Back

Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
Category: General Endoscopy
E0275 - Safety and Efficacy of Etomidate and Propofol in ERCP: A Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio
- AM
Adnan Malik, MD
Mountain Vista Medical Center
Mesa, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Adnan Malik, MD1, Waseem Amjad, MD2, Umer Farooq, MD3, Shailendra Singh, MD4
1Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ; 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 3Loyola Medicine/MacNeal Hospital, Berwyn, IL; 4University of West Virginia, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Patients undergoing Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) are commonly hemodynamically unstable. Proper choice of the anesthetic drug is important to decrease morbidity and mortality. Therefore, we aim to compare the safety and efficacy of etomidate and propofol in ERCP undergoing patients.
Methods: We searched the following literature databases for relevant articles till May 2022: PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. The inclusion criteria were randomized control trials that compared both drugs in patients who underwent ERCP procedures. The efficacy outcomes were induction time, procedure duration, recovery time, patients' satisfaction, and endoscopists' satisfaction. The safety outcomes were bradycardia, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, injection-site pain, myoclonus, and other adverse events. Then, the data were extracted and analyzed using whether random or fixed effect models according to the heterogeneity.
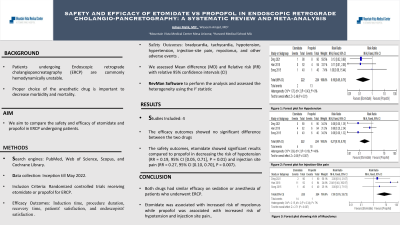
Results: Four studies were eligible for qualitative synthesis and meta-analysis. The efficacy outcomes showed no significant difference between the two drugs. While in the safety outcomes, etomidate showed significant results compared to propofol in decreasing the risk of hypotension (RR = 0.19, 95% CI [0.05, 0.71], P = 0.01) and injection site pain (RR = 0.27, 95% CI [0.10, 0.70], P = 0.007). On the other hand, etomidate was associated with higher myoclonus risk compared to propofol (RR = 7.58, 95% CI [1.76, 32.73], P = 0.007).
Discussion: Both drugs showed the same efficacy on sedation or anesthesia of patients who underwent ERCP. Etomidate was associated with increased risk of myoclonus while propofol was associated with increased risk of hypotension and injection site pain. Further clinical trials are needed to verify these findings. Also, the combination of both drugs should be investigated to decrease the risk of complications resulting from single drug administration.
Disclosures:
Adnan Malik, MD1, Waseem Amjad, MD2, Umer Farooq, MD3, Shailendra Singh, MD4. E0275 - Safety and Efficacy of Etomidate and Propofol in ERCP: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mountain Vista Medical Center, Mesa, AZ; 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 3Loyola Medicine/MacNeal Hospital, Berwyn, IL; 4University of West Virginia, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Patients undergoing Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) are commonly hemodynamically unstable. Proper choice of the anesthetic drug is important to decrease morbidity and mortality. Therefore, we aim to compare the safety and efficacy of etomidate and propofol in ERCP undergoing patients.
Methods: We searched the following literature databases for relevant articles till May 2022: PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. The inclusion criteria were randomized control trials that compared both drugs in patients who underwent ERCP procedures. The efficacy outcomes were induction time, procedure duration, recovery time, patients' satisfaction, and endoscopists' satisfaction. The safety outcomes were bradycardia, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, injection-site pain, myoclonus, and other adverse events. Then, the data were extracted and analyzed using whether random or fixed effect models according to the heterogeneity.
Results: Four studies were eligible for qualitative synthesis and meta-analysis. The efficacy outcomes showed no significant difference between the two drugs. While in the safety outcomes, etomidate showed significant results compared to propofol in decreasing the risk of hypotension (RR = 0.19, 95% CI [0.05, 0.71], P = 0.01) and injection site pain (RR = 0.27, 95% CI [0.10, 0.70], P = 0.007). On the other hand, etomidate was associated with higher myoclonus risk compared to propofol (RR = 7.58, 95% CI [1.76, 32.73], P = 0.007).
Discussion: Both drugs showed the same efficacy on sedation or anesthesia of patients who underwent ERCP. Etomidate was associated with increased risk of myoclonus while propofol was associated with increased risk of hypotension and injection site pain. Further clinical trials are needed to verify these findings. Also, the combination of both drugs should be investigated to decrease the risk of complications resulting from single drug administration.
Disclosures:
Adnan Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waseem Amjad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umer Farooq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shailendra Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Malik, MD1, Waseem Amjad, MD2, Umer Farooq, MD3, Shailendra Singh, MD4. E0275 - Safety and Efficacy of Etomidate and Propofol in ERCP: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
