Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
Category: IBD
E0383 - Characteristics, Treatment and Outcome of Patients With Previously Diagnosed Autoimmune Disease After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Exposure

Antonio Pizuorno Machado, MD
University of Texas Health Science Center
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
1University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX; 2MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 3University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 4UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) can predispose to immune related adverse events (irAEs) and autoimmune disease (AD) flare-ups. irAE characteristics among patients with previously diagnosed AD have not been well studied. We aim to describe the clinical course, complications, treatment, and outcomes of patients with AD on ICIs.
Methods: This is a retrospective chart review of adult cancer patients at the MD Anderson Cancer Center diagnosed with AD (based on ICD code) prior to the first dose of ICI treatment between 01/01/2010 and 04/30/2021. Patients’ clinical course, treatment and outcomes related to both AD and irAE were collected and analyzed.
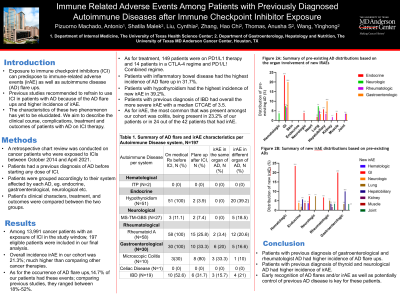
Results: A total of 197 patients were included in this study. A majority of our sample were female (55.4%) most frequently having melanoma (28.4%) and receiving PD-1/L1 inhibitors (83.7%). Forty-two patients (21.3%) developed a new irAE after starting immunotherapy, while 29 had an AD flare (14.7%). Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) had the highest rate of AD flare (31.7%), while patients with hypothyroidism had the highest incidence of new irAEs at 39.2%. Patients with IBD had more severe adverse events however with a median CTCAE grade of 3.5. In our cohort, all patients that were diagnosed with a new irAE were treated with immunosuppressive therapy. AD flares were managed similarly. With regards to irAE manifestations, colitis was the most common presentation in our cohort; at least 24 patients (23.2%) excluding those patients with a diagnosis of (IBD and microscopic colitis) had this type of complication. This was followed by pneumonitis in 9 patients (4.5%) and transaminitis in 7 patients (3.5%).
Discussion: Studies on the correlation between prior AD and immunotherapy are still lacking. Our findings suggest that patients with GI and rheumatologic ADs had higher incidence of AD flare up than new irAE development, while patients with thyroid and neurologic ADs appeared to have higher incidence of new irAEs compared to AD flare. Patients with prior AD experiencing a flare or a new irAE after immunotherapy tend to require more aggressive immunosuppressive treatment for symptom control. Thorough evaluation of baseline disease status, the appropriate medical management prior to ICI, and early recognition of inflammatory exacerbation could be key factors to ensure long-term success with treating and improving outcomes of these patients.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1. Summary of irAE characteristics per Autoimmune Disease system, N=197 | |||||||||
Autoimmune Disease per system | Active AD status before ICI, N (%) | On medical Rx before ICI, N (%) | Flare up after ICI, N (%) | Type of ICI | Peak CTCAE grade of flare up (median, IQR) | Required IMS for flare up, N (% of those that had flare) | New irAE in different organ from AD, N (%) | Peak CTCAE of irAE (median, IQR) | IMS required for irAE, N (% of those that had irAE) |
Hematological |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITP (N=2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | PD1/L1=2 (100) | N/A | N/A | 0 (0) | N/A | N/A |
Endocrine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hypothyroidism (N=51) | 0 (0) | 51 (100) | 2 (3.9) | Combined= 9 (17.6); PD1/L1=42 (82.3) | Grade 2 in 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 20 (39.2) | 2(1-3) | 20 (100) |
Neurological |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MS-TM-GBS (N=27) | 27 (100) | 3 (11.1) | 2 (7.4) | Combined= 1 (3.8); PD1/L1= 21 (77.7); CTLA-4=5 (18.5) | N/A | 2 (100) | 5 (18.5) | 1(1-1.5) | 5 (100) |
Rheumatological |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rheumatoid A (N=58) | 0 (0) | 58 (100) | 15 (25.8) | Combined= 1 (1.7); PD1/L1= 57 (98.2); | N/A | 15 (100) | 12 (20.6) | 2.5(2-3) | 9 (75) |
Gastroenterological (N=30) | 0 (0) | 30 (100) | 10 (33.3) | Combined=3 (10); PD1/L1=27 (90) | N/A | 10 (100) | 5 (16.6) | N/A | 5 (100) |
Microscopic Colitis (N=10) | 0 (0) | 3(30) | 8 (80) | PD1/L1=10 (100) | N/A | 8 (100) | 1 (10) | N/A | 1 (100) |
Celiac Disease (N=1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | PD1/L1=1 (100) | N/A | N/A | 0 (0) | N/A | N/A |
IBD (N=19) | 1 (5.2) | 10 (52.6) | 6 (31.7) | Combined=3 (15.7); PD1/L1=16 (84.2) | N/A | 6 (100) | 4 (21) | 3.5(3-4) | 4 (100) |
Footnote: IMS=immunosuppressant. ITP=Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura. MS=Multiple Sclerosis. TM= Transverse Myelitis. GBS=Guillain Barre Syndrome. IBD=Inflammatory Bowel Disease. *all the patients had baseline low activity at the time of ICI initiation. Flare up occurred when the symptoms progressed from baseline activity. | |||||||||
Disclosures:
Antonio Pizuorno Machado, MD1, Malek Shatila, MD2, Cynthia Liu, MD3, Hao Chi Zhang, MD4, Anusha S. Thomas, MD2, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD2. E0383 - Characteristics, Treatment and Outcome of Patients With Previously Diagnosed Autoimmune Disease After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Exposure, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
