Back

Poster Session E - Tuesday Afternoon
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
E0039 - Isolated IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis a Rare Mimicker of Malignant Strictures
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
3:00 PM – 5:00 PM ET
Location: Crown Ballroom

Has Audio

Marcel R. Robles, MD
Tufts University School of Medicine, St. Elizabeth's Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Marcel R. Robles, MD1, Michael Malkowski, MD1, Guoliang Zheng, MD2, Sandeep Krishnan, MBBS, PhD3
1Tufts University School of Medicine, St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA; 3St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, Brighton, MA
Introduction: IgG4 related sclerosis cholangitis (IgG4-RSC) is the biliary presentation of a systemic condition known as IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). It is a rare cause of cholangitis characterized by dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells. It is a multi organ disease with male predominance which is most commonly associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Isolated IgG4-RSC is exceedingly rare form of this disease often misdiagnosed as cholangiocarcinoma or pancreatic cancer.
Case Description/Methods: A 74-year-old diabetic man presented to the emergency department with complaints of a 44 pound weight loss within the last two months prior to presentation and a 1 month history of generalized pruritus, skin discoloration and pale stool. Exam was notable for scleral icterus, jaundice and no abdominal pain. Laboratory evaluation showed total bilirubin of 14.2 mg/dl, direct bilirubin > 10 mg/dl, AST 61 and ALT 60 with alkaline phosphatase of 328, lipase was normal. CA 19-9 antigen was 212, CEA and AFP were normal. A computed tomography (CT) of abdomen was obtained which showed no pancreatic mass however noted intra and extra-biliary ductal dilation with common bile duct measuring up to 1.8 cm. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed a focal wall thickening involving mid and lower portion CBD causing severe stenosis concerning for malignancy. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) was planned. ERCP demonstrated a proximal dilatation with 2 cm long stricture located at the distal end of bile duct. A sphincteroctomy was performed, biliary tree was swept with 12-15 mm ballon, multiple biopsies were obtained and CBD stent was replaced. Via EUS, a biopsy of CBD was obtained using a trans-duodenal approach. Pathology ultimately revealed plasma cells with IgG4 positive forms. Serum IgG4 was 246 mg/dl. Patient was diagnosed with IgG4 sclerosis cholangitis and he was started on systemic steroids with an adequate response.
Discussion: IgG4-RSC often initially presents as painless jaundice, weight loss or abdominal pain. Our case illustrates challenges in diagnosis given initial strong suspicion for malignancy. A combination of imaging, serological studies and biopsy are needed for diagnosis. Serum IgG4 is a non-specific test however concentration >135 mg/dl is often considered suspicious. Timely diagnosis and treatment with systemic steroids is essential in order to prevent secondary infection or permanent fibrosis.
Disclosures:
Marcel R. Robles, MD1, Michael Malkowski, MD1, Guoliang Zheng, MD2, Sandeep Krishnan, MBBS, PhD3. E0039 - Isolated IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis a Rare Mimicker of Malignant Strictures, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Tufts University School of Medicine, St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA; 3St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, Brighton, MA
Introduction: IgG4 related sclerosis cholangitis (IgG4-RSC) is the biliary presentation of a systemic condition known as IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). It is a rare cause of cholangitis characterized by dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells. It is a multi organ disease with male predominance which is most commonly associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Isolated IgG4-RSC is exceedingly rare form of this disease often misdiagnosed as cholangiocarcinoma or pancreatic cancer.
Case Description/Methods: A 74-year-old diabetic man presented to the emergency department with complaints of a 44 pound weight loss within the last two months prior to presentation and a 1 month history of generalized pruritus, skin discoloration and pale stool. Exam was notable for scleral icterus, jaundice and no abdominal pain. Laboratory evaluation showed total bilirubin of 14.2 mg/dl, direct bilirubin > 10 mg/dl, AST 61 and ALT 60 with alkaline phosphatase of 328, lipase was normal. CA 19-9 antigen was 212, CEA and AFP were normal. A computed tomography (CT) of abdomen was obtained which showed no pancreatic mass however noted intra and extra-biliary ductal dilation with common bile duct measuring up to 1.8 cm. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed a focal wall thickening involving mid and lower portion CBD causing severe stenosis concerning for malignancy. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) was planned. ERCP demonstrated a proximal dilatation with 2 cm long stricture located at the distal end of bile duct. A sphincteroctomy was performed, biliary tree was swept with 12-15 mm ballon, multiple biopsies were obtained and CBD stent was replaced. Via EUS, a biopsy of CBD was obtained using a trans-duodenal approach. Pathology ultimately revealed plasma cells with IgG4 positive forms. Serum IgG4 was 246 mg/dl. Patient was diagnosed with IgG4 sclerosis cholangitis and he was started on systemic steroids with an adequate response.
Discussion: IgG4-RSC often initially presents as painless jaundice, weight loss or abdominal pain. Our case illustrates challenges in diagnosis given initial strong suspicion for malignancy. A combination of imaging, serological studies and biopsy are needed for diagnosis. Serum IgG4 is a non-specific test however concentration >135 mg/dl is often considered suspicious. Timely diagnosis and treatment with systemic steroids is essential in order to prevent secondary infection or permanent fibrosis.

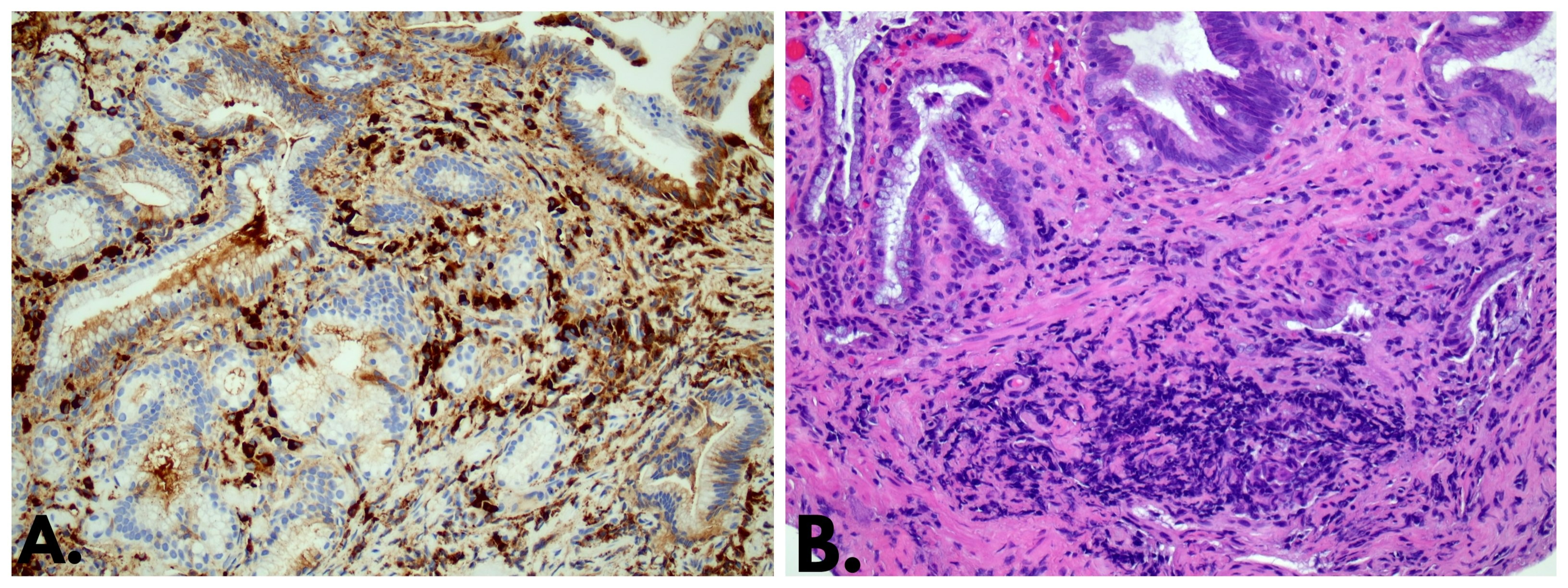
Figure: A. Magnification 200x. IGG4 immunohistochemical staining with surrounding bile duct mucosa.
B. Magnification 200x. Bile duct mucosa with extensive inflammation and lymphoid aggregates in the bottom of image.
B. Magnification 200x. Bile duct mucosa with extensive inflammation and lymphoid aggregates in the bottom of image.
Disclosures:
Marcel Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Malkowski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guoliang Zheng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandeep Krishnan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marcel R. Robles, MD1, Michael Malkowski, MD1, Guoliang Zheng, MD2, Sandeep Krishnan, MBBS, PhD3. E0039 - Isolated IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis a Rare Mimicker of Malignant Strictures, ACG 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Charlotte, NC: American College of Gastroenterology.
