Back

Poster Session D - Tuesday Morning
Category: Liver
D0547 - It’s Not Always Hepatorenal Syndrome
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- KA
Khalid Ahmed, MD
The Wright Center for GME
Scranton, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Khalid Ahmed, MD1, Lakshmi P. Pappoppula, MD1, Abdul Ahad Ehsan Sheikh, MD1, Ahmed Hassan, MBBS2, Hunain Aslam, MD1, Beshir Saeed, MD1
1The Wright Center for GME, Scranton, PA; 2CN Internal Medicine, Arlington, VA
Introduction: Bile cast nephropathy (BCN) or Cholemic Nephrosis (CN) is a form of acute renal dysfunction that happens in the background of liver dysfunction and hyperbilirubinemia. We report an interesting case of BCN, in a patient who developed Acute Kidney Injury in the setting of hyperbilirubinemia due to Hepatitis A.
Case Description/Methods: A 58-year-old female presented with 4 days history of intractable nausea and vomiting. There was no associated abdominal pain or fever however she noted yellow discoloration of her skin and eyes. Her past medical history included Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, Hypothyroidism, Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia. Patient traveled to Arizona 2 months prior but denied any sick contacts, insect bites, herbal supplements, antibiotic use, drug use, alcohol/tobacco use or tattooing. On physical exam she was noted to be hemodynamically stable and afebrile with significant scleral icterus and jaundice. Abdomen was nontender without any organomegaly. Blood work showed Total bilirubin 7.9, Direct bilirubin 6.1, ALT 4792, AST 5228, ALK 313, Cr 2.8, BUN 32 and eGFR 19, INR 2.35. Elevated urobilinogen on UA. Imaging showed hepatic steatosis. Hepatitis-A IgM was positive. Management included supportive therapy. In the following days total Bilirubin levels reached above 20, Creatine >8 and GFR < 10. Patient was initiated on hemodialysis with significant improvement in her symptoms. Renal biopsy showed pigmented casts, consistent with BCN or CN. On the day of discharge, AST levels were 63, ALT was 76, alkaline phosphatase of 189 although total bilirubin was elevated at 20.5. Outpatient hemodialysis was arranged and patient was discharged home.
Discussion: Jaundice related nephropathy can lead to renal failure which is referred to as CN. Although the pathophysiology of CN is unclear, studies have shown tubular injury in mice from excretion of toxic bile acids in urine. Severe bilirubin elevations can cause acute renal injury, exacerbated by obstructive nephropathy secondary to bile cast formation. Such patients should be investigated for the possibility of CN and a renal biopsy is indicated. Therapy involves reducing bilirubin levels, but patients commonly require hemodialysis. By presenting this case, we encourage physicians to keep a broad differential in cases with hyperbillirubenemia and acute kidney injury. We found two cases of BCN in patients with acute Hepatitis A in our literature review. To our knowledge, there has not been a specific association between these entities.
Disclosures:
Khalid Ahmed, MD1, Lakshmi P. Pappoppula, MD1, Abdul Ahad Ehsan Sheikh, MD1, Ahmed Hassan, MBBS2, Hunain Aslam, MD1, Beshir Saeed, MD1. D0547 - It’s Not Always Hepatorenal Syndrome, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Wright Center for GME, Scranton, PA; 2CN Internal Medicine, Arlington, VA
Introduction: Bile cast nephropathy (BCN) or Cholemic Nephrosis (CN) is a form of acute renal dysfunction that happens in the background of liver dysfunction and hyperbilirubinemia. We report an interesting case of BCN, in a patient who developed Acute Kidney Injury in the setting of hyperbilirubinemia due to Hepatitis A.
Case Description/Methods: A 58-year-old female presented with 4 days history of intractable nausea and vomiting. There was no associated abdominal pain or fever however she noted yellow discoloration of her skin and eyes. Her past medical history included Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, Hypothyroidism, Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia. Patient traveled to Arizona 2 months prior but denied any sick contacts, insect bites, herbal supplements, antibiotic use, drug use, alcohol/tobacco use or tattooing. On physical exam she was noted to be hemodynamically stable and afebrile with significant scleral icterus and jaundice. Abdomen was nontender without any organomegaly. Blood work showed Total bilirubin 7.9, Direct bilirubin 6.1, ALT 4792, AST 5228, ALK 313, Cr 2.8, BUN 32 and eGFR 19, INR 2.35. Elevated urobilinogen on UA. Imaging showed hepatic steatosis. Hepatitis-A IgM was positive. Management included supportive therapy. In the following days total Bilirubin levels reached above 20, Creatine >8 and GFR < 10. Patient was initiated on hemodialysis with significant improvement in her symptoms. Renal biopsy showed pigmented casts, consistent with BCN or CN. On the day of discharge, AST levels were 63, ALT was 76, alkaline phosphatase of 189 although total bilirubin was elevated at 20.5. Outpatient hemodialysis was arranged and patient was discharged home.
Discussion: Jaundice related nephropathy can lead to renal failure which is referred to as CN. Although the pathophysiology of CN is unclear, studies have shown tubular injury in mice from excretion of toxic bile acids in urine. Severe bilirubin elevations can cause acute renal injury, exacerbated by obstructive nephropathy secondary to bile cast formation. Such patients should be investigated for the possibility of CN and a renal biopsy is indicated. Therapy involves reducing bilirubin levels, but patients commonly require hemodialysis. By presenting this case, we encourage physicians to keep a broad differential in cases with hyperbillirubenemia and acute kidney injury. We found two cases of BCN in patients with acute Hepatitis A in our literature review. To our knowledge, there has not been a specific association between these entities.

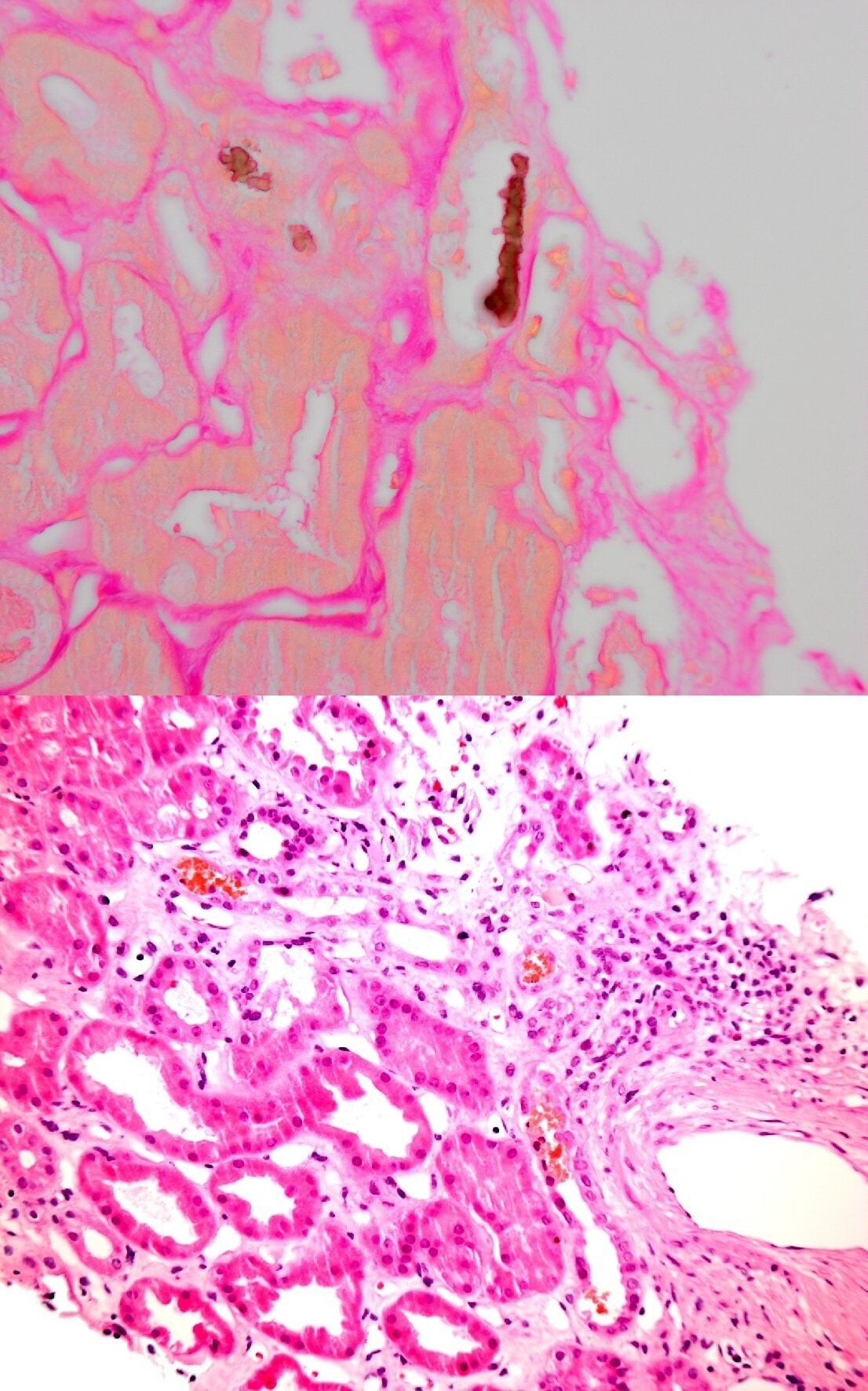
Figure: Picture above: Positive Fouchet Test
Picture below: Tubular Injury and Pigmented Casts
Picture below: Tubular Injury and Pigmented Casts
Disclosures:
Khalid Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lakshmi Pappoppula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Ahad Ehsan Sheikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hunain Aslam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Beshir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Ahmed, MD1, Lakshmi P. Pappoppula, MD1, Abdul Ahad Ehsan Sheikh, MD1, Ahmed Hassan, MBBS2, Hunain Aslam, MD1, Beshir Saeed, MD1. D0547 - It’s Not Always Hepatorenal Syndrome, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
