Back

Poster Session C - Monday Afternoon
Category: Colon
C0149 - Submucosal Mucin Droplets: A Rare Endoscopic Sign of Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Mucinous Features
Monday, October 24, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Ekin Inal
Marmara University School of Medicine
Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey
Presenting Author(s)
Ekin Inal, 1, Linda Y. Zhang, MBBS2, Saowanee Ngamruengphong, MD3
1Marmara University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 2Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD; 3Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Introduction: Adenocarcinoma with mucinous features (AM) accounts for 10-15% of colon carcinoma. There have been no known endoscopic features of AM. We present a case with colonic AM, with visible extracellular mucin at the time of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
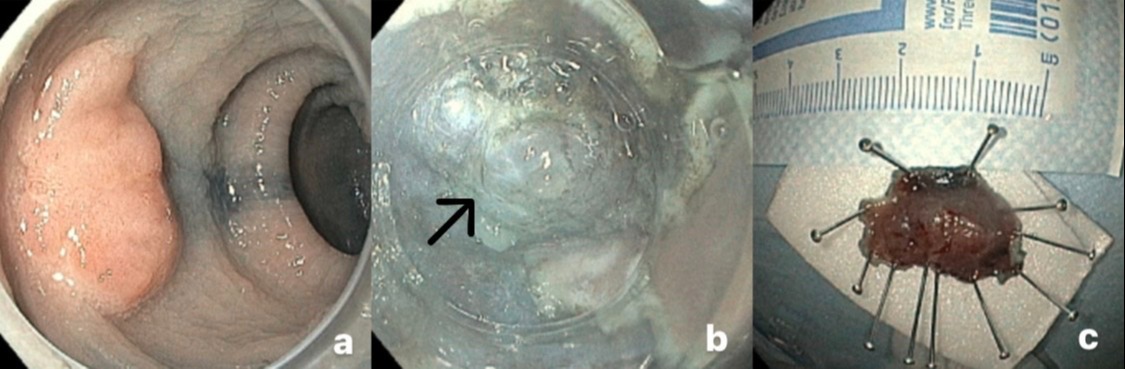
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old Caucasian female was referred for endoscopic resection of a 20 mm polyp in the sigmoid colon. Prior incomplete endoscopic mucosal resection was performed at an outside institution and pathology had shown tubulovillous adenoma with HGD and a focus of small irregular glands in a desmoplastic stroma suspicious of invasion. There were no visible features of deep invasion, thus ESD was performed. For submucosal lifting, an ORISE gel (Boston Scientific, MA, USA) was used. Submucosal dissection was difficult due to the presence of severe submucosal fibrosis. During ESD, several thick, clear mucus-like droplets were noted protruding from underneath the lesion. The lesion was successfully removed en bloc without severe bleeding or muscle injury. Pathology showed an invasive well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with mucinous features. Neoplastic cells were focally seen < 1mm from the deep margin and although there was no lymphovascular invasion or tumor budding, acellular mucin present at the deep margin. The patient proceeded to a sigmoid colectomy and the surgical specimen demonstrated no residual carcinoma. All margins were negative for dysplasia and nineteen lymph nodes were negative for tumor.
Discussion: Colorectal AM is characterized by the presence of extracellular mucin entailing < 50% of tumor volume. In this case, extracellular mucin was visualized from underneath the tumor during ESD and pathology subsequently confirmed the diagnosis of AM. To our knowledge, this phenomenon has not previously been reported. Mucinous histologic type, compared to nonmucinous adenocarcinoma is associated with a higher T staging at diagnosis, greater risk of metachronous metastases and worse survival. Due to high-risk pathologic feature found on the ESD specimen, the patient proceeded to subsequent surgical resection.
Importantly, new synthetic submucosal lifting agents such as ORISE gel can demonstrate a similar appearance to mucin in earlier stages and can result in a foreign body granulomatous reaction in later stages. The impact of this agent on the pathological evaluation of ESD specimens should be noted to avoid misdiagnosis.
Disclosures:
Ekin Inal, 1, Linda Y. Zhang, MBBS2, Saowanee Ngamruengphong, MD3. C0149 - Submucosal Mucin Droplets: A Rare Endoscopic Sign of Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Mucinous Features, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Marmara University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 2Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD; 3Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Introduction: Adenocarcinoma with mucinous features (AM) accounts for 10-15% of colon carcinoma. There have been no known endoscopic features of AM. We present a case with colonic AM, with visible extracellular mucin at the time of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old Caucasian female was referred for endoscopic resection of a 20 mm polyp in the sigmoid colon. Prior incomplete endoscopic mucosal resection was performed at an outside institution and pathology had shown tubulovillous adenoma with HGD and a focus of small irregular glands in a desmoplastic stroma suspicious of invasion. There were no visible features of deep invasion, thus ESD was performed. For submucosal lifting, an ORISE gel (Boston Scientific, MA, USA) was used. Submucosal dissection was difficult due to the presence of severe submucosal fibrosis. During ESD, several thick, clear mucus-like droplets were noted protruding from underneath the lesion. The lesion was successfully removed en bloc without severe bleeding or muscle injury. Pathology showed an invasive well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with mucinous features. Neoplastic cells were focally seen < 1mm from the deep margin and although there was no lymphovascular invasion or tumor budding, acellular mucin present at the deep margin. The patient proceeded to a sigmoid colectomy and the surgical specimen demonstrated no residual carcinoma. All margins were negative for dysplasia and nineteen lymph nodes were negative for tumor.
Discussion: Colorectal AM is characterized by the presence of extracellular mucin entailing < 50% of tumor volume. In this case, extracellular mucin was visualized from underneath the tumor during ESD and pathology subsequently confirmed the diagnosis of AM. To our knowledge, this phenomenon has not previously been reported. Mucinous histologic type, compared to nonmucinous adenocarcinoma is associated with a higher T staging at diagnosis, greater risk of metachronous metastases and worse survival. Due to high-risk pathologic feature found on the ESD specimen, the patient proceeded to subsequent surgical resection.
Importantly, new synthetic submucosal lifting agents such as ORISE gel can demonstrate a similar appearance to mucin in earlier stages and can result in a foreign body granulomatous reaction in later stages. The impact of this agent on the pathological evaluation of ESD specimens should be noted to avoid misdiagnosis.

Figure: Endoscopic identification of a laterally spreading lesion with mucin protruding during ESD in the sigmoid colon
Disclosures:
Ekin Inal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Linda Zhang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saowanee Ngamruengphong: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Ekin Inal, 1, Linda Y. Zhang, MBBS2, Saowanee Ngamruengphong, MD3. C0149 - Submucosal Mucin Droplets: A Rare Endoscopic Sign of Colonic Adenocarcinoma With Mucinous Features, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
