Back

Poster Session B - Monday Morning
Category: Liver
B0605 - Chronic Graft versus Host Disease Masquerading CMV Colitis After Liver Transplantation: A Clinical Challenge
Monday, October 24, 2022
10:00 AM – 12:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Hamid-Reza Moein, MD
Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center
Charlotte, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Hamidreza Moein, MD, Carl Jacobs, MD, Peter Lalli, PhD, Mark Russo, MD, MPH, FACG
Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, Charlotte, NC
Introduction: Graft versus host disease (GVHD) after solid organ transplantation is a rare but serious complication with high mortality that typically occurs 1-8 weeks post liver transplantation (LT). Steroids are first line treatment and data on second line treatment are less widely available.
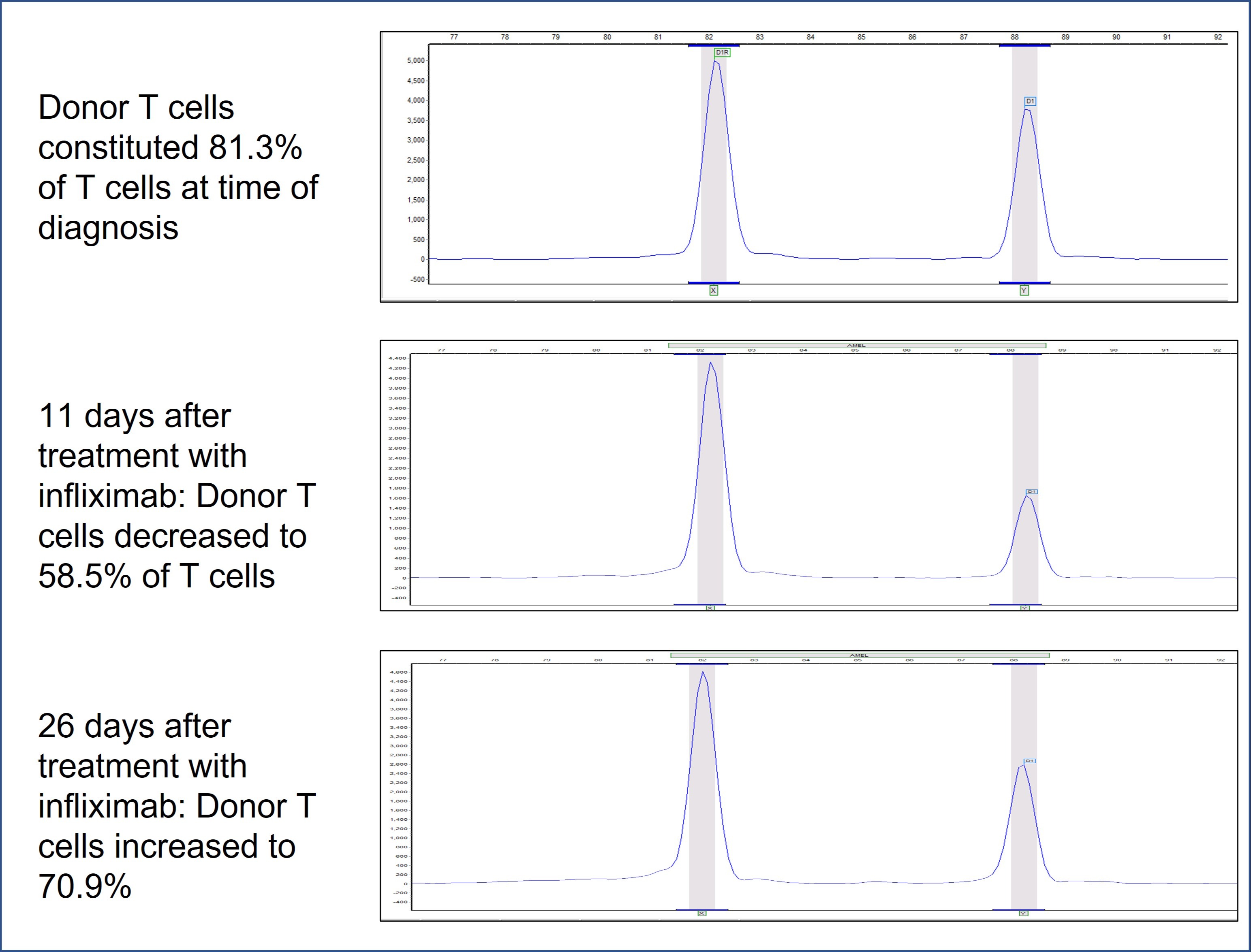
Case Description/Methods: 54-years-old woman with history of alcohol-related cirrhosis went under LT with a positive cytomegalovirus (CMV) and HCV male donor. She was discharged home without any major complications. Immune suppression included tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, (MMF) and prednisone taper. She was admitted to hospital 3 months later with diarrhea and acute kidney injury. C. difficile PCR was negative, CMV PCR was positive, and biopsies obtained during colonoscopy revealed severe CMV colitis. She was started on ganciclovir. Tacrolimus was reduced and MMF was discontinued. Fever and diarrhea were continued despite CMV treatment and later she developed a diffuse skin rash. This initially thought to be due to ganciclovir, but skin biopsy was concerning for GVHD. Gastric and colon biopsies and peripheral blood chimerism (donor T cell 81.3%; normal < 1%) confirmed GVHD. She was started on steroid therapy with minimal improvement in diarrhea as well as minimal improvement after the addition of topical budesonide and octreotide. Her course was complicated by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and status epilepticus and was intubated. Tacrolimus was stopped. She then developed pancytopenia with severe neutropenia despite discontinuation of ganciclovir. Bone marrow biopsy showed 10.7% donor alleles. Infliximab was initiated. Stool output decreased and neutropenia resolved after 1 week. Seizures were controlled and she was extubated. Chimerism analysis of peripheral blood after 11 days showed significant reduction of donor T cells (58.5%). However, after 2 weeks, diarrhea worsened and donor T cells increased to 70.9% in blood. Ruxolitinib and cyclosporin were started in addition to infliximab but she developed septic shock and expired.
Discussion: Persistent diarrhea and skin rash after liver transplantation may be signs of GVHD but these symptoms can also be seen in more common conditions such as C. difficile infection, drug reaction, and CMV colitis. Biopsy and chimerism analysis might both be needed for diagnosis of GVHD in patients with low pretest probability. Post LT GVHD that is refractory to steroid therapy may respond to infliximab. Sepsis is the most common cause of mortality in LT GVHD.
Disclosures:
Hamidreza Moein, MD, Carl Jacobs, MD, Peter Lalli, PhD, Mark Russo, MD, MPH, FACG. B0605 - Chronic Graft versus Host Disease Masquerading CMV Colitis After Liver Transplantation: A Clinical Challenge, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, Charlotte, NC
Introduction: Graft versus host disease (GVHD) after solid organ transplantation is a rare but serious complication with high mortality that typically occurs 1-8 weeks post liver transplantation (LT). Steroids are first line treatment and data on second line treatment are less widely available.
Case Description/Methods: 54-years-old woman with history of alcohol-related cirrhosis went under LT with a positive cytomegalovirus (CMV) and HCV male donor. She was discharged home without any major complications. Immune suppression included tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, (MMF) and prednisone taper. She was admitted to hospital 3 months later with diarrhea and acute kidney injury. C. difficile PCR was negative, CMV PCR was positive, and biopsies obtained during colonoscopy revealed severe CMV colitis. She was started on ganciclovir. Tacrolimus was reduced and MMF was discontinued. Fever and diarrhea were continued despite CMV treatment and later she developed a diffuse skin rash. This initially thought to be due to ganciclovir, but skin biopsy was concerning for GVHD. Gastric and colon biopsies and peripheral blood chimerism (donor T cell 81.3%; normal < 1%) confirmed GVHD. She was started on steroid therapy with minimal improvement in diarrhea as well as minimal improvement after the addition of topical budesonide and octreotide. Her course was complicated by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and status epilepticus and was intubated. Tacrolimus was stopped. She then developed pancytopenia with severe neutropenia despite discontinuation of ganciclovir. Bone marrow biopsy showed 10.7% donor alleles. Infliximab was initiated. Stool output decreased and neutropenia resolved after 1 week. Seizures were controlled and she was extubated. Chimerism analysis of peripheral blood after 11 days showed significant reduction of donor T cells (58.5%). However, after 2 weeks, diarrhea worsened and donor T cells increased to 70.9% in blood. Ruxolitinib and cyclosporin were started in addition to infliximab but she developed septic shock and expired.
Discussion: Persistent diarrhea and skin rash after liver transplantation may be signs of GVHD but these symptoms can also be seen in more common conditions such as C. difficile infection, drug reaction, and CMV colitis. Biopsy and chimerism analysis might both be needed for diagnosis of GVHD in patients with low pretest probability. Post LT GVHD that is refractory to steroid therapy may respond to infliximab. Sepsis is the most common cause of mortality in LT GVHD.

Figure: Sample micrographs from short tandem repeat (STR) testing (chimerism analysis) on isolated T cells from peripheral blood
Disclosures:
Hamidreza Moein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carl Jacobs indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Lalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Russo: Moderna – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Hamidreza Moein, MD, Carl Jacobs, MD, Peter Lalli, PhD, Mark Russo, MD, MPH, FACG. B0605 - Chronic Graft versus Host Disease Masquerading CMV Colitis After Liver Transplantation: A Clinical Challenge, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
