, Allan Joseph, MD4, Danny Alevy, 5, Kevin Lo, MD1, Zurab Azmaiparashvili, MD6, Julia Liu, MD, MS7, Jennifer Christie, MD8. D0687 - Impact of Anxiety and Depression Treatment on Symptom Severity and Quality of Life in Patients With Gastroparesis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 2Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 3Morehouse Internal Medicine GME, Atlanta, GA; 4MoreHouse University, Atlanta, GA; 5University of Georgia, Atlanta, GA; 6Einstein Medical Center, Paoli, PA; 7Morehouse School of Medicine, Decatur, GA; 8Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: The association between symptoms of gastroparesis and treatment of concomitant anxiety or depression remains understudied.
Methods: Eligible patients identified from review of ICD codes associated with gastroparesis and anxiety or depression from our hospital underwent structured telephone interviews. The PAGI-SYM scale– which characterizes the severity of gastrointestinal symptoms and PAGI-QOL – which examines the impact of symptoms to quality of life were utilized to assess patient outcomes. Scores vary from 0 (none or absent) to 5 (very severe). A total score for each questionnaire was computed. Spearman rank correlation was used to determine associations between PAGI scores and treatment follow up and compliance for anxiety and depression which was patient reported. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: 33 patients were included for analysis. The mean age was 48.4±10.6 and 88% were female. 70% were African American while 24% were Caucasian. 91% were diagnosed with depression, 9% had anxiety alone while 67% had both. More than half followed up with a psychiatrist (53%) with 82% taking medications for their anxiety or depression. However, only 55% of the patients were compliant with their psychiatric medications. Based on the PAGI-SYM score, postprandial fullness, bloating and upper abdominal pain were within the 3 range (affected a good bit of time) while the rest of the symptoms were reported as < 3. The mean total PAGI-SYM score was 3.1±1.3. Most of the PAGI-QOL scale scores were also within the 3 range and the most affected scale was diet (3.5±1.3) while the least affected was relationships (2.2±1.7). The mean total PAGI-QOL score was 3.1±1.2 (see Figure 1). There was a significant positive correlation between PAGI-QOL scores and PAGI-SYM (Rho:0.52, p=0.006) with higher symptom scores associated with greater negative effects on quality of life. However, there were no significant correlations between PAGI-QOL and PAGI-SYM scores with patients receiving treatment for psychiatric illness, medication compliance, and follow-up with a psychiatrist in our cohort.
Discussion: Gastrointestinal symptoms in patient with gastroparesis negatively impact on quality of life, however there were no significant correlations between symptom severity or QOL and psychiatrist follow up, treatment, or medication use for anxiety or depression in this patient cohort. Additional studies involving larger cohorts are needed.

Figure: Figure 1. Mean scores by subscale and total Patient Assessment of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders-Quality of Life (PAGI-QOL)
Disclosures:
Simone Jarrett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krystal Mills indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jabez Beazer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kingsley Njoku indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Alevy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allan Joseph indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danny Alevy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Lo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zurab Azmaiparashvili indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julia Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer Christie: Allergan – Grant/Research Support. Blue Cross Blue Shield – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Evoke Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Grail – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Guardant Pharma – Grant/Research Support. Syneos Health – Grant/Research Support.
Simone A. Jarrett, MD1, Krystal Mills, MD2, Jabez K. Beazer, MD3, Kingsley Njoku, MD2, Ryan Alevy, BS2, Allan Joseph, MD4, Danny Alevy, 5, Kevin Lo, MD1, Zurab Azmaiparashvili, MD6, Julia Liu, MD, MS7, Jennifer Christie, MD8. D0687 - Impact of Anxiety and Depression Treatment on Symptom Severity and Quality of Life in Patients With Gastroparesis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
